-
TB and human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) continue to pose significant threats to global public health. The dual burden of TB/HIV comorbidity creates a synergistic effect that substantially amplifies disease severity and mortality. HIV/AIDS compromises cellular immunity, dramatically increasing the likelihood that latent TB infection will progress to active disease by 19-fold, while TB simultaneously accelerates HIV replication and diminishes the effectiveness of ART. In 2023, an estimated 6.1% of global TB cases and 12.9% of TB-related deaths were attributed to HIV comorbidity. As the third-highest TB-burdened country globally, China confronts substantial challelnges in managing TB/HIV comorbidity, with notable regional disparities in screening coverage and treatment outcomes. This study provides updated epidemiological trends of TB/HIV comorbidity in China during 2020–2024, extending previous comprehensive analyses conducted from 2015–2019.
-
We collected annual TB/HIV comorbidity surveillance reports from all 32 PLADs in China, encompassing comprehensive data on bidirectional screening protocols, treatment initiation rates, and clinical outcomes. For people living with HIV (PLHIV), TB screening protocols included systematic symptom assessment (evaluating cough, sputum production, and hemoptysis) combined with chest radiography and sputum mycobacterial examination when clinically indicated. HIV testing among TB patients was performed using standardized serological assays following national guidelines.
We prepared all datasets in Microsoft Excel and conducted statistical analyses using R (version 4.2.1, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, https://www.r-project.org/). To evaluate temporal trends in screening and treatment proportions, we applied the Cochran-Armitage test for trend analysis, setting statistical significance at α=0.05. We generated provincial-level spatial distribution maps using the sf and tmap packages in R, incorporating China’s official administrative boundaries as approved under map review number GS(2020)0650 (National Platform for Common GeoSpatial Information Services, https://cloudcenter.tianditu.gov.cn/administrativeDivision).
-
During 2020–2024, a total of 5,970,062 PLHIV were registered (including newly diagnosed and follow-up cases), with numbers increasing from 1,061,665 to 1,321,458, representing an annual growth rate of 5.6% (Table 1). The proportion undergoing symptom screening demonstrated significant improvement, rising from 95.4% to 98.3% (Z=150.14, P<0.01). Similarly, the proportion receiving TB examination increased substantially from 90.2% to 94.3% (Z=136.43, P<0.01). However, the overall TB detection rate was 0.5%, showing a declining trend from 0.7% to 0.5% (Z=−16.34, P<0.01).
Year 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 Total TB screening among PLHIV PLHIV 1,061,665 1,156,204 1,187,549 1,243,186 1,321,458 5,970,062 Symptom screening 1,012,713 (95.4) 1,118,173 (96.7) 1,159,403 (97.6) 1,219,011 (98.1) 1,299,330 (98.3) 5,808,630 (97.3) TB examination 957,844 (90.2) 1,052,723 (91.1) 1,088,922 (91.7) 1,161,113 (93.4) 1,246,274 (94.3) 5,506,876 (92.2) TB cases diagnosed 6,972 (0.7) 4,416 (0.4) 4,993 (0.5) 5,862 (0.5) 5,748 (0.5) 27,991 (0.5) HIV testing among TB patients TB cases notified 625,395 585,640 512,926 572,812 546,386 2,843,159 Known HIV-positive cases 3,719 (0.6) 3,143 (0.5) 2,834 (0.6) 3,260 (0.6) 3,735 (0.7) 16,691 (0.6) HIV testing performed 419,332 (67.1) 404,638 (69.1) 335,509 (65.4) 385,760 (67.3) 375,488 (68.7) 1,920,727 (67.6) Newly tested HIV-positive 1,097 (0.3) 1,013 (0.3) 1,081 (0.3) 1,101 (0.3) 1,047 (0.3) 5,339 (0.3) Total HIV-positive 4,816 (1.1) 4,156 (1.0) 3,915 (1.2) 4,361 (1.1) 4,782 (1.3) 22,030 (1.1) Treatment initiation for TB/HIV comorbidity TB/HIV comorbid cases 6,410 5,304 4,980 6,347 6,795 29,836 Anti-TB treatment 5,892 (91.9) 4,921 (92.8) 4,194 (84.2) 5,517 (86.9) 4,726 (69.6) 25,250 (84.6) ART 5,680 (88.6) 4,711 (88.8) 4,006 (80.4) 4,881 (76.9) 5,767 (84.9) 25,045 (83.9) Concurrent anti-TB & ART 5,287 (82.5) 4,488 (84.6) 3,390 (68.1) 4,113 (64.8) 3,861 (56.8) 21,139 (70.9) Either anti-TB treatment or ART 6,285 (98.1) 5,144 (97.0) 4,810 (96.6) 6,285 (99.0) 6,632 (97.6) 29,156 (97.7) Anti-TB treatment outcome for prior-year cohort Cases notified 10,751 5,784 3,068 3,997 4,513 28,113 Treatment success 9,521 (88.6) 4,996 (86.4) 2,709 (88.3) 3,386 (84.7) 3,743 (82.9) 24,355 (86.6) Death 515 (4.8) 411 (7.1) 193 (6.3) 341 (8.5) 398 (8.8) 1,858 (6.6) Treatment failure 646 (6.0) 377 (6.5) 151 (4.9) 58 (1.5) 77 (1.7) 1,309 (4.7) Other 69 (0.6) 0 (0) 15 (0.5) 212 (5.3) 295 (6.5) 591 (2.1) Table 1. Bidirectional screening and treatment for TB/HIV comorbidity in China, 2020−2024 [n (%)].
Substantial regional variation was observed in TB screening practices, with rates ranging from 45.2% (Tibet) to 98.7%. Six provinces (Hainan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Jilin, Guizhou, Tibet) fell below the 90% screening threshold (Figure 1A). TB prevalence among PLHIV also varied considerably across regions, ranging from 0.1% (Tianjin) to 1.0% (Guizhou), with Tibet excluded from analysis due to extreme outlier values (11.2%) (Figure 1B).
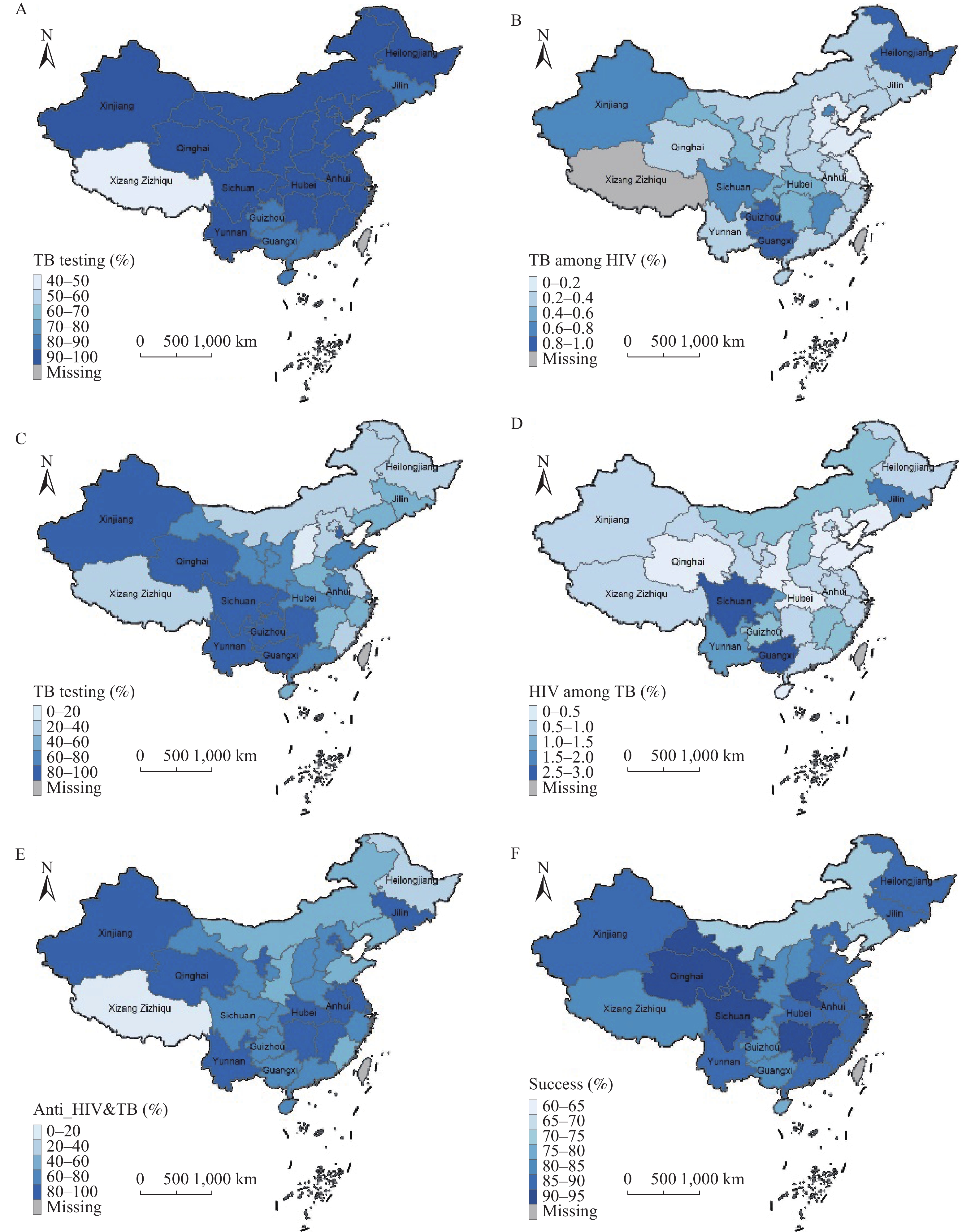 Figure 1.
Figure 1.Regional Disparities in Bidirectional Screening and Treatment for TB/HIV Comorbidity in China, 2020–2024. (A) Proportion of tuberculosis examination among people living with HIV; (B) Tuberculosis prevalence among people living with HIV. Data from Tibet excluded from analysis due to extreme values; (C) Proportion of HIV testing among tuberculosis patients; (D) Prevalence of HIV/AIDS among tuberculosis patients; (E) Proportion of concurrent antiretroviral therapy and anti-TB treatment among notified TB/HIV patients; (F) Proportion of anti-TB treatment success among TB/HIV comorbid patients.
Abbreviation: TB=Tuberculosis; HIV/AIDS=human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; PLADs=provincial-level administrative divisions; PLHIV=people living with HIV; ART=antiretroviral therapy; CAD=computer-aided detection; LF-LAM=lateral flow lipoarabinomannan; CRP=C-reactive protein.
Map approval number: GS 京(2025)1851号.
During 2020–2024, 2,843,159 TB patients were registered, representing a 3.3% annual decrease from 625,395 to 546,386 (Table 1). The proportion receiving HIV testing increased from 67.1% to 68.7% (Z=7.83, P<0.01). Known HIV-positive cases accounted for 0.6% of registered TB patients, increasing from 0.6% to 0.7% (Z=6.24, P<0.01). Among newly tested patients, the HIV positivity rate was 0.3%, rising from 0.26% to 0.28% (Z=2.71, P=0.01). The overall HIV prevalence among TB patients increased from 1.1% to 1.3% (Z=6.35, P<0.01).
HIV testing rates among PLADs ranged from 18.8% to 98.4%, with a median of 62.5% (IQR: 36.2%, 84.7%), and the lowest rates observed in northern and western regions (Figure 1C). HIV prevalence among TB patients varied from 0.1% to 2.7%, with a median of 0.8% (IQR: 0.5%, 1.1%). The highest prevalence rates were recorded in Sichuan (2.7%), Guangxi (2.7%), and Jilin (2.1%) (Figure 1D).
During 2020–2024, a total of 31,783 TB/HIV comorbid patients were registered, with numbers increasing from 6,410 to 8,742 (Table 1). Of these patients, 91.7% received either ART or anti-TB treatment. The overall proportion receiving concurrent anti-TB and ART declined significantly from 82.5% in 2020 to 56.8% in 2024 (Z=−39.13, P<0.01). Treatment success rates for the prior-year cohort demonstrated a concerning downward trend, decreasing from 88.6% in 2020 to 82.9% in 2024 (Z=−9.43, P<0.01). Conversely, mortality rates increased substantially from 4.8% to 8.8% over the same period (Z=10.19, P<0.01).
Regional variations in treatment outcomes were substantial. The proportion of patients receiving concurrent treatment ranged from 14.4% to 95.4% across PLADs, with a median of 75.7% (IQR: 61.7%, 83.0%) (Figure 1E). Similarly, anti-TB treatment success rates varied considerably, ranging from 58.3% to 92.5%, with seven PLADs achieving success rates below 80% (Figure 1F).
-
During 2020–2024, tuberculosis diagnosis among people living with HIV declined from 0.7% to 0.5%, with an overall detection rate of 0.5% — lower than the 0.9% rate observed in 2015–2019. This downward trend aligns with China’s sustained decline in tuberculosis incidence across the general population. Although the overall HIV prevalence among tuberculosis patients (1.1%) remains below the global level (6.8%), it has demonstrated an upward trajectory over the past five years. The persistent substantial burden of TB/HIV comorbid patients indicates that China remains a high-burden country for TB/HIV comorbidity, necessitating continued strengthening of bidirectional screening efforts.
During this period, China achieved steady improvements in TB/HIV bidirectional screening compared with the 2015–2019 period, with tuberculosis screening among people living with HIV increasing to 94.3%, and HIV testing among tuberculosis patients reaching 68.7%. However, significant regional disparities persist, particularly in western and central provincial-level administrative divisions (e.g., Xizang’s tuberculosis screening among people living with HIV at 45.2%). Limited healthcare resources, geographic accessibility challenges, and stigma represent major barriers to TB/HIV bidirectional case-finding. Chest radiography remains the primary tool for tuberculosis screening, but limited interpretive capacity at grassroots levels poses a significant constraint. Substantial evidence supports the use of computer-aided detection (CAD) to replace human readers for tuberculosis screening, addressing diagnostic bottlenecks in resource-limited settings and enhancing case detection. For mycobacterial testing, molecular diagnostics (e.g., Xpert MTB/RIF) and lateral flow lipoarabinomannan (LF-LAM) assays demonstrate superior sensitivity compared to traditional sputum smear microscopy, particularly among people living with HIV, and are suitable for decentralized implementation. C-reactive protein (CRP) testing provides specific diagnostic value among treatment-naive people living with HIV, offering a viable alternative in areas lacking bacteriological testing capabilities. Targeted investments in medical resources, diagnostic equipment, and reagents should be prioritized in remote regions. Provinces with screening rates below 90% (e.g., Guangxi, Guizhou, Xizang) can prioritize implementing computer-aided detection and lateral flow lipoarabinomannan assays.
Over the past five years, the proportion of TB patients undergoing HIV testing reached 67.6%, representing an improvement from the 55% observed in 2015–2019, yet remaining below the global benchmark of 80% for HIV testing among diagnosed TB patients in 2023. The World Health Organization (WHO) advocates “provider-initiated HIV testing” for all TB patients and promotes test acceptability through anti-discrimination policies. The suboptimal coverage likely stems from both limited equipment availability and HIV-related stigma. As emphasized in WHO guidelines, health services should adhere to medical ethics, avoid stigma, ensure non-discrimination, and uphold the right to health. To address stigma-related barriers, concrete multi-faceted interventions are needed, including: implementing structured community education programs to increase awareness; training healthcare workers in non-discriminatory communication practices; supporting peer education initiatives led by successfully treated TB/HIV patients; and integrating anti-stigma messaging into broader TB/HIV health promotion campaigns. Provinces with testing rates below 60% (e.g., parts of western China) require targeted service model optimization: integrating HIV testing into initial TB consultation workflows to minimize patient burden, and adopting rapid testing technologies to reduce operational barriers.
This period also witnessed a decline in anti-TB treatment success rates alongside increased mortality, suggesting a correlation with suboptimal coverage of concurrent ART and anti-TB treatment. Previous studies indicate that more than half of TB/HIV-related deaths occur within 3 months of TB diagnosis, with early treatment interruptions and adverse drug effects serving as key factors contributing to treatment failure and mortality. Early initiation of both ART and anti-TB treatment represents a critical intervention for achieving favorable outcomes in TB/HIV patients, as ART suppresses HIV replication and maintains CD4+ T cell levels. The WHO has recommended initiating ART within 2 weeks of TB treatment initiation for PLHIV, regardless of CD4 count, while strengthening adverse event monitoring to improve treatment success and reduce mortality risks.
Several limitations characterize this study. First, data reliance on routine reporting may undercount unregistered cases. Second, the data collection method for treatment enrollment shifted from aggregated reporting to individual case-based tracking since 2023. This methodological change likely contributed to the observed decline in concurrent treatment proportions (from over 80% before 2022 to below 70% since 2023). Nevertheless, the persistent downward trend since 2023 suggests underlying systemic challenges. Critically, the lack of integrated TB/HIV electronic medical records limits real-time data sharing between programs, hindering coordinated care delivery. Future analyses using consistent methodology are essential to confirm the true trajectory.
In summary, while China has achieved progress in bidirectional TB/HIV screening, significant regional disparities persist alongside declining treatment success rates and rising mortality rate. We recommend prioritizing enhanced inter-facility collaboration, scaling up efficient diagnostic technologies, optimizing treatment workflows, and reducing disease stigma through health education and community interventions to ultimately improve survival outcomes for TB/HIV comorbid patients.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:




