-
Introduction: With the popularity of smartphones, mobile phone dependence (MPD) has become a public health issue of great concern worldwide, especially among middle school students. It can not only lead to physical and mental health problems such as eyestrain, anxiety, and depression, but also increase the risk of safety accidents due to distraction. The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence of MPD among middle school students in Guangzhou in 2023, identify its risk factors, and examine the consequences associated with excessive phone use.
Methods: From April to May 2023, a total of 1,928 students from 4 junior high schools and 4 senior high schools in Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province, were recruited through multi-stage cluster random sampling. The Mobile Phone Dependence Scale for Middle School Students (MPD Scale), consisting of 16 items with a maximum score of 80, was used. A score above 48 indicates MPD. SPSS 26.0 was used for statistical analysis.
Results: A total of 1,928 questionnaires were collected, of which 1,883 were valid. The overall prevalence of MPD in this study was 10.0%, with 7.3% among junior high school students and 12.4% among senior high school students. Logistic regression showed that female sex, higher grade level, authoritarian paternal parenting style, extended phone usage duration, and specific motivations for phone use were associated with the risk of MPD. The prevalence of injury due to distraction by phone was 29.4% in the MPD group, which was significantly higher than that of the non-MPD group (10%).
Conclusions: This study provides up-to-date data on the prevalence of MPD among middle school students in Guangzhou and reveals multiple factors that are associated with its development. Females and high school students should be particularly concerned as high-risk groups. To reduce the risk of MPD occurrence, families are encouraged to adopt democratic parenting styles and promote students’ healthy phone use habits. In addition, preventing MPD may help reduce the risk of unintentional injuries due to mobile phone distraction.
-
Mobile phones offer significant convenience but also introduce a range of negative health-related concerns, among which mobile phone dependence (MPD) is particularly alarming. MPD, also referred to as mobile phone addiction, mobile phone abuse, or problematic mobile phone use, is a growing concern worldwide. It can lead to symptoms such as eye strain, anxiety, and depression (1). Additionally, excessive mobile phone use poses safety risks, such as injuries due to distractions while walking or crossing streets (2). Middle school students are especially vulnerable to MPD due to their developmental stage and increased exposure to mobile technology. Research on the correlation between various factors, such as socioeconomic status, and MPD has yielded inconsistent results among adolescents, leading to ongoing debate (3). This study, which uses data from a cross-sectional survey conducted from April to May 2023 in Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province, China, aims to assess the current prevalence of MPD among middle school students, identify its risk factors, and examine the associated consequences.
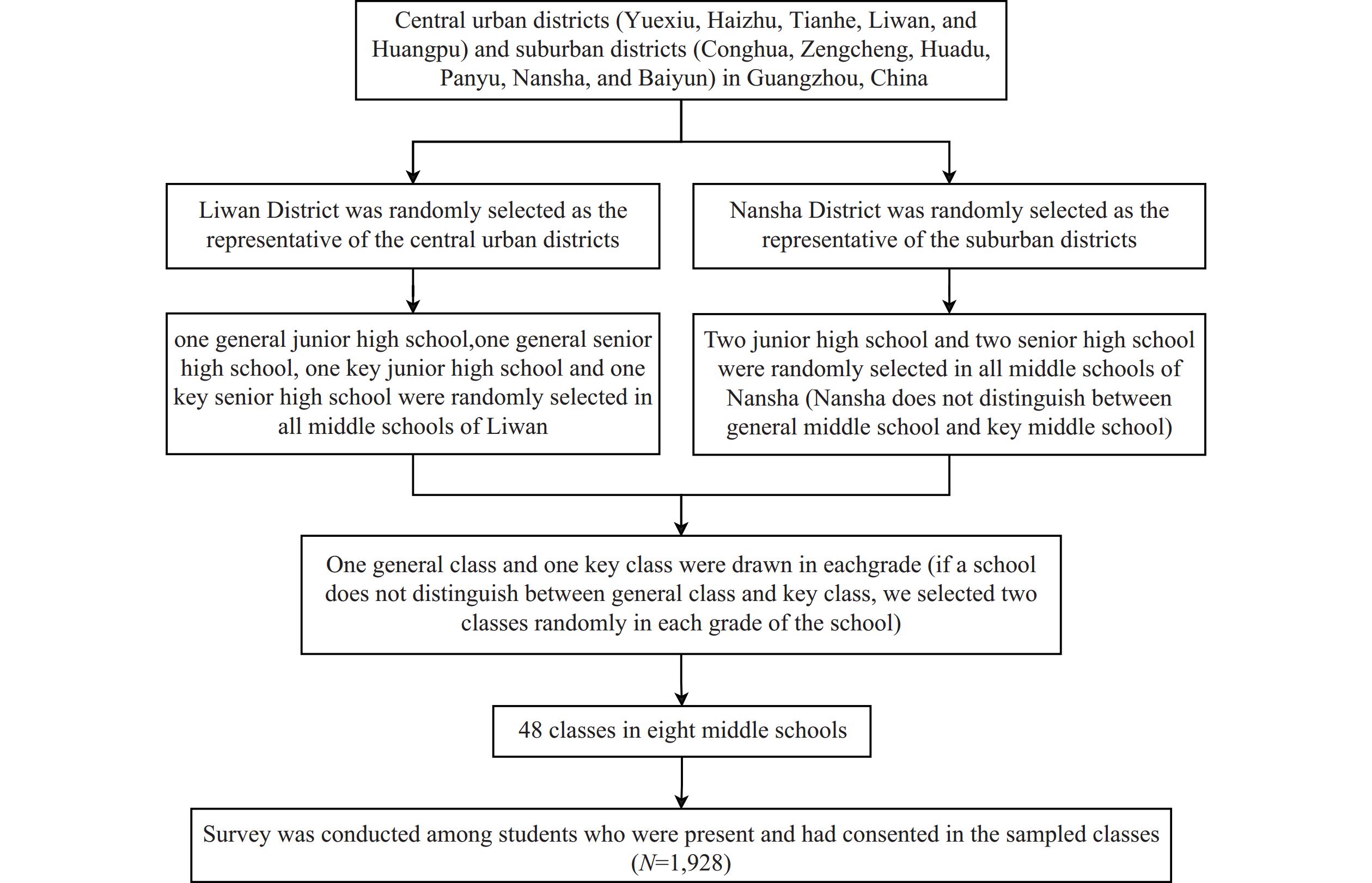
This cross-sectional study was conducted from April to May 2023 in Guangzhou, where junior and senior high school students were selected through multi-stage cluster random sampling (Figure 1). Based on Guangzhou’s economic development and anticipated high mobile phone ownership among middle school students, an MPD prevalence of 15.0% was estimated. This estimate was informed by Qiu et al.’s 2021 Guangzhou survey (4), which reported a 13.5% prevalence among senior one students. Using the formula
$ n=Z_{\alpha}^2p(1-p)/d^2 $ for simple random sampling (α=0.05, d=0.15p), the initial sample size was calculated. To account for the multi-stage cluster sampling design, we increased this estimate by 50%. Assuming a 90% response rate, the final minimum required sample size was 1,613 students. The study employed Wang’s (5) Mobile Phone Dependence Scale for Middle School Students (MPD Scale), comprising 16 items with a maximum score of 80, where scores exceeding 48 indicate MPD. Demographic data, mobile phone usage patterns, and usage consequences were collected. Parenting style and parental care levels were self-reported through standardized questions after participants received clear explanations of response options. All investigators underwent comprehensive training, and school personnel provided support to ensure data quality and authenticity. Prior to survey administration, both participants and their legal guardians received detailed study information. Respondents who incompletely filled out the MPD Scale (allowing one missing item with mean value interpolation) or provided illogical or non-serious responses to multiple-choice questions were excluded.Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics (version 26.0; SPSS, Inc., Armonk, NY, USA). Continuous data were presented as mean (standard deviation, SD) and median, and categorical variables were presented as counts and percentages. The Wilcoxon rank sum test compared MPD scale scores between MPD and non-MPD groups. Group comparisons utilized chi-square tests or Fisher’s exact tests for univariate analyses. We employed stepwise binary logistic regression to identify MPD-associated factors, with variables selected based on previous research and preliminary statistical analyses. The odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) were calculated to quantify the impact of independent variables. Statistical significance was set at P<0.05 (two-tailed).
In this study, 1,928 questionnaires were collected, with 1,883 meeting eligibility criteria (97.67% effective rate). The MPD scale demonstrated good internal consistency with a Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of 0.88. Participants had a mean age of 15.33 years (SD=1.71 years). The overall MPD prevalence among middle school students in Guangzhou was 10.0%, with differential rates between junior high (7.3%) and senior high students (12.4%). The mean total score on the MPD Scale was 35.74 (Table 1). Across all participants, including those diagnosed with MPD, scores were highest in the prominence dimension, followed by abstinence and compulsivity, with significant differences observed between MPD and non-MPD groups across all three dimensions.
Dimensions* All participants Participants with MPD Participants without MPD P Mean SD Median Mean SD Median Mean SD Median Abstinence 2.1 0.9 2.0 3.6 0.6 3.5 1.9 0.7 2.0 <0.001 Compulsivity 1.7 0.7 1.6 2.8 0.8 2.8 1.6 0.6 1.4 <0.001 Prominence 2.9 0.8 3.0 3.9 0.5 3.8 2.8 0.8 2.8 <0.001 Total score 35.7 10.6 35.0 55.1 5.9 54.0 33.6 8.7 34.0 <0.001 Abbreviation: SD=standard deviation; MPD=mobile phone dependence.
* Abstinence: This refers to the emotional reactions, such as anxiety and irritability, that occur when an individual is suddenly unable to use their phone or cannot use it normally. Compulsivity: This refers to an individual exhibiting a compelling desire and urge to use the mobile phone, finding it challenging to disengage, and potentially experiencing delusions associated with phone use. Prominence: This is when behavior is dominated by the use of the mobile phone, primarily manifested as overuse of the phone and excessive checking of the phone in daily life.Table 1. Scores of each item at different dimensions and total score of MPD scale.
The univariate analysis comparing MPD and non-MPD groups revealed significant differences (P<0.05) across multiple variables: sex, grade, personality, perceived study pressure, academic achievement, father’s education level, father’s parenting style, father’s caring for their children, number of mobile phones owned, duration of mobile phone ownership, daily mobile phone usage time, motivation and application of mobile phone use, and monthly internet data usage. Notable disparities emerged in mobile phone use consequences between groups, particularly in injury occurrence due to excessive phone focus (29.4% in the MPD group vs. 10% in the non-MPD group) (Table 2). These findings indicate that excessive mobile phone use significantly increases the risk of physical injuries, including collisions with stationary objects and falls.
Variables Total (n=1,883) Non-MPD group (n=1,694) MPD group (n=189) Fisher* /χ2 P Sex 8.473 0.004 Male 1,035 (55.0) 950 (56.1) 85 (45.0) Female 848 (45.0) 744 (43.9) 104 (55.0) Grade 13.200 <0.001 Junior high school 873 (46.4) 809 (47.8) 64 (33.9) Senior high school 1,010 (53.6) 885 (52.2) 125 (66.1) Academic performance† 1%–25% in grade 585 (31.1) 529 (31.2) 56 (29.6) 13.503 0.004 26%–50% in grade 587 (31.2) 541 (31.9) 46 (24.3) 51%–75% in grade 508 (27.0) 455 (26.9) 53 (28.0) 76%–100% in grade 203 (10.8) 169 (10.0) 34 (18.0) Physical activity 5.161 0.156 Once a day 491 (26.1) 437 (25.8) 54 (28.6) 4–6 times a week 848 (45.0) 777 (45.9) 71 (37.6) 1–3 times a week 500 (26.6) 441 (26.0) 59 (31.2) Never play sports 44 (2.3) 39 (2.3) 5 (2.6) Perceived study pressure 22.593 <0.001 Low/no stress 61 (3.2) 53 (3.1) 8 (4.2) Appropriate stress 1,044 (55.4) 970 (57.3) 74 (39.2) Heavy/very heavy stress 778 (41.3) 671 (39.6) 107 (56.6) Father’s Education§ 10.497 0.033 Elementary school or below 100 (5.3) 84 (5.0) 16 (8.5) Junior high school 668 (35.5) 597 (35.2) 71 (37.6) Senior high/technical secondary school 636 (33.8) 588 (34.7) 48 (25.4) Junior college/vocational university 253 (13.4) 221 (13.2) 32 (16.9) Bachelor’s degree or above 226 (12.0) 204 (12.0) 22 (11.6) Father’s parenting style§ 18.413 <0.001 Democratic 1,023 (54.3) 947 (55.9) 76 (40.2) Authoritarian 401 (21.3) 343 (20.2) 58 (30.7) Indulgent 442 (23.5) 389 (23.0) 53 (28.0) Spoiling 17 (0.9) 15 (0.9) 2 (1.1) Father’s caring for their children§ 12.475 0.002 Very caring 935 (49.7) 864 (51.0) 71 (37.6) Average 807 (42.9) 708 (41.8) 99 (52.4) Doesn’t care 141 (7.5) 122 (7.2) 19 (10.1) Time spent on mobile phone on rest days 66.104 <0.001 0 to 2 hours 530 (28.1) 499 (29.5) 31 (16.4) More than 2 hours to 6 hours 960 (51.0) 884 (52.2) 76 (40.2) More than 6 hours 393 (20.9) 311 (18.4) 82 (43.4) Main motivation for using mobile phone 20.969 <0.001 Information access 334 (17.7) 319 (18.8) 15 (7.9) Interpersonal communication or self-expression 668 (35.5) 599 (35.4) 69 (36.5) Entertainment 816 (43.3) 713 (42.1) 103 (54.4) Others 65 (3.5) 63 (3.7) 2 (1.1) Finger fatigue, stiffness, or pain¶ Yes 227 (12.1) 172 (10.2) 55 (29.4) 58.323 <0.001 No 1,646 (87.9) 1,514 (89.8) 132 (70.6) Eyes blurred or hurting¶ 54.318 <0.001 Yes 630 (33.6) 522 (30.9) 108 (57.8) No 1,245 (66.4) 1,166 (69.1) 79 (42.2) Tinnitus¶ 29.258 <0.001 Yes 150 (8.0) 116 (6.9) 34 (18.2) No 1,725 (92.0) 1,572 (93.1) 153 (81.8) Being injured because of phone distractions¶ 60.423 <0.001 Yes 223 (11.9) 168 (10.0) 55 (29.4) No 1,646 (88.1) 1,514 (90.0) 132 (70.6) Abbreviation: MPD=mobile phone dependence.
* Fisher: Fisher exact test.
† The ranking of academic performance is self-reported, therefore the proportions are not perfectly divided into quartiles.
§ The corresponding variables for mothers do not show significant differences between the two groups.
¶ There are missing data: 10, 8, 8, and 14 missing values for the respective variables.Table 2. Basic information, mobile phone use, and consequences of phone use among middle school students in Guangzhou, China.
In the multivariable binary logistic regression analysis, using the non-MPD group as a reference, several significant risk factors for MPD development emerged. Female students demonstrated heightened susceptibility [adjusted OR (aOR)=1.772, 95% CI: 1.239, 2.532], as did high school students (aOR=1.479, 95% CI: 1.014, 2.155). Paternal authoritarian parenting style (aOR=2.023, 95% CI: 1.315, 3.111) and mobile phone usage exceeding 6 hours during rest days (aOR=3.115, 95% CI: 1.829, 5.307) were identified as substantial risk factors. Additionally, specific motivations for mobile phone use significantly increased MPD risk, including interpersonal communication or self-expression (aOR=2.197, 95% CI: 1.183, 4.079) and entertainment (aOR=2.527, 95% CI: 1.381, 4.624) (Table 3). A separate multivariable binary logistic regression model (not presented in tables) revealed that students with MPD exhibited a significantly higher likelihood of sustaining phone-related distraction injuries compared to those without MPD (aOR=3.359, 95% CI: 2.276, 4.957).
Variables aOR* 95% CI P Sex Male (reference) Female 1.772 1.239, 2.532 0.002 Grade Junior high school (reference) Senior high school 1.479 1.014, 2.155 0.042 Father’s parenting style† Democratic (reference) Authoritarian 2.023 1.315, 3.111 0.001 Indulgent 1.485 0.978, 2.255 0.064 Spoiling 1.527 0.321, 7.259 0.594 Time spent on mobile phone on rest days 0 to 2 hours More than 2 hours to 6 hours 1.288 0.785, 2.115 0.316 More than 6 hours 3.115 1.829, 5.307 0.001 Main motivation for using mobile phone Information access (reference) Interpersonal communication or self-expression 2.197 1.183, 4.079 0.013 Entertainment 2.527 1.381, 4.624 0.003 Others 0.755 0.093, 6.129 0.793 Abbreviation: aOR=adjusted odds ratio; CI=confidence interval.
* Variables whose P value less than 0.05 in the univariate analysis were included to establish a multivariable binary logistic regression model.
† Democratic parenting style is one where parents engage in an equal and respectful relationship with their children, allowing for the full expression of their individual personalities. Authoritarian parenting style is characterized by absolute authority and a preference for control, which can inhibit the full expression of the child’s individual personality. Permissive parenting style is characterized by a lack of enforced rules and restrictions, a high level of trust in the child’s life and academic decisions, and the delegation of most control to the child. Indulgent parenting style is characterized by excessively fulfilling any needs of the child, over-pampering, allowing the child’s temperament to dictate, and indulging the child.Table 3. Results on multivariable binary logistic regression analysis of MPD.
-
The prevalence of MPD in this study — 7.3% among junior high students and 12.4% among senior high students — was notably lower than rates reported in 2012 and 2021 (4,6). Logistic regression analysis identified several significant risk factors associated with MPD development, including female sex, higher grade level, authoritarian paternal parenting style, extended phone usage duration, and specific motivations for phone use.
The results align with previous research indicating that females demonstrate higher susceptibility to MPD than males (aOR=1.772). This sex-based disparity may be attributed to adolescent females’ heightened need for emotional fulfillment through social relationships and their tendency to express emotions via mobile phone messaging applications. The study also revealed that senior high school students exhibited greater vulnerability to MPD (aOR=1.479) compared to junior high students. This observation is consistent with research conducted among middle school students in Xiamen City, Fujian Province, China, which documented increased mobile phone dependency in senior high school cohorts (7). This elevated risk may stem from the intense academic pressures and college entrance examination stress faced by Chinese senior high school students, potentially leading to challenges in regulating mobile phone usage as a stress-coping mechanism (7). To address these concerns, we recommend that senior high schools implement regular psychological counseling services and optimize academic pressure management strategies to help students develop healthier coping mechanisms and reduce mobile phone dependency.
This study demonstrated that students whose fathers exhibited authoritarian parenting styles faced a significantly higher risk of developing MPD (aOR=2.023). This finding aligns with research from Indonesia that established a positive correlation between authoritarian parenting and mobile phone dependency (8). Moreover, existing literature indicates that family cohesion exhibits an inverse relationship with mobile phone dependency (9), while individuals raised in emotionally supportive, harmonious family environments are more likely to develop secure family attachments, thereby reducing their susceptibility to MPD (10). These findings underscore the critical role of family dynamics in MPD development and highlight the importance of considering familial environments when designing intervention strategies.
The analysis identified several behavioral risk factors for MPD, including mobile phone usage exceeding 6 hours during rest days (aOR=3.115), utilization primarily for interpersonal communication or self-expression (aOR=2.197), and entertainment-focused usage (aOR=2.527). The increased availability of free time may contribute to excessive mobile phone engagement. These findings emphasize the necessity of implementing targeted guidance for middle school students regarding appropriate technology usage patterns and fostering healthier attitudes toward digital device engagement.
Among the consequences related to MPD, our results revealed significantly higher rates of physical symptoms in the MPD group compared to the non-MPD group, including finger pain, ocular discomfort, and tinnitus, indicating substantial adverse physiological effects. Most notably, students with MPD demonstrated a markedly elevated risk of sustaining injuries due to phone-related distractions (aOR=3.359). The immersive nature of mobile content can significantly diminish environmental awareness, increasing susceptibility to falls, collisions, and potentially serious accidents. As mobile phone adoption and usage duration continue to rise, the incidence of such injuries may correspondingly increase (11). Therefore, implementing targeted interventions to mitigate MPD is crucial for preventing mobile phone-related injuries.
This study has several limitations. First, the reliance on self-reported data introduces potential information bias. Second, the cross-sectional design precludes definitive causal inference. Future research should employ longitudinal methodologies to address these limitations.
Nevertheless, this study provides contemporary data on MPD prevalence and identifies key risk factors for its development. Our findings indicate that female students and high school students require particular attention in intervention strategies. The promotion of democratic parenting styles within families may reduce MPD risk. Additionally, evidence-based educational programs should be developed to foster healthy mobile phone usage patterns. Most critically, reducing MPD prevalence could substantially decrease the risk of unintentional injuries caused by mobile phone-related distractions — an urgent public health concern requiring immediate attention to prevent accidents among middle school students. A comprehensive approach involving societal, educational, familial, and individual interventions is essential to effectively address MPD and protect adolescent health.
-
We extend our gratitude to the staff involved in the field investigation and the relevant departments of various schools for their cooperation.
-
Received ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of the Guangzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention, China (approval number: GZCDC-ECHR-2021P0063).
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:





