2025 Vol. 7, No. 48
The comorbidity of tuberculosis (TB) and human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) represents a persistent global public health challenge. This study examines the epidemiological trends of TB/HIV comorbidity in China during 2020–2024, extending previous analyses from the 2015–2019 period.
We collected annual TB/HIV comorbidity surveillance data from 32 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) in China, encompassing bidirectional screening protocols, treatment initiation rates, and clinical outcomes. TB screening among people living with HIV (PLHIV) incorporated systematic symptom assessment and chest X-ray or sputum examination. HIV testing for TB patients employed standard serological methodologies. We performed statistical analyses and generated spatial distribution maps using R 4.2.1.
During 2020–2024, 5,970,062 PLHIV were registered nationwide, with TB examination coverage increasing significantly from 90.2% (957,844/1,061,665) to 94.3% (1,246,274/1,321,458) (P<0.01). The overall TB detection rate among PLHIV was 0.5% (27,991/5,506,876). Among 2,843,159 registered TB patients, HIV testing coverage rose from 67.1% (419,332/625,395) to 68.7% (375,488/546,386) (P<0.01), yielding an overall HIV positivity rate of 1.1% (22,030/1,937,418). We identified 31,783 TB/HIV comorbid patients, of whom 70.9% (21,139/29,836) received concurrent antiretroviral therapy (ART) and anti-TB treatment. Treatment success rates declined significantly from 88.6% (9,521/10,751) in 2020 to 82.9% (3,743/4,513) in 2024 (P<0.01), while mortality rate increased from 4.8% (515/10,751) to 8.8% (398/4,513) (P<0.01).
Although bidirectional screening coverage has improved, substantial regional disparities persist alongside concerning trends of declining treatment success rates and increasing mortality. Enhanced implementation of efficient diagnostic technologies, optimized treatment protocols, and comprehensive stigma reduction initiatives are essential to improve survival outcomes for TB/HIV comorbid patients.
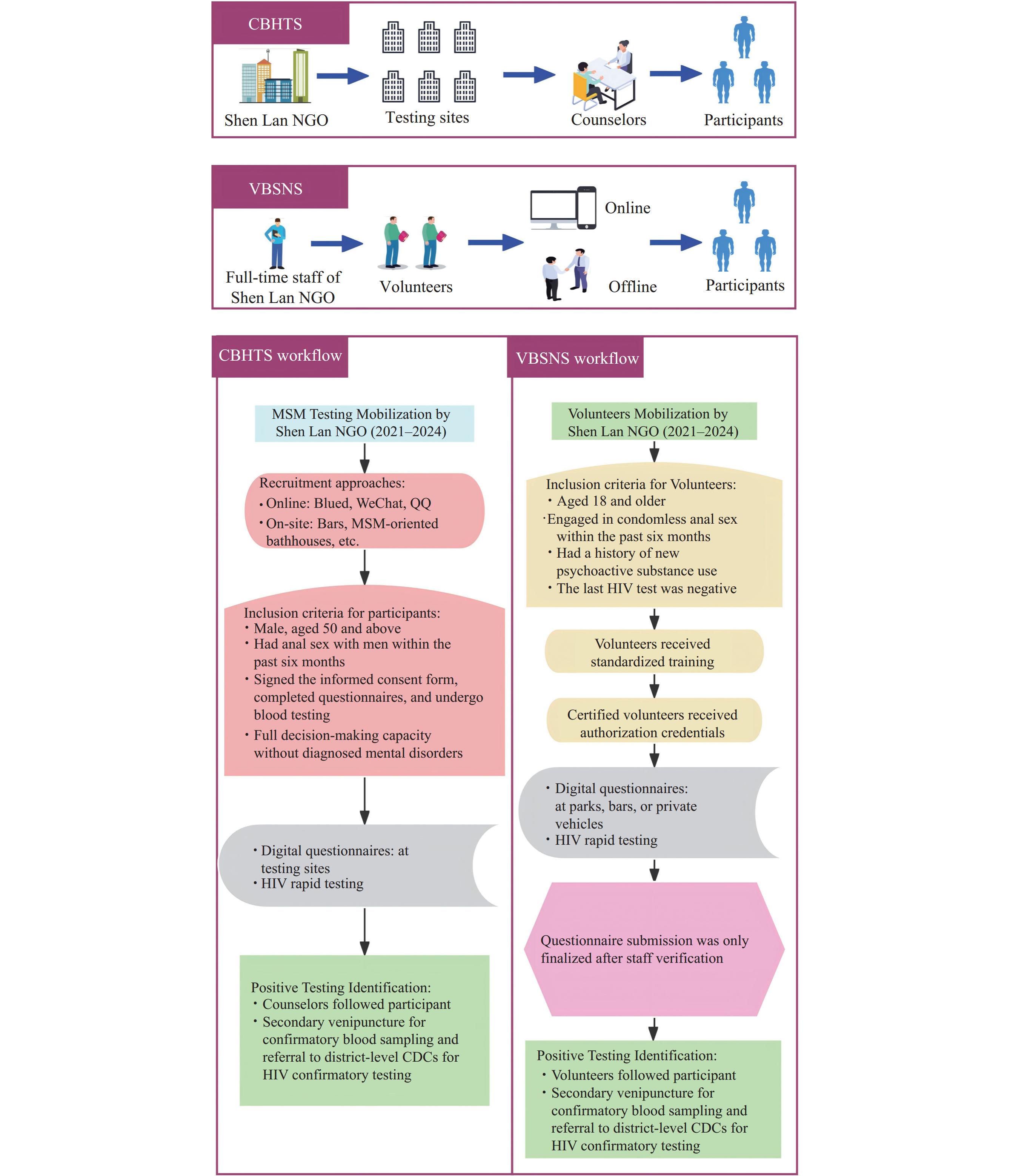
HIV prevalence among men who have sex with men (MSM) aged 50 and above has been increasing. This population has a low testing rate and insufficient knowledge of human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) prevention. At present, limited strategies are available for improving the testing coverage among elderly MSM.
By comparing with the traditional testing strategy, our study found that Volunteer-Based Social Network HIV Testing Services (VBSNS) could significantly improve the testing coverage and newly reported HIV-positive cases of elderly MSM in the remote suburbs of Tianjin Municipality.
Our study confirmed the feasibility of VBSNS among the elderly MSM population in suburban areas and provides a reference model for improving testing coverage in remote areas.
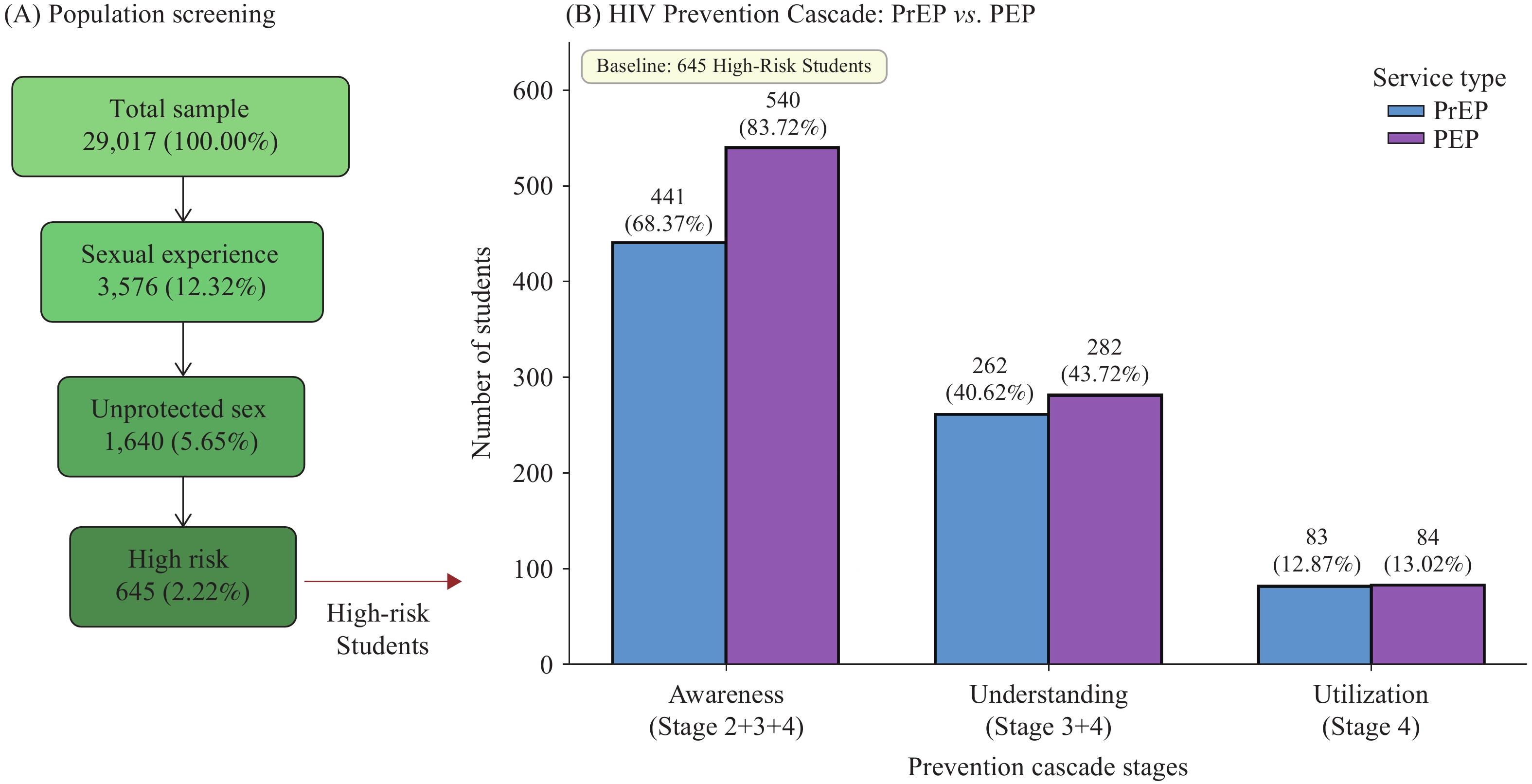
Chinese university students face elevated human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) risks, yet pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) uptake remain low despite proven efficacy.
Among 645 high-risk students, 12.87% utilized PrEP and 13.02% utilized PEP. High HIV knowledge strongly predicted awareness [PrEP: adjusted odds ratio (aOR)=5.62; PEP: aOR=3.42], yet among students who understood the services, 70% did not access them. This finding indicates that structural barriers, rather than knowledge deficits, represent the primary constraint limiting cascade effectiveness.
Educational interventions alone are insufficient to improve service uptake; comprehensive strategies that simultaneously address both knowledge deficits and systemic barriers are essential for expanding PrEP and PEP access.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed