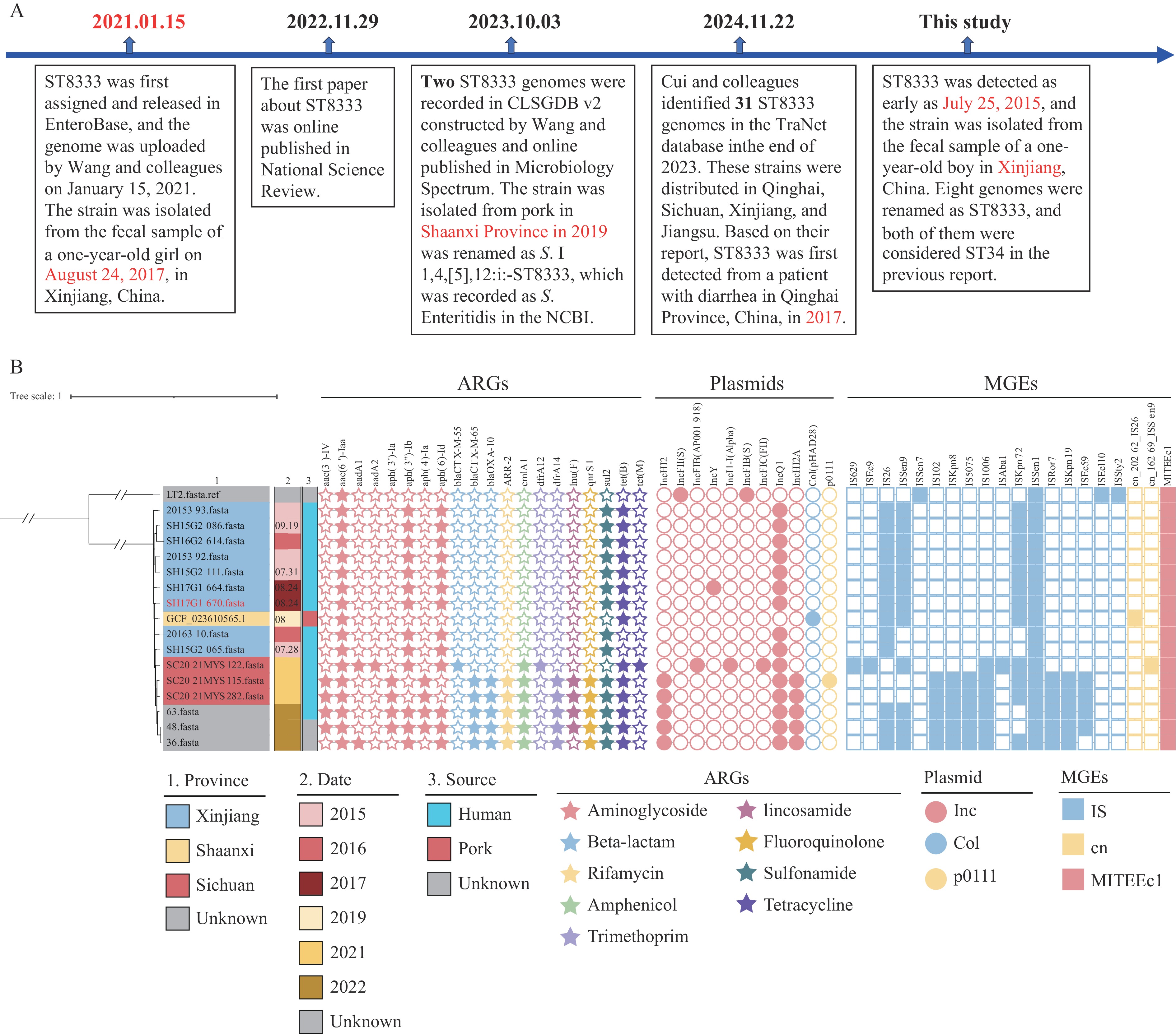
2025 Vol. 7, No. 43
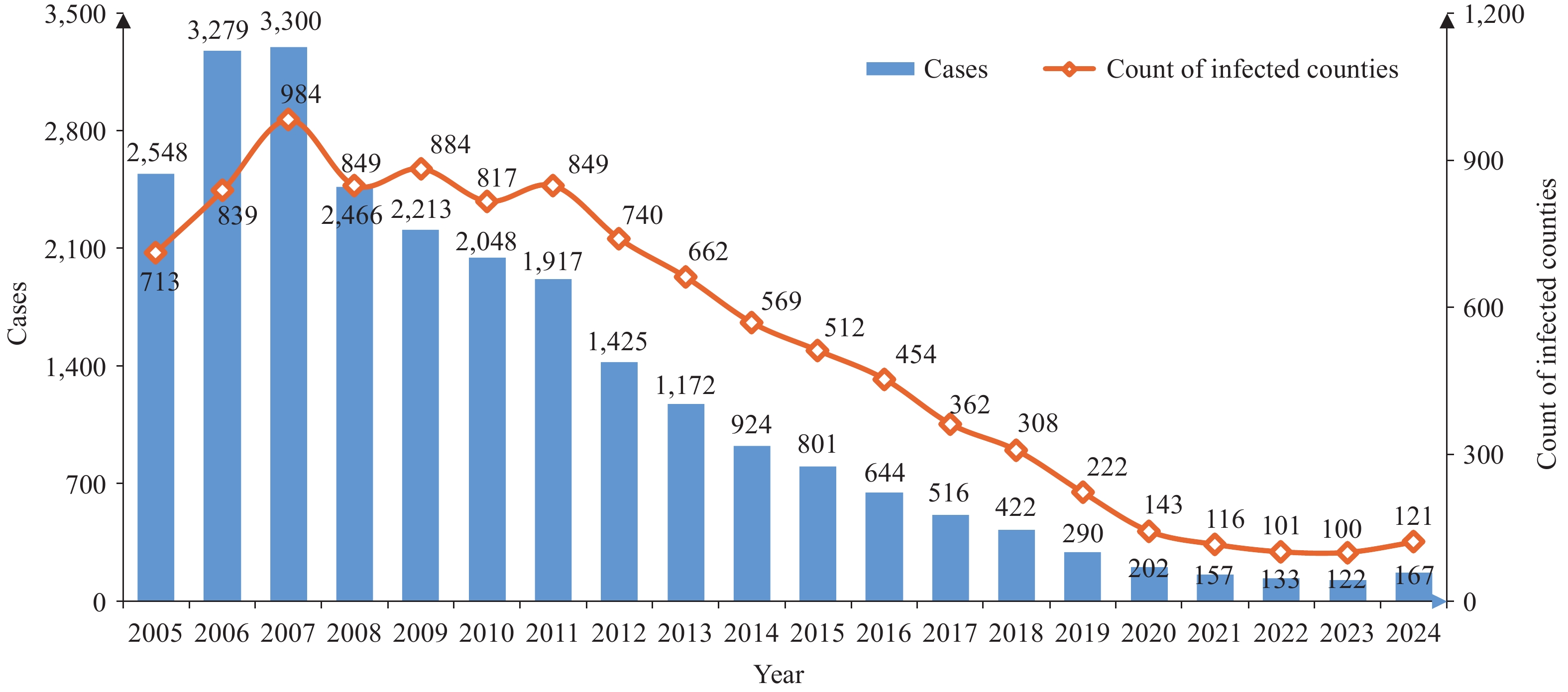
Rabies remains a significant zoonotic disease in China. Following comprehensive control measures implemented since 2006, annual human cases declined steadily from 2008 through 2023. However, 2024 witnessed a 36.9% increase in cases compared with 2023, indicating possible changes in transmission dynamics or control effectiveness. This study analyzes the epidemiological characteristics and spatiotemporal patterns of rabies from 2005 to 2024 to inform targeted prevention strategies.
We employed descriptive epidemiological methods to analyze the spatiotemporal distribution and demographic characteristics of rabies cases in China. Spatial clustering was assessed using global and local Moran’s I statistics (P<0.05). Retrospective space-time scan analysis (2005–2024) was performed using SaTScan software to identify significant disease clusters. We conducted spatial frequency analysis by calculating the number of years each county reported at least one case during the study period; counties reporting cases in ≥10 years were classified as high-frequency areas.
Following a peak of 3,300 cases in 2007, rabies incidence declined continuously for 16 years before resurging in 2024 (167 cases, representing a 36.9% increase compared with 2023). Cases remained geographically concentrated, with 76.0% occurring in six central and southern provincial-level administrative divisions. The majority of affected counties (74%) reported only a single case. Males (70.0%), farmers (68.6%), and individuals aged 41–70 years (53.8%) comprised the highest-risk populations. Spatial analysis revealed that High-High clusters decreased in number over time. These clusters also shifted geographically: from widespread distribution across southwestern provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) during 2005–2014 to concentration in central agricultural zones during 2020–2024, particularly along the border regions of Henan, Hunan, Hubei, and Anhui PLADs. We identified 352 high-frequency counties. Spatiotemporal scan statistics detected seven significant clusters during 2005–2024, all located in central and southwestern regions. Outbreaks within these clusters peaked during summer and autumn months (July–November) from 2006 to 2013, with no new clusters emerging after 2014.
Our findings demonstrate that China’s rabies control efforts have successfully transitioned the epidemic from widespread endemic transmission to sporadic occurrence with localized clustering. The 2024 resurgence occurred predominantly in historically endemic hotspots identified through spatial analysis. Sustaining these control achievements will require implementing precision prevention strategies specifically targeted at these persistent high-risk counties.
Recent sentinel surveillance has revealed a rising prevalence of human adenovirus type 21 (HAdV-21) among HAdV infections in China. This study aimed to elucidate the molecular features of currently circulating HAdV-21 strains in China.
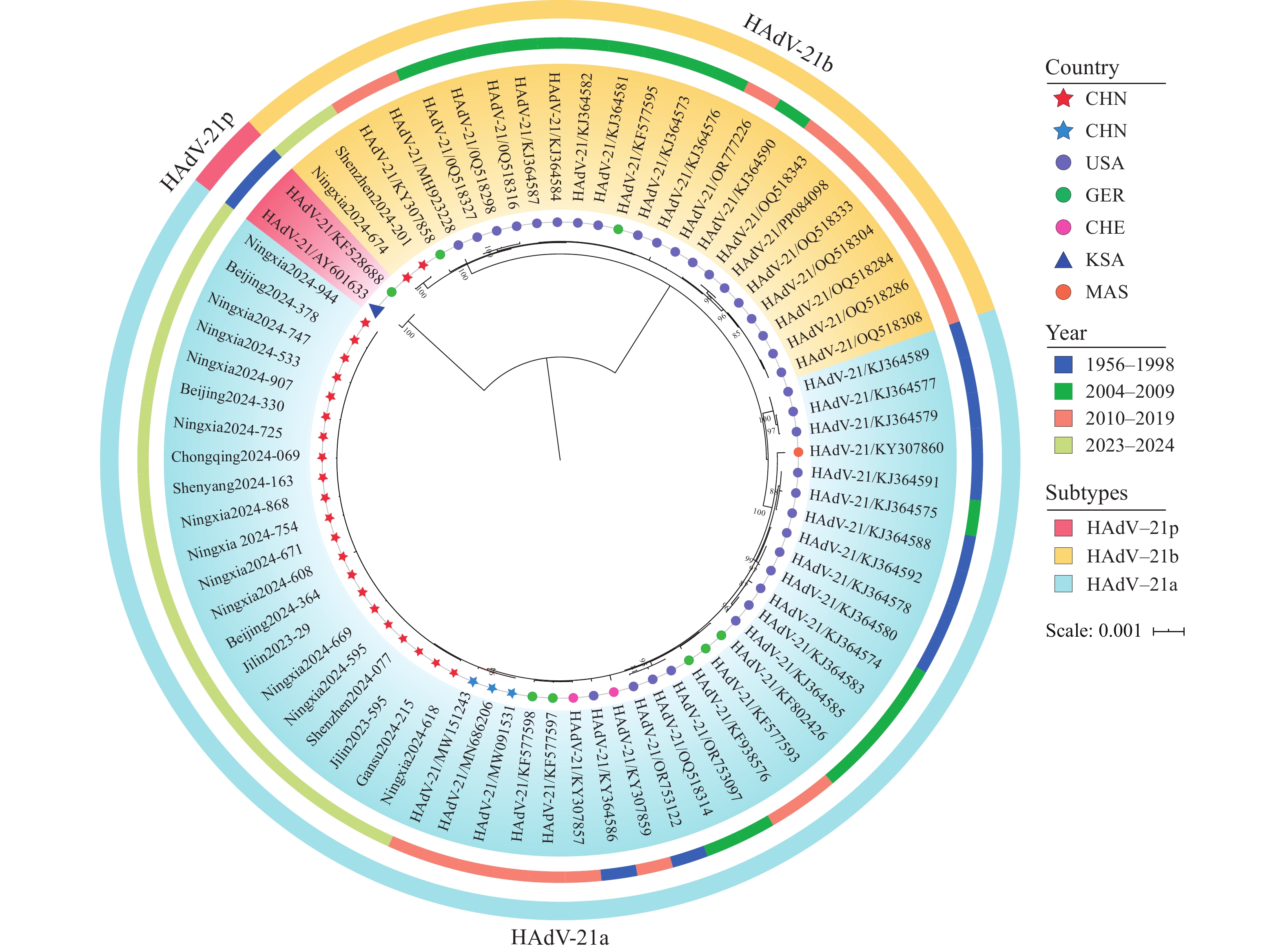
Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) was performed on 23 HAdV-21 strains isolated from acute respiratory infection cases, 56.5% involving lower respiratory tract infections, across 7 Chinese sentinel surveillance provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) (2023–2024). These sequences, along with 50 previously reported HAdV-21 genomes from 6 countries (1956–2019), were integrated into a WGS dataset for comprehensive phylogenetic, genetic variation, and recombination analyses.
WGS categorized the HAdV-21 strains into 3 subtypes: HAdV-21a, HAdV-21b, and historical HAdV-21p (isolated in the 1950s). HAdV-21a (1956–2024, involving 5 of the 6 countries) and HAdV-21b (2005–2024, involving 3 of the 6 countries) exhibited extensive spatiotemporal distributions. Recent Chinese strains (2023–2024) belonged to HAdV-21a and HAdV-21b (HAdV-21a/b), showing extremely high genetic homology with Chinese 2019 strains (genetic distance: 0.00007) and global strains (distance: <0.00040). Phylogenetic analysis confirmed that HAdV-21a/b shared a common ancestor and maintained a highly conserved genome despite decades of circulation. Sequence variation analysis identified shared and subtype-specific mutations in these two subtypes. Recombination pattern analysis further revealed that HAdV-21a/b acquired an HAdV-3-derived fragment in the E4 region (breakpoint: nt32,843).
Recombinant HAdV-21a/b subtypes have co-circulated in China in recent years with remarkable genetic conservation. Enhanced surveillance is essential to quantify associated disease burden and guide targeted prevention and control strategies.
Dengue fever is primarily transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes. While most cases are asymptomatic or mild, some may progress to severe complications. Laboratory diagnosis relies on detection of nucleic acid, antigen, or antibodies in blood specimens.
A patient who developed dengue fever 1 day before delivery had dengue virus RNA, NS1 antigen, and IgM detected in breast milk within 10 days of symptom onset. Nucleic acid and NS1 turned negative by day 15, while IgM antibodies remained positive and turned negative by day 22, suggesting potential transmission risk via early breastfeeding.
Breastfeeding should be avoided until 22 days post-onset, after confirming clearance of viral RNA and IgM from breast milk and excluding infection in the infant. Household members of pregnant women exhibiting suspected dengue symptoms should seek immediate medical attention for dengue NS1 antigen testing during dengue season.
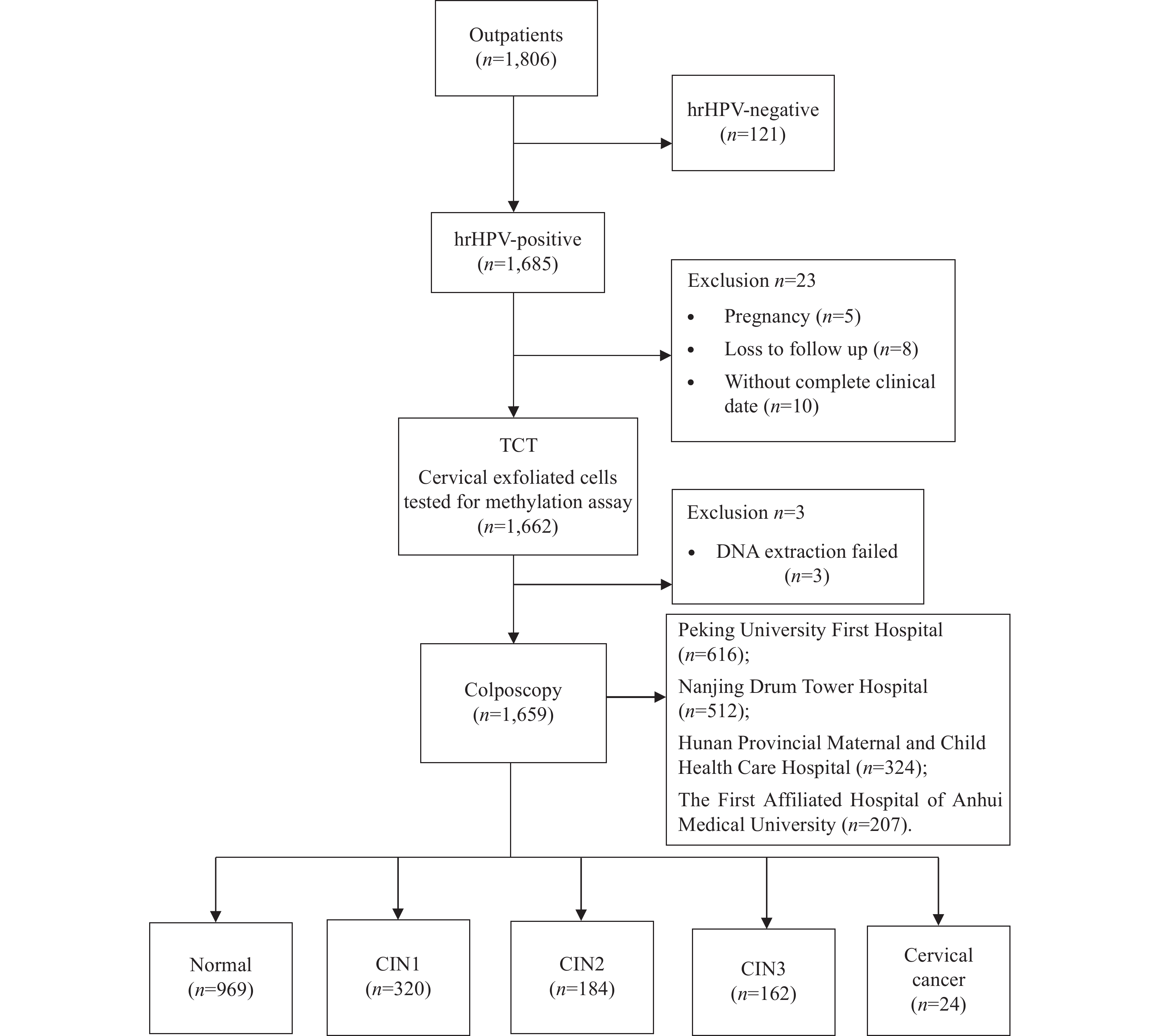
Persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) is recognized as the primary cause of cervical cancer and its precancerous lesions. However, most HPV infections are transient and naturally clear. Currently effective triage tools for distinguishing between transient HPV infections and clinically relevant hrHPV-induced diseases are lacking, leading to excessive referrals and overtreatment.
This is the first large-scale, prospective, multicenter study to evaluate the triage performance of host DNA six-methylation marker assay (ASTN1, DLX1, ITGA4, RXFP3, SOX17, and ZNF671) in women who are hrHPV-positive in China. Compared with HPV genotyping and cytology [≥ atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS)] screening, the six-methylation marker assay demonstrated superior triage performance, with sensitivities of 82.2% and 90.3% and specificities of 92.4% and 84.1% for cervical intraepithelial grade II/III and worse (CIN2+ and CIN3+), respectively. Further subgroup analysis of women <30 years of age revealed its efficacy. The methylation positivity rate increased with the severity of cervical lesions, and the most significant marker was ZNF671. Moreover, the six-methylation marker assay required the fewest colposcopy referrals, with only 1.32 and 2.39 per CIN2+ and CIN3+ cases, respectively, highlighting its strong health and economic advantages.
The large number of women with HPV infections in China each year has led to excessive cytological screenings and colposcopy referrals. A feasible triage tool for women who are hrHPV-positive significantly reduces unnecessary medical resource utilization and offers substantial health and economic benefits.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed