2025 Vol. 7, No. 6
Physical inactivity among older adults is increasing globally. Analyzing the characteristics and influencing factors of physical activity patterns (PAPs) can inform the design of targeted physical activity (PA) promotion strategies for diverse subgroups.
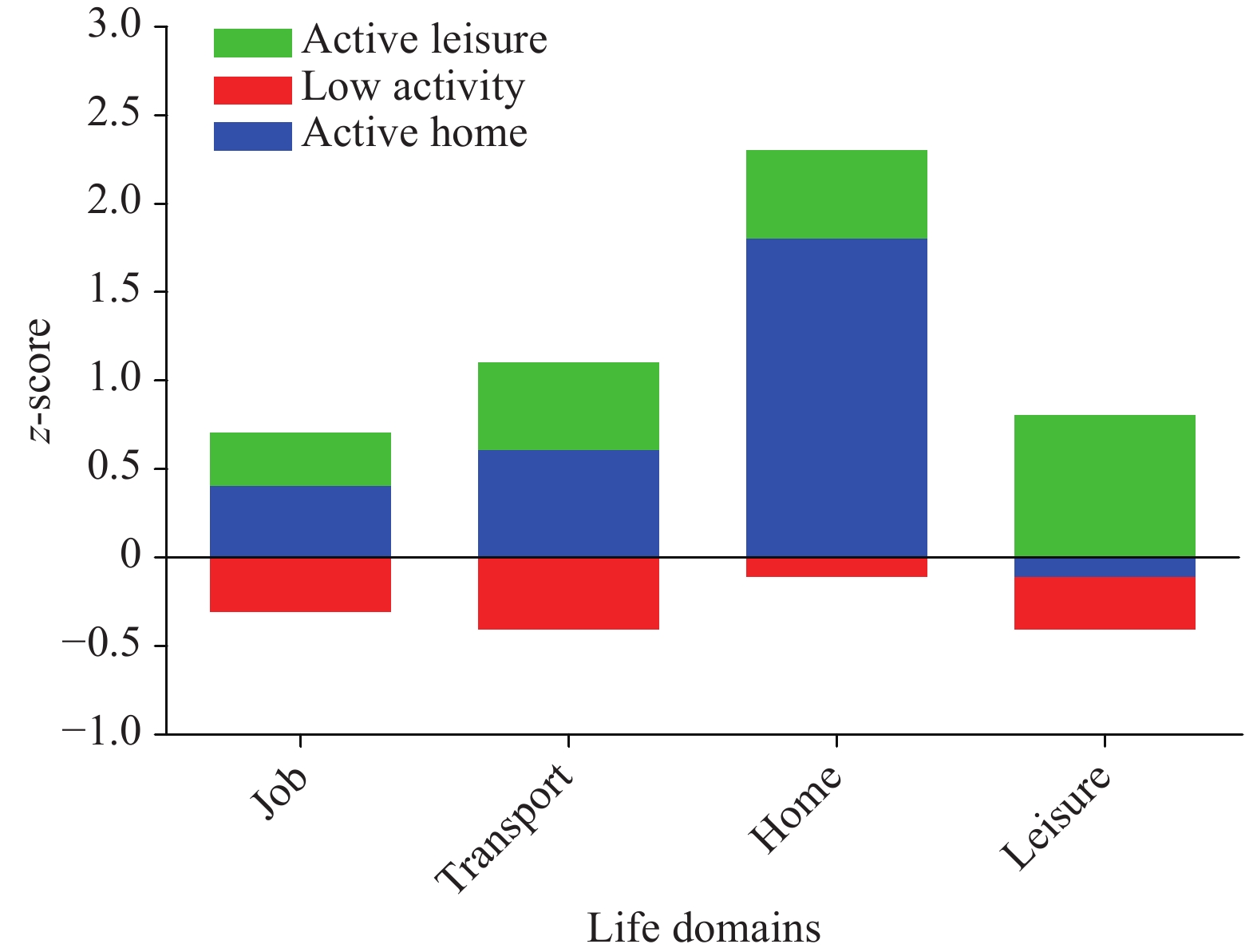
Analysis of national data from 2020 revealed three distinct PAPs among Chinese older adults across life domains: low activity (LA) cluster (53.3%), active leisure (AL) cluster (31.4%), and active home (AH) cluster (15.3%). The AL cluster demonstrated superior psychological status, physical fitness, and built environment conditions compared to both AH and LA clusters. The AH cluster exhibited better physical fitness and built environment characteristics than the LA cluster.
The distinct characteristics among clusters suggest that targeted interventions and policies may be beneficial for each subgroup. These interventions should incorporate enhanced psychosocial support, built environment modifications, and evidence-based guidance for physical fitness improvement, specifically tailored to each cluster’s unique characteristics and needs.
The risk factors for mobile phone dependence (MPD) remain inconsistent and debated in the literature. Previous studies in China reported MPD prevalence rates of 26.2% among junior high students and 27.9% among senior high students in 2012. A 2021 study in Guangzhou City found a prevalence of 13.5% among first-year senior high students.
This study reveals that the overall MPD prevalence among middle school students in Guangzhou was 10.0% in 2023, with distinct rates between junior high (7.3%) and senior high (12.4%) students. The research identifies key risk factors for MPD development and documents injury patterns associated with excessive phone use.
These findings provide an evidence base for developing targeted interventions to reduce both MPD occurrence and associated injuries among middle school students.
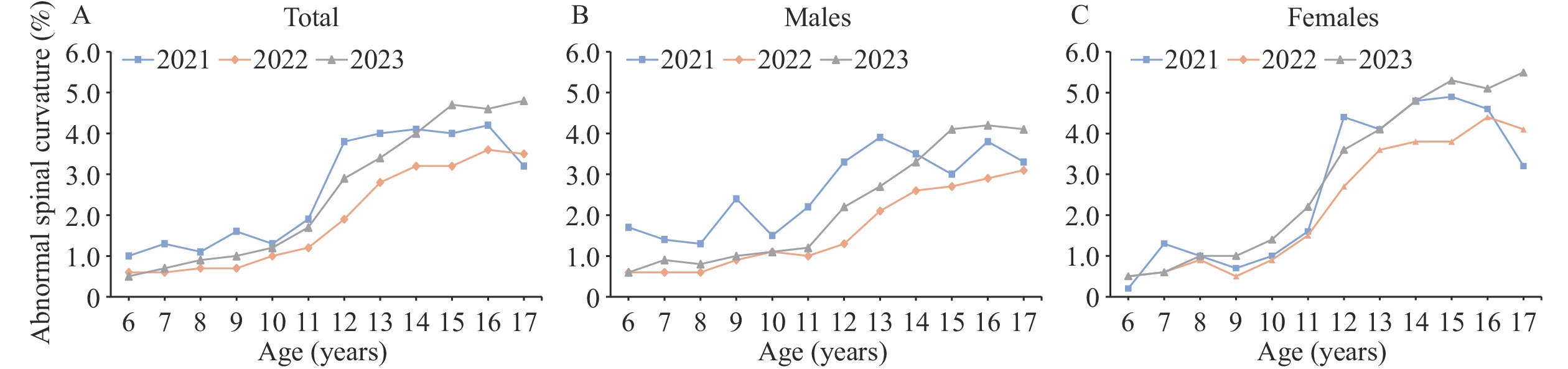
Spinal curvature abnormalities have emerged as a major public health challenge for children and adolescents in China, with detection rates showing a concerning upward trend in recent years.
This population-based surveillance study revealed a 2.1% detection rate of abnormal spinal curvature among children and adolescents aged 6–17 years in Jiangsu Province. The findings emphasize the critical need for early intervention programs targeting modifiable risk factors, including insufficient physical activity, inadequate sleep duration, and improper reading and writing posture.
The increasing burden of abnormal spinal curvature requires targeted attention, particularly for high school students and females during growth spurts. A comprehensive approach combining early lifestyle interventions, such as adequate outdoor activities, with appropriate referrals to public health specialists and orthopedic surgeons may enhance risk mitigation. Success in addressing this challenge requires coordinated multisectoral collaboration and active parental engagement.
Self-harm represents a significant public health challenge that disproportionately affects young adults. Understanding individual- and institutional-level risk factors is crucial for developing and implementing effective mental wellness intervention programs for college students.
The prevalence of youth self-harm fluctuated between 2.21% and 3.83% from 2019 to 2023. Risk factors associated with self-harm included unhealthy lifestyle behaviors, particularly internet addiction, while the implementation of regular family psychological forums was associated with reduced self-harm risk.
Effective campus-based psychosocial support systems must incorporate person-centered approaches and context-specific needs, optimize resource allocation through targeted interventions, and prioritize high-risk groups exhibiting unhealthy lifestyle behaviors.
Cervical cancer is a common malignancy in women, with persistent human papillomavirus (HPV) infection as its primary cause. Understanding the progression from HPV infection to cervical cancer is crucial. Mathematical models play a key role in converting clinical trial data into long-term health forecasts, helping decision-makers tackle challenges posed by limited data and uncertain outcomes. This paper reviews transmission dynamics models and advancements in simulating HPV transmission leading to cervical cancer. It evaluates preventive and control measures, focusing on the impact of HPV vaccination across different vaccine types, doses, age groups, and both genders. These model-based assessments aim to provide insights for developing effective strategies to prevent and control HPV-related cervical cancer.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed