2026 Vol. 8, No. 2
Alcohol is a Group 1 carcinogen; in China, high alcohol use substantially contributes to the non-communicable diseases (NCDs) burden.
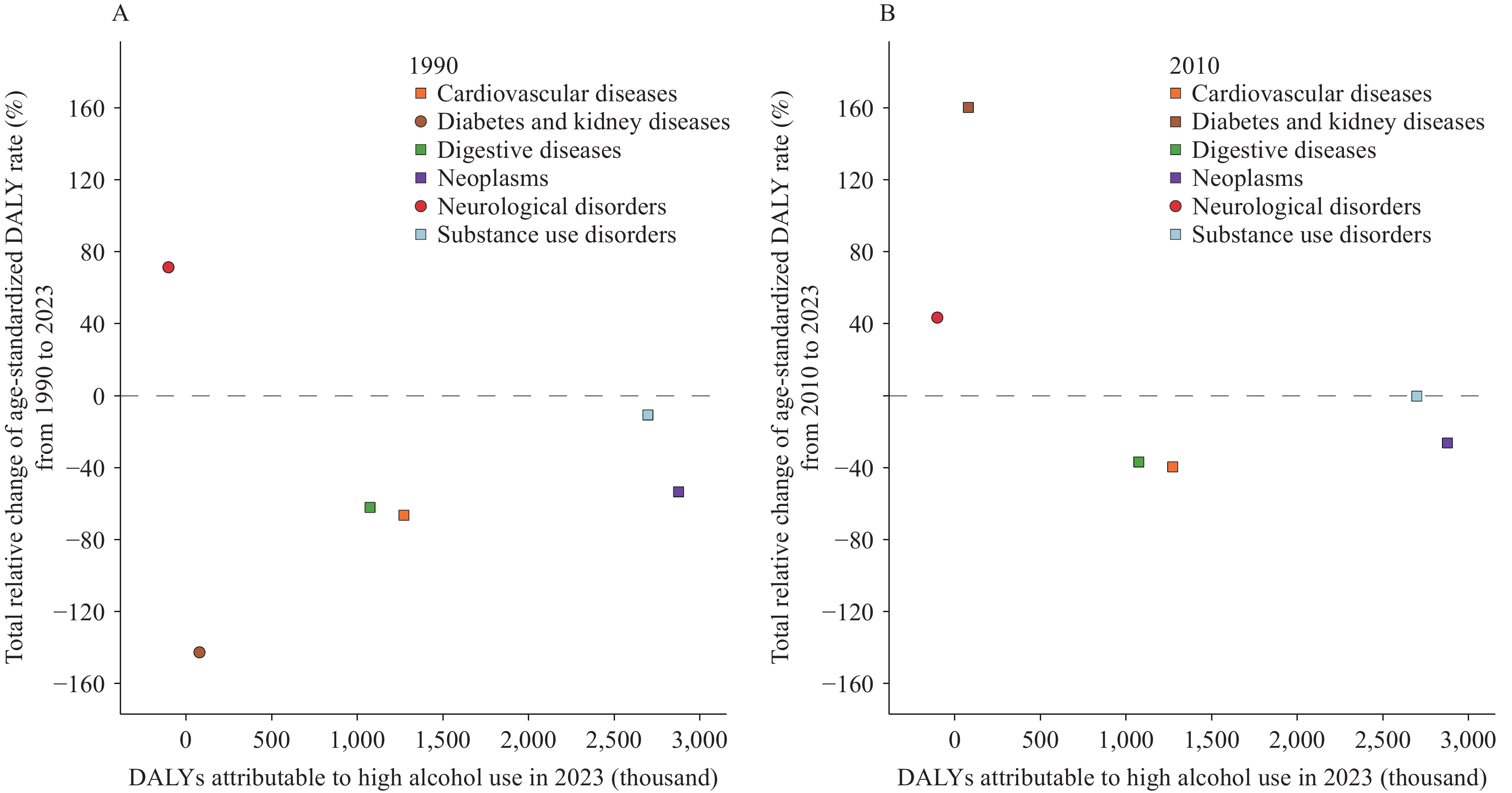
From 1990–2023, age-standardized high alcohol use-attributable NCDs death and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) rates declined markedly (−57.6%, −46.9%), while absolute numbers rose slightly (11.8%, 6.9%). In 2023, neoplasms led DALYs, followed by substance use disorders; diabetes and kidney diseases are smaller but rising (160.22%, 2010–2023). Sex disparity persists (male-to-female NCDs DALY ratio 10.64). Provincial and disease-specific burdens are linked.
Prioritize substance use disorders and monitor rising diabetes and kidney diseases; continue reducing the neoplasms burden; tailor prevention by age, sex, region and cause.
In 2018, past-month and past-year alcohol use prevalence among Chinese adults aged 18+ years was 28.3% and 39.8%, respectively.
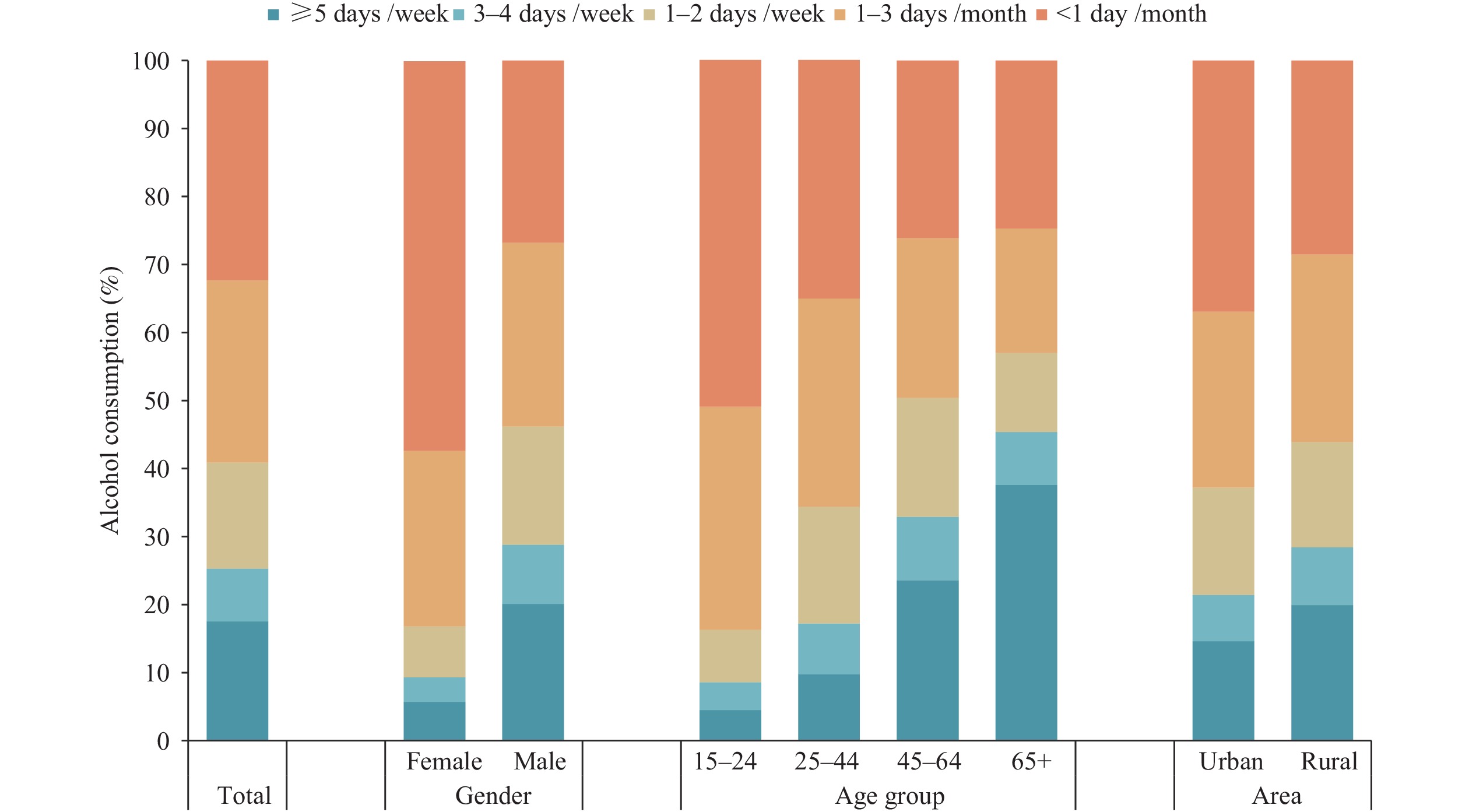
In 2024, alcohol use prevalence among Chinese individuals aged 15+ years was 20.3% (past-month) and 27.6% (past-year), with higher rates observed among males and young to middle-aged adults. Notably, over 40% of current drinkers engaged in heavy episodic drinking (HED).
Gender-specific intervention strategies targeting males and young to middle-aged adults are needed. The high prevalence of HED among current drinkers warrants particular attention in prevention efforts.
Co-infection outbreaks involving norovirus and rotavirus in school settings highlight the essential role of stringent hygiene protocols and rapid, coordinated public health responses in mitigating acute gastroenteritis transmission.
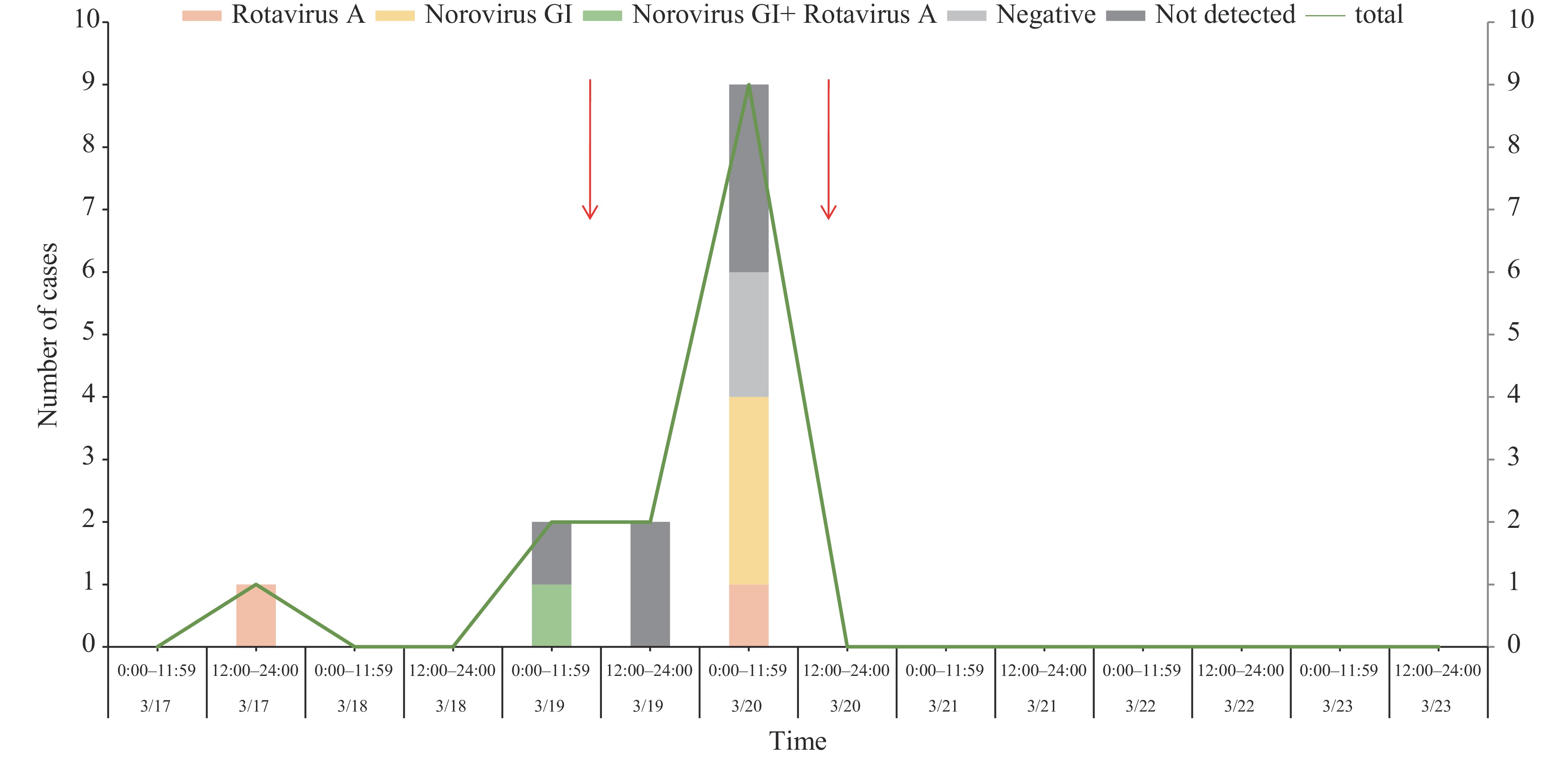
This outbreak revealed a norovirus-rotavirus co-infection outbreak in a primary school. The outbreak affected 14 cases within a single class (38.9% attack rate), all presenting with mild symptoms. Laboratory testing revealed co-infection in 1 anal swab sample and 4 environmental samples (both norovirus GI and rotavirus A positive). Importantly, family-based active case surveillance identified 1 asymptomatic norovirus GI carrier.
It is worth noting that individuals with atypical symptoms and socially active individuals warrant heightened attention during outbreak investigations. Pathogen identification is critical, as different pathogens exhibit distinct transmission characteristics that inform control strategies. This outbreak provides valuable real-world evidence to guide future outbreak response protocols.
Traditional dietary surveys are time-consuming, and manual recording may lead to omissions. Improvement during data collection is essential to enhance accuracy of nutritional surveys. In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have been rapidly developed, which can provide text-processing functions and assist investigators in conducting dietary surveys.
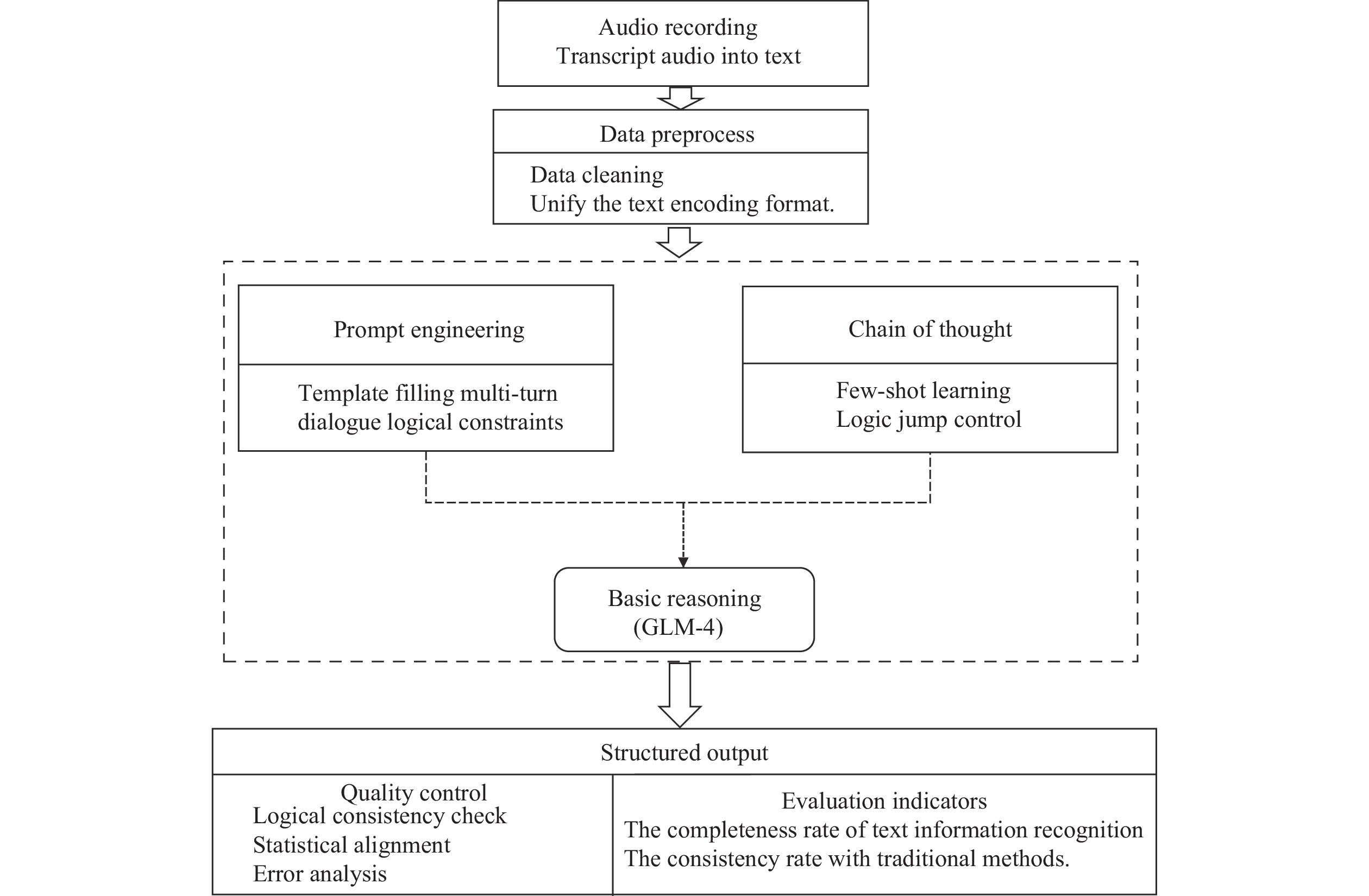
Thirty-eight participants from 15 families in the Huangpu and Jiading districts of Shanghai were selected. A standardized 24-hour dietary recall protocol was conducted using an intelligent recording pen that simultaneously captured audio data. These recordings were then transcribed into text. After preprocessing, we used GLM-4 for prompt engineering and chain-of-thought for collaborative reasoning, output structured data, and analyzed its integrity and consistency. Model performance was evaluated using precision and F1 scores.
The overall integrity rate of the LLM-based structured data reached 92.5%, and the overall consistency rate compared with manual recording was 86%. The LLM can accurately and completely recognize the names of ingredients and dining and production locations during the transcription. The LLM achieved 94% precision and an F1 score of 89.7% for the full dataset.
LLM-based text recognition and structured data extraction can serve as effective auxiliary tools to improve efficiency and accuracy in traditional dietary surveys. With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence, more accurate and efficient auxiliary tools can be developed for more precise and efficient data collection in nutrition research.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed