2025 Vol. 7, No. 5
Integrated congenital heart disease (CHD) services were implemented in Beijing in 2022. This study analyzed prenatal diagnosis patterns and neonatal mortality data for duct-dependent CHDs before and after implementation to provide insights for service optimization.
We conducted a retrospective analysis of 487 cases of duct-dependent CHDs identified through the Beijing Birth Defects Monitoring System from January 2021 to December 2022. The study population included fetuses and infants from 13 weeks gestation to one year after birth. Cases underwent descriptive analysis focusing on disease occurrence, diagnostic timing, and mortality outcomes.
The prenatal diagnosis rate for duct-dependent CHDs increased from 93.39% in 2021 to 93.91% in 2022, while delayed diagnosis rates decreased from 4.28% to 3.91%. Genetic diagnosis rates improved from 27.92% to 31.94%. Live birth rates following prenatal diagnosis increased substantially from 28.75% to 40.28%. Outcomes varied significantly by CHD subtypes, with complete transposition of the great arteries with intact ventricular septum achieving an 82.14% live birth rate, while hypoplastic left heart syndrome cases resulted in no live births. Notably, neonatal mortality decreased markedly from 7.23% to 3.03%.
Beijing’s integrated service model for CHDs has effectively strengthened the connection between secondary and tertiary prevention strategies, reduced unnecessary pregnancy terminations, and improved neonatal survival outcomes.
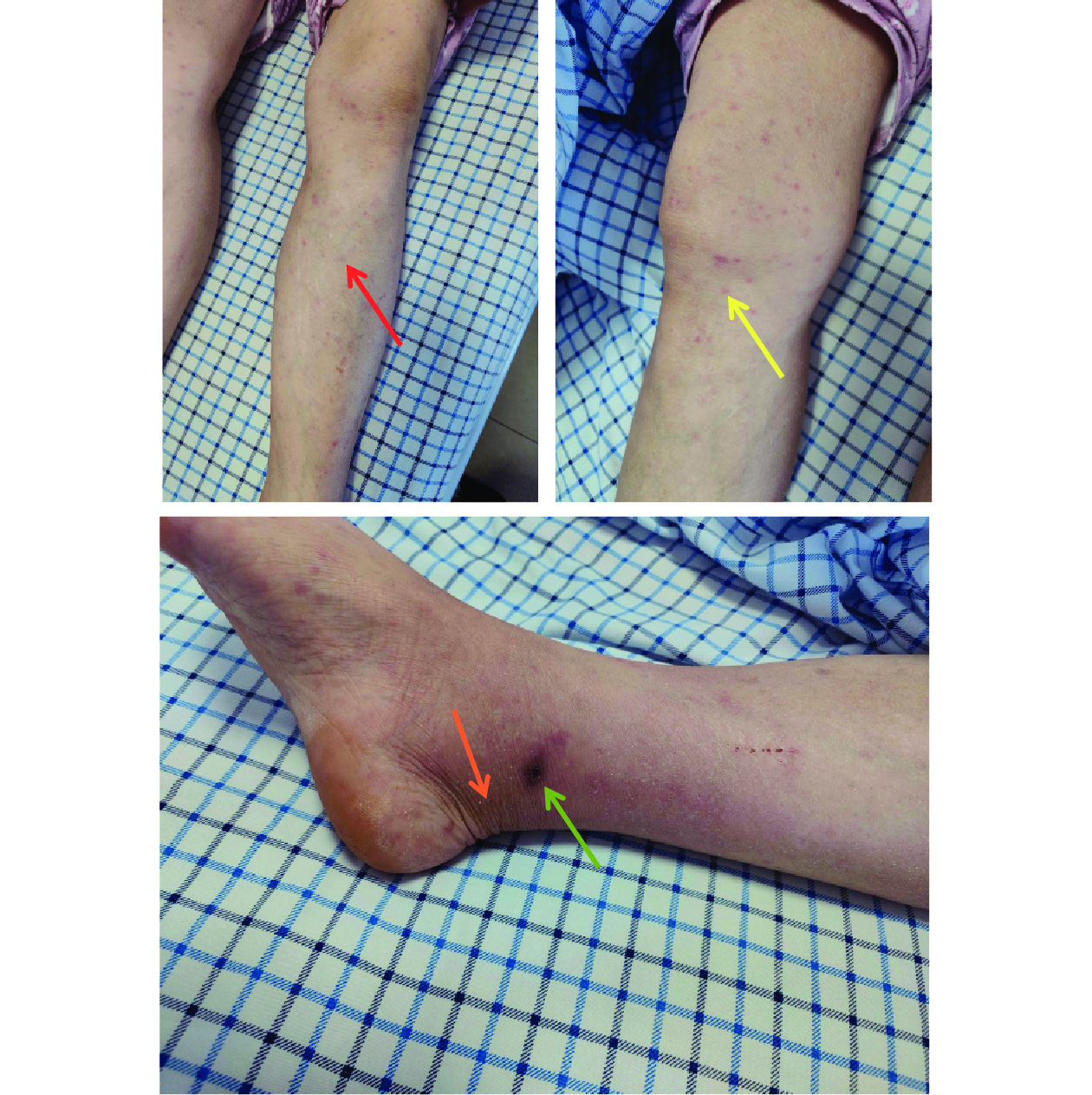
Scrub typhus is an acute infectious disease caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi that is transmitted primarily through the bite of infected chigger mite larvae. The disease prevalence is closely associated with environments characterized by high moisture levels and abundant vegetation.
This study documents the first confirmed case of scrub typhus in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. The patient presented with characteristic clinical manifestations, including abnormal biochemical indicators and positive serum-specific IgM antibodies against scrub typhus. Epidemiological evidence suggests local acquisition of the disease.
Enhanced surveillance and preventive measures for scrub typhus are essential in this region, particularly for individuals residing in or visiting areas where the disease may be endemic.
Childhood trauma represents a critical risk factor for substance use among young populations globally, presenting a substantial public health challenge.
This comprehensive investigation elucidates the distinct associations between specific subtypes of childhood trauma and substance use behaviors within the Chinese youth population. The findings demonstrate significantly elevated risks for smoking, e-cigarette use, and alcohol consumption, particularly among individuals who have experienced severe or multiple forms of childhood trauma.
Implementation of targeted interventions and support systems is essential for individuals with childhood trauma histories. Healthcare providers should emphasize early identification and trauma-informed care approaches. Policy frameworks promoting early intervention and sustained support mechanisms are crucial for reducing substance use behaviors and enhancing population health outcomes.
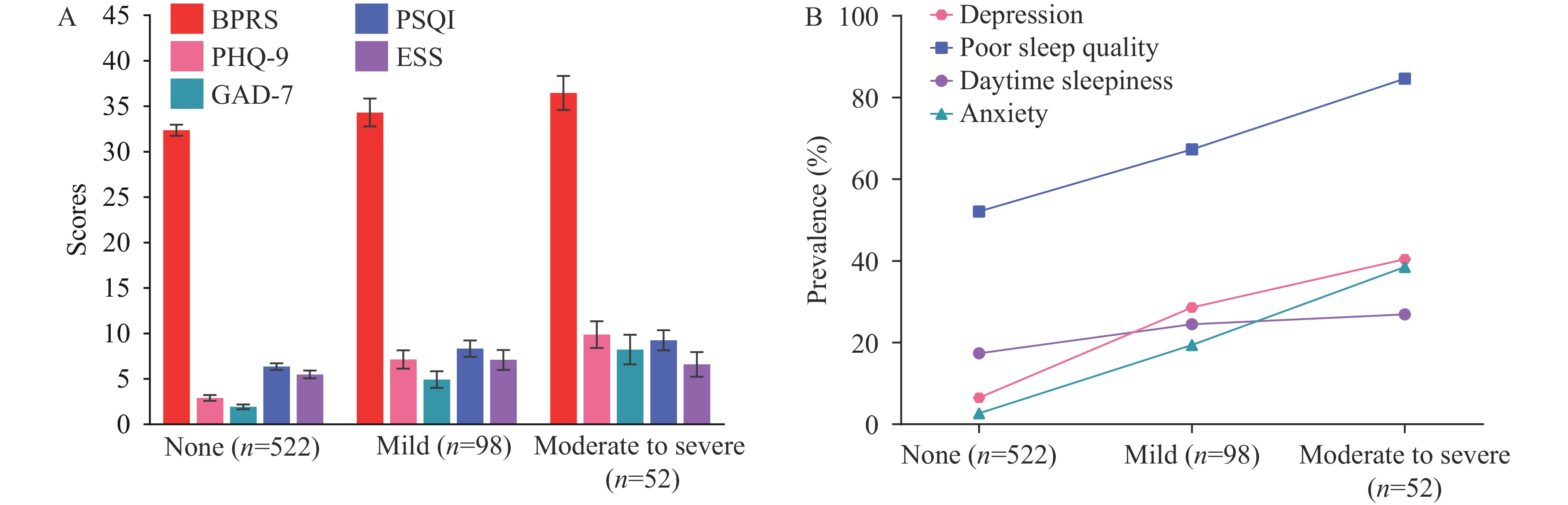
Suicide behaviors are prevalent among inpatients with schizophrenia. However, the relationships between psychiatric symptoms, sleep disturbances, and suicide risk remain poorly understood in these high-risk populations.
In a study of 672 schizophrenia inpatients across 9 hospitals in 4 Chinese provinces, the prevalence of suicide risk was 22.3% [95% confidence interval (CI): 19.3%, 25.6%]. The study identified significant associations between suicide risk and multiple clinical factors, including poor sleep quality, depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, and other psychiatric manifestations such as thinking disorder and activation.
Understanding the common sleep-related and psychiatric factors associated with suicide risk in hospitalized schizophrenia patients will enable clinicians and policymakers to better identify clinical risk indicators and enhance the quality of suicide prevention and treatment programs.
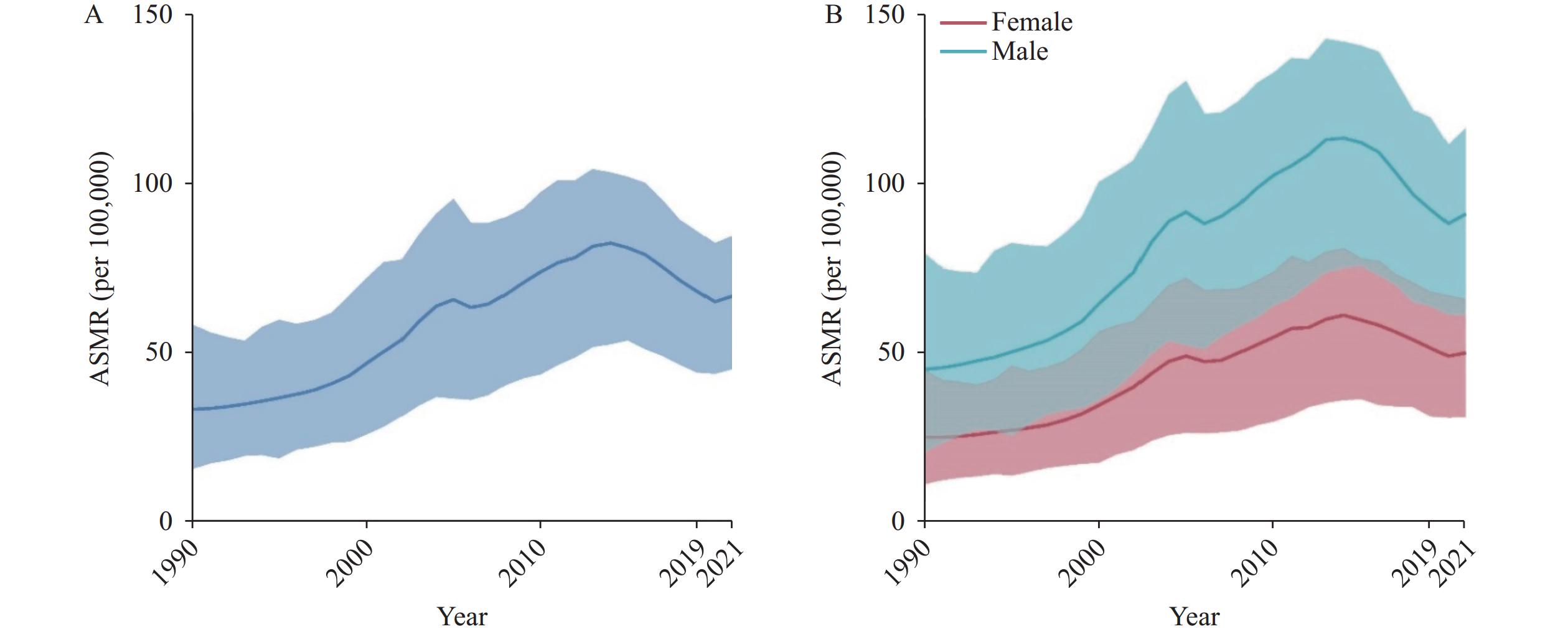
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) represents a major cause of mortality and disability in China’s population. Ambient particulate matter pollution (APMP) has been established as a significant risk factor contributing to CVD development.
Analysis of data from 1990 to 2021 reveals a substantial increase in APMP-attributable CVD mortality across China. While recent trends show decreased mortality risk associated with APMP-attributable CVD, birth cohort analysis demonstrates continued risk elevation in males but declining risk in females born after 1971.
Enhanced surveillance and regulation of APMP, coupled with targeted health promotion strategies, are crucial, particularly for elderly populations and males who show increased vulnerability.
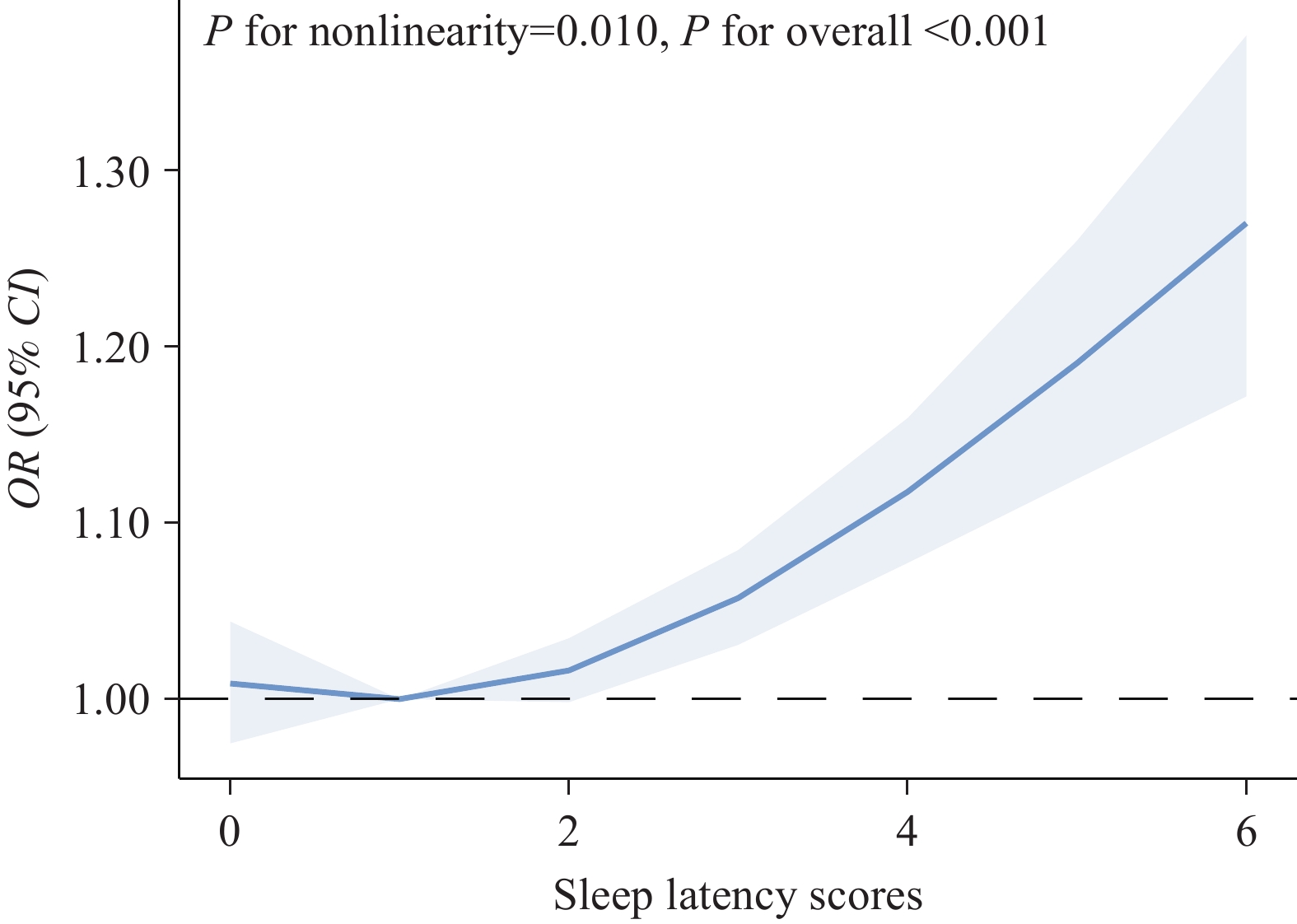
Short sleep duration and poor sleep quality have been epidemiologically associated with cardiometabolic disorders. However, limited research has examined the relationship between prolonged sleep latency, an increasingly prevalent sleep disorder, and hypertension.
Approximately 25% of residents in 4 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) in the southern China experienced prolonged sleep latency. Both occasional and habitual prolonged sleep latency were significantly associated with increased odds of hypertension.
Given the increasing prevalence of hypertension, health initiatives should focus on raising awareness about prolonged sleep latency and implementing targeted interventions to mitigate hypertension risk.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed