2025 Vol. 7, No. 7
This study aimed to analyze the epidemiological characteristics and clinical symptoms of mpox cases with and without human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) reported in China in 2023, providing evidence for coordinated prevention and control strategies for both infections.
All confirmed mpox cases reported in 2023 were extracted from China’s Information System for Disease Control and Prevention. Data were collected from the surveillance system and epidemiological investigations. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 24.0, with group comparisons conducted using t-tests and chi-square tests.
Among 1,712 confirmed mpox cases in China during 2023, 802 (46.8%) were people with human immunodeficiency virus (PWH). Of the 1,702 male cases, 97.3% of PWH and 91.1% of those without HIV self-identified as men who have sex with men (MSM). Age distribution showed 79.4% of PWH and 87.6% of those without HIV were under 40 years old, while 64.2% of PWH and 71.3% of those without HIV were reported from eastern regions. Cardinal symptoms at diagnosis occurred at similar rates between those with and without HIV, including rash (90.9% vs. 93.4%), fever (52.5% vs. 53.8%), and lymphadenopathy (23.8% vs. 25.4%). Among coinfected cases, individuals diagnosed with HIV after mpox or within one year before mpox demonstrated higher rates of immunodeficiency and lower rates of HIV viral suppression.
Male mpox cases with HIV was more likely to be MSM, older, and reported from central and western regions compared to those without HIV. No significant differences were observed in cardinal symptom occurrence between groups. These findings emphasize the importance of implementing integrated prevention strategies targeting both HIV and mpox, particularly among key populations.
Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) is the predominant respiratory pathogen causing acute respiratory tract infection (ARTI). Globally, HRSV infection represents the leading cause of acute respiratory morbidity and hospitalization in children under 2 years of age. HRSV infection continues to pose a significant public health challenge worldwide. Through epidemiological surveillance of HRSV in children with ARTI, we can elucidate its incidence patterns and epidemic characteristics to inform evidence-based prevention and control strategies.
We collected upper and lower respiratory tract specimens and clinical data from children under 14 years of age with ARTI. HRSV was detected using Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction to analyze its incidence and epidemic characteristics.
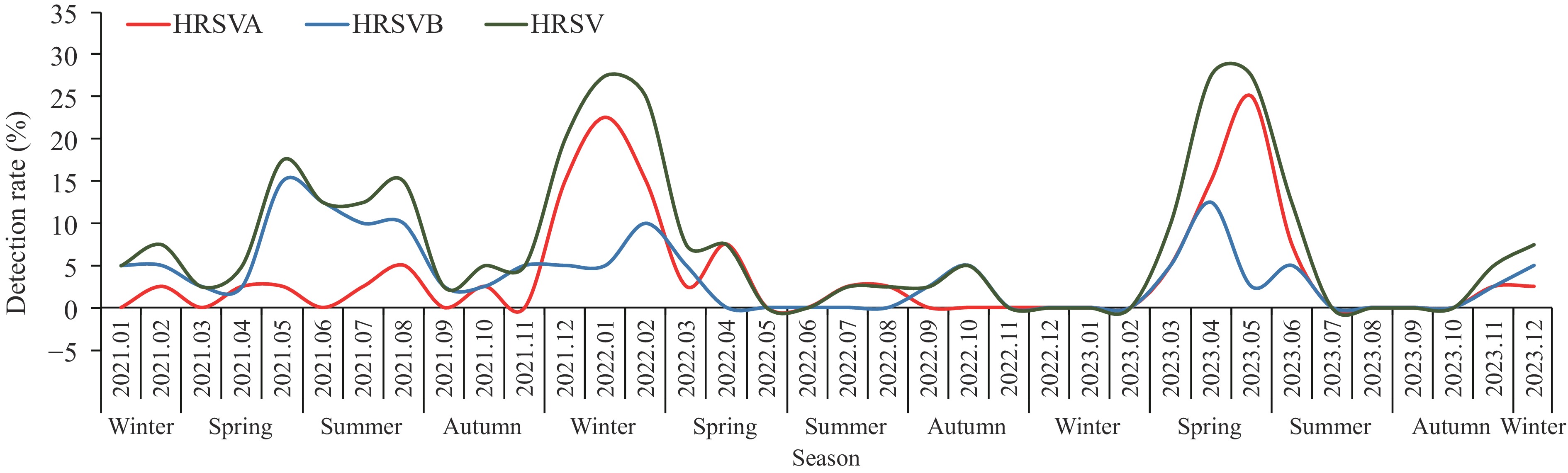
Among 1,440 specimens, the overall HRSV detection rate was 7.8% (HRSVA and HRSVB detection rates were 4.0% and 3.8%, respectively). Detection rates peaked in spring (12.2%), followed by winter (10.3%), with the lowest rates in autumn (2.8%) (P<0.05). HRSVB was the dominant subtype throughout 2021, while HRSVA predominated during 2022 and the first half of 2023. Detection rates were significantly higher in children under 5 years compared to older children, with lower respiratory tract infections in the 0–2 years age group showing notably higher detection rates (18.1%) than upper respiratory tract infections (8.1%) (P<0.05).
HRSV exhibited consistent circulation among children with ARTI in the Shijiazhuang area from 2021 to 2023, characterized by winter and spring outbreaks and alternating predominance of subtypes A and B. Infections predominantly affected children under 5 years of age.
This study investigated temporal changes in rotavirus group A (RVA) prevalence, epidemiological characteristics, and genotype distribution patterns among diarrhea outpatients in Shanghai Municipality, China.
We conducted prospective active surveillance of diarrheal disease in pediatric and adult outpatients in Shanghai. Stool specimens were analyzed for five viral and twelve bacterial pathogens. Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) was employed for RVA detection, followed by genotyping of RVA-positive specimens through partial amplification of VP7 and VP4 genes.
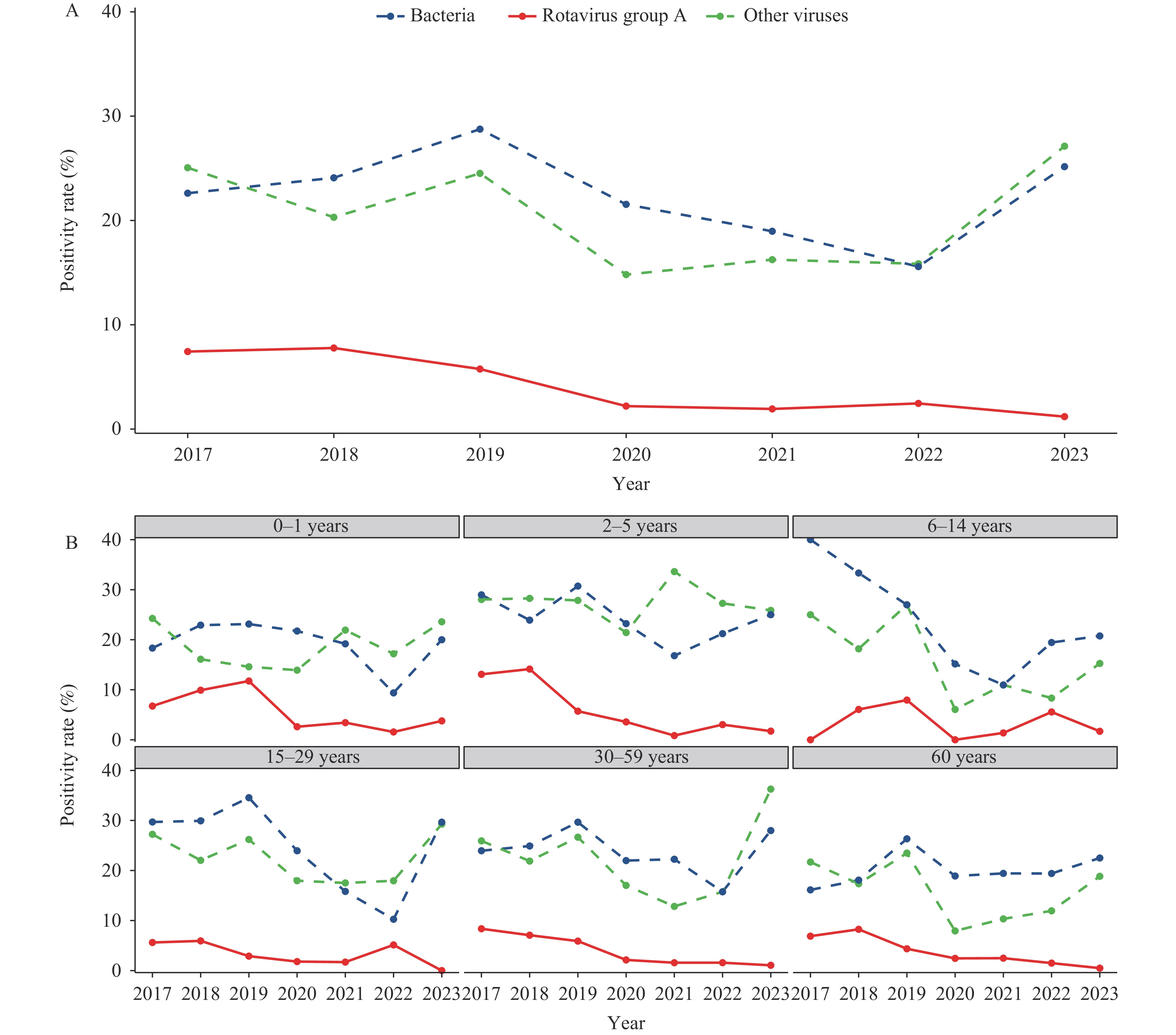
The study analyzed 2,331 diarrhea cases in children aged 0–14 years and 8,418 cases in individuals aged ≥15 years between January 2017 and December 2023. Overall RVA positivity rates decreased significantly from 7.43% in 2017 to 1.19% in 2023 (P=0.024). The most pronounced decline occurred in children aged 2–5 years, where positivity rates fell from 13.08% to 1.72%. Adults aged ≥30 years also showed a substantial reduction. Among RVA-positive pediatric cases (≤14 years), the proportion of cases aged 6–14 years increased from 2.33% to 18.18%. While G9P[8] remained the predominant strain, its prevalence decreased from 77.78% to 31.25%, concurrent with the emergence of G8P[8] strains.
RVA prevalence has shown a marked decline since 2018–2019, accompanied by a shift in age distribution toward older children. The diminishing dominance of G9P[8] strains coincided with the emergence of G8P[8] strains. Continued epidemiological and genetic surveillance of rotavirus diarrhea, coupled with real-world effectiveness evaluations of domestic vaccines, remains crucial for optimizing rotavirus immunization strategies.
The clinical durations of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease (sCJD) patients typically do not exceed 2 years, though considerable variation exists. The factors influencing survival among Chinese sCJD patients remain incompletely characterized.
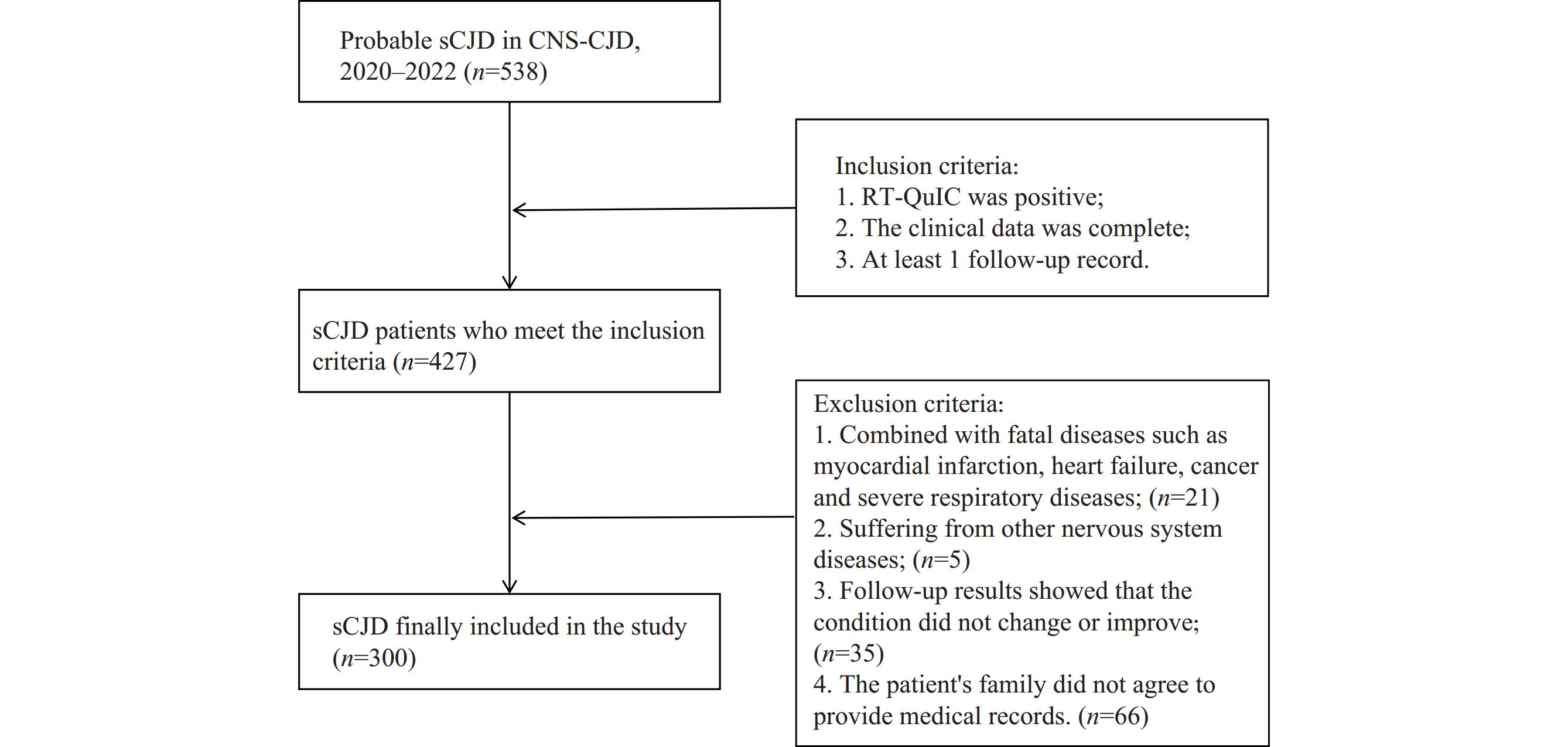
A comprehensive evaluation of 31 factors across 7 categories was conducted in a retrospective cohort of 300 probable Chinese sCJD patients. The analysis revealed that patients over 65 years of age at onset, those presenting with pyramidal or extrapyramidal dysfunction, those showing high signal intensity in caudate/putamen on magnetic resonance imaging, and those not receiving nasal feeding demonstrated significantly shorter survival times.
This study provides the first systematic documentation of potential risk factors affecting survival times in Chinese sCJD patients, establishing an evidence base for developing and implementing targeted intervention strategies.
Yellow fever (YF) is a highly lethal mosquito-borne infectious disease endemic to tropical regions for which no antiviral treatments currently exist. Vaccination remains the most effective preventive measure and is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for YF control and prevention. However, the YF vaccination associated Adverse Events following Immunization (AEFI) cases occur globally occasionally.
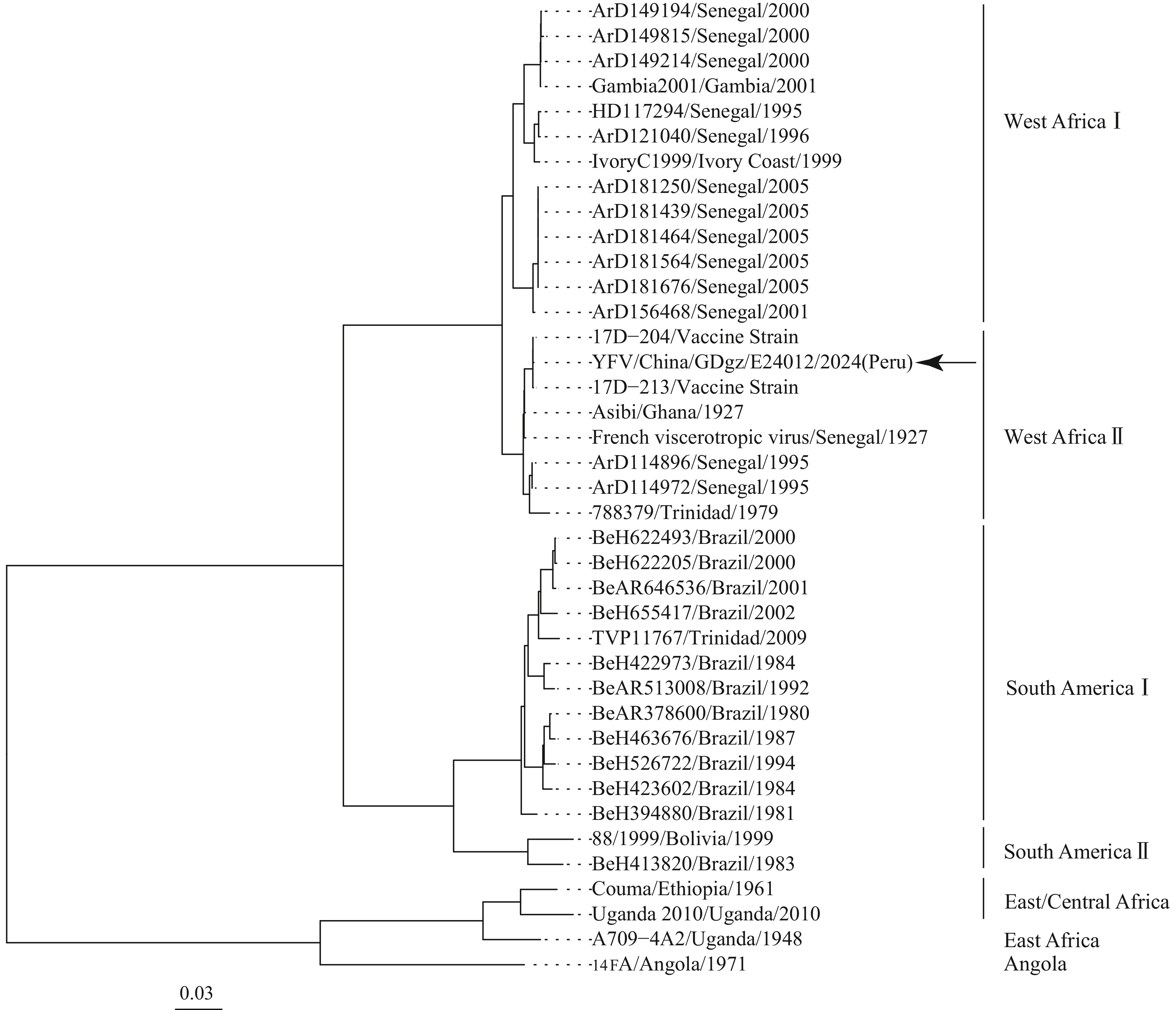
This report describes the first imported suspected YF case in China in 2024, which was a 46-year-old Peruvian man with a recent YF vaccination history. Guangdong CDC employed Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing (tNGS) analysis to determine whether the patient was infected by the wild-type YF virus strain or experienced an AEFI. tNGS analysis successfully yielded a 10.2 kb viral genomic sequence and BLAST analysis revealed high similarity to the YF vaccine strain 17D-213. Phylogenetic analysis classified the sequence within the West Africa II genotype, clustering with the 17D vaccine strain and showing 99.89%–99.79% homology with vaccine strains, while demonstrating only 85.4%–84.9% similarity to wild-type YF virus strains from South America. Based on this evidence, an expert panel consultation concluded that this case represented YF AEFI.
The implementation of tNGS technology enables more precise and expeditious pathogen sequencing, providing critical evidence for accurate disease diagnosis and informed public health interventions.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed