2025 Vol. 7, No. 42
The Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR) vaccine plays a crucial role in preventing mumps. Before the implementation of the two-dose MMR vaccine policy, baseline data on mumps virus antibody seroprevalence and geometric mean concentrations (GMCs) among children and adolescents in Fujian Province were available.
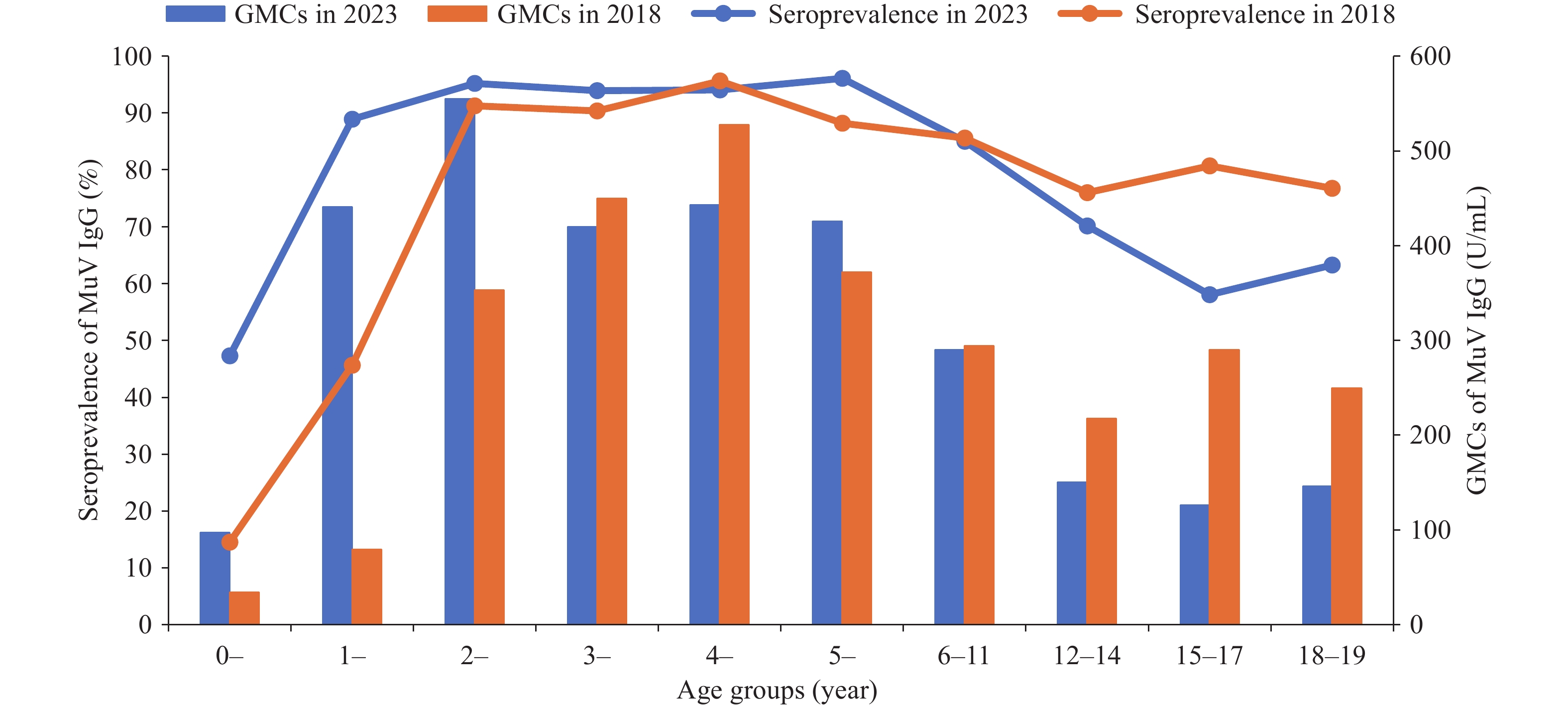
This report provides a post-policy evaluation following the introduction of Fujian’s two-dose MMR policy in June 2020. The 2023 survey shows an overall seroprevalence of 79.53% and a GMC of 265.61 U/mL. Compared with 2018, significant improvements were observed in children under 2 years; however, a concerning decline was noted among adolescents aged 15–17 years. Antibody levels peaked shortly after vaccination, and two doses were found to confer significantly higher immunity than one dose within a 270-day period.
The two-dose MMR policy has been effective in improving early childhood immunity. However, the observed waning immunity in adolescents underscores the urgent need for ongoing serological surveillance, particularly in individuals aged 6–19 years, to inform potential recommendations for booster vaccinations.
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs), including the 13-valent PCV (PCV13), effectively reduce the nasopharyngeal carriage of vaccine-type Streptococcus pneumoniae (S. pneumoniae) and prevent invasive pneumococcal disease in children. However, an increasing prevalence of non-vaccine serotypes and serotype replacement has been documented globally, with notable variations in the predominant replacement serotypes across different geographic settings.
This study demonstrated that PCV13 vaccination significantly reduced the pharyngeal detection of S. pneumoniae among children with acute respiratory infections, with three to four doses decreasing the detection rate by 30.2%. This reduction encompassed both vaccine and non-vaccine serotypes. Additionally, non-PCV13 serotypes, particularly 10A and 15A/15F, were predominant in positive samples, underscoring the current dominance of non-vaccine serotypes in the study population.
The PCV13 program successfully reduced pneumococcal detection rates, particularly among children who complete the 3–4 dose series. Continued surveillance of circulating S. pneumoniae serotypes is essential to monitor serotype replacement patterns and develop future vaccination strategies.
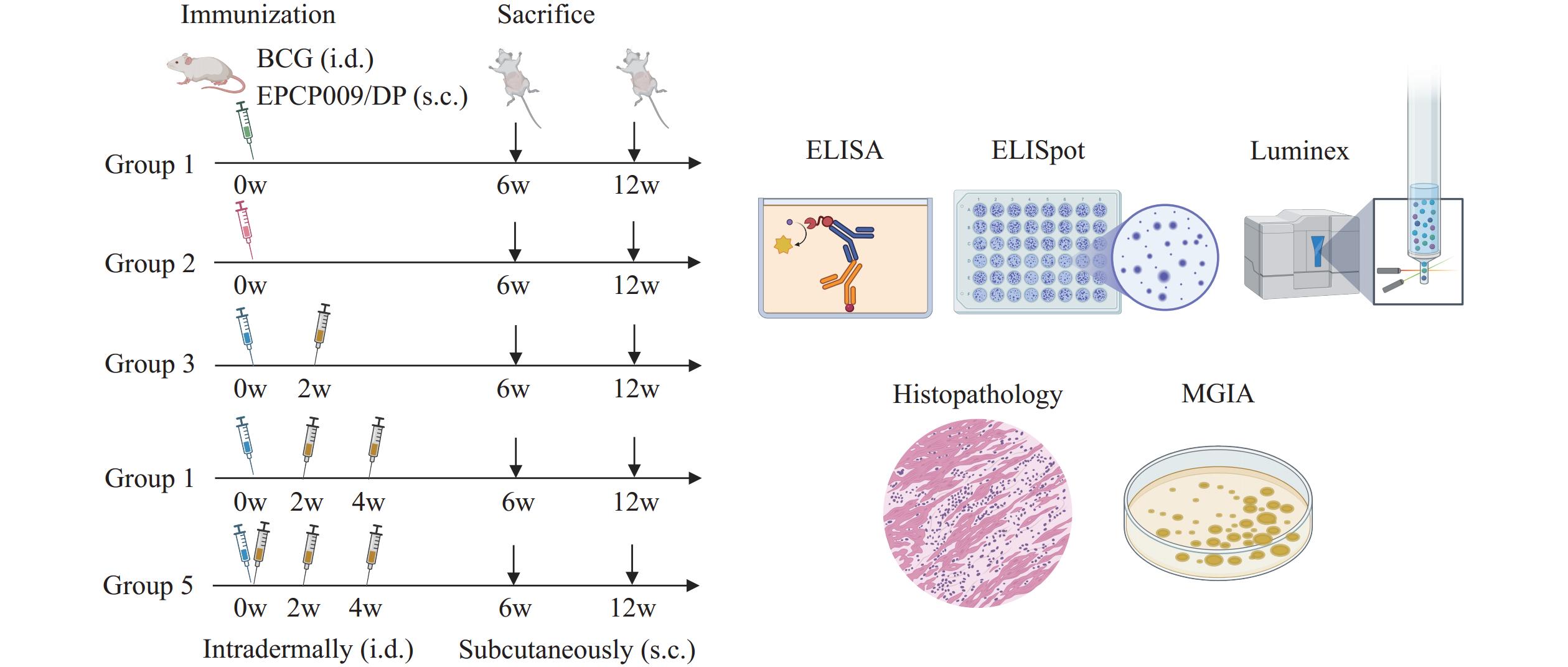
At present, relatively few theoretical studies exist on the immunization strategies of tuberculosis vaccines, especially regarding the types of subunit protein vaccines suitable for combined application with Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG).
The study demonstrated that EPCP009, a novel subunit vaccine candidate, maintains BCG colonization in murine spleens while enhancing protection. Notably, a single dose of EPCP009 combined with BCG was superior to multiple doses in terms of both short-term (6-week) and long-term (12-week) protection.
These studies provide a theoretical basis for enhancing the immune strategy of tuberculosis vaccines and contribute to the development of combined BCG and subunit protein vaccines.
This study aimed to establish a robust method for monitoring measles vaccine-induced immunity and assessing population-level serostatus.
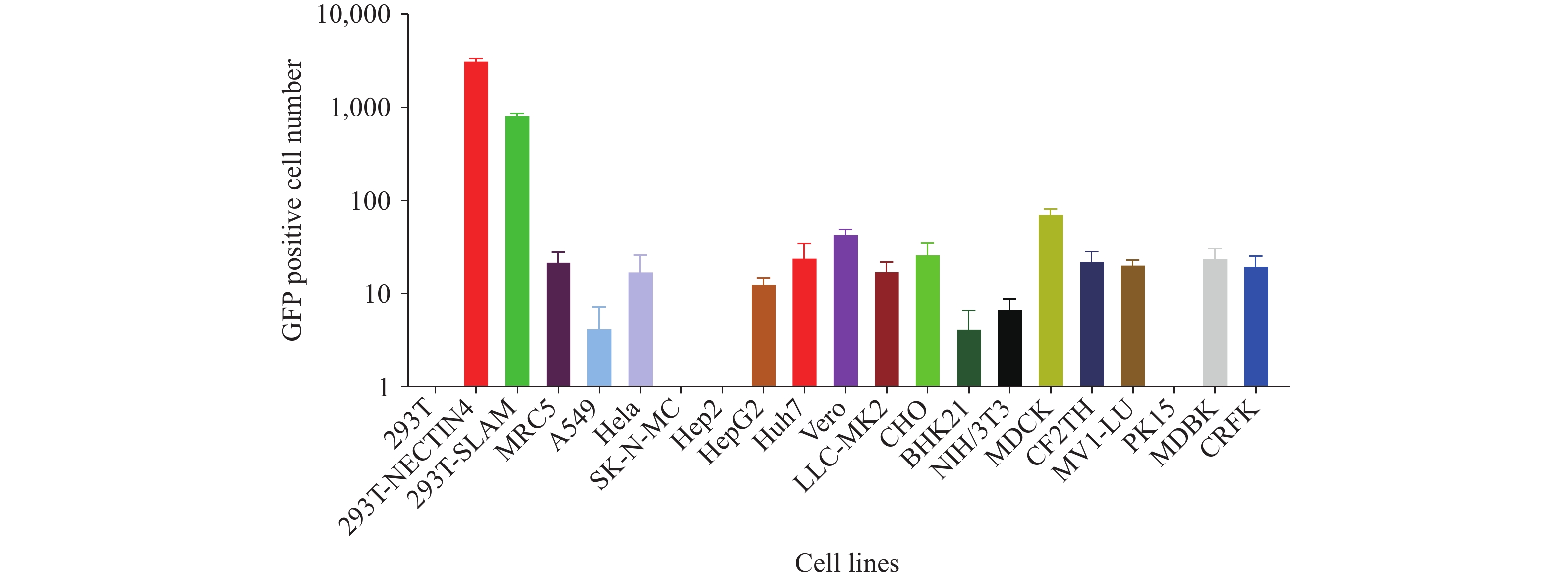
This study constructed a vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)-based pseudotyped virus system expressing envelope proteins from seven major circulating measles genotypes (H1, B3, D4, D8, D9, D11, G3) and the Schwarz vaccine strain (genotype A), thereby enabling a high-throughput neutralization assay for antibody detection.
Vaccination induced a substantial increase in neutralizing antibody geometric mean titers (GMT) post-immunization (4,808 after the first dose; 5,326 after the second dose), with antibody levels remaining elevated in 4-year-old children (GMT: 3,834). Cross-neutralization activity against different genotypes varied by less than 6.4-fold, demonstrating broad protective immunity. However, 12% of adult sera tested were seronegative, revealing the presence of susceptible populations.
This study confirms the robust immunogenicity of the current measles vaccine and establishes a valuable tool for serosurveillance and long-term immunity assessment.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed