2025 Vol. 7, No. 47
The recent inclusion of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in China’s national basic public health services (NBPHS) represents a historic milestone — marking the first time a chronic respiratory disease has been incorporated into this programme. This article examines the medical and socio-economic significance of integrating COPD management into the NBPHS, evaluates current efforts to address the disease burden, and discusses their alignment with broader health objectives outlined in Healthy China 2030.
Potentially inappropriate medication (PIM) use is a global challenge. The World Health Organization’s 2017 Medication Without Harm initiative set a target to reduce medication-related harm by 50% within five years. However, trends and disease burden related to PIM use in China have remained unclear.
This study found that from 2015 to 2023, the prevalence of PIM use and the associated cardiovascular disease mortality and morbidity nearly halved. Nonetheless, substantial disparities persist across sex, age, urban–rural status, and geographic region. Inner Mongolia and Tianjin exhibited the most pronounced reductions after 2018.
Develop population-based systems to monitor medication use. Integrate rational-use training and public education into essential public health services, and strengthen implementation at the primary care level, particularly in northern and northeastern provinces.
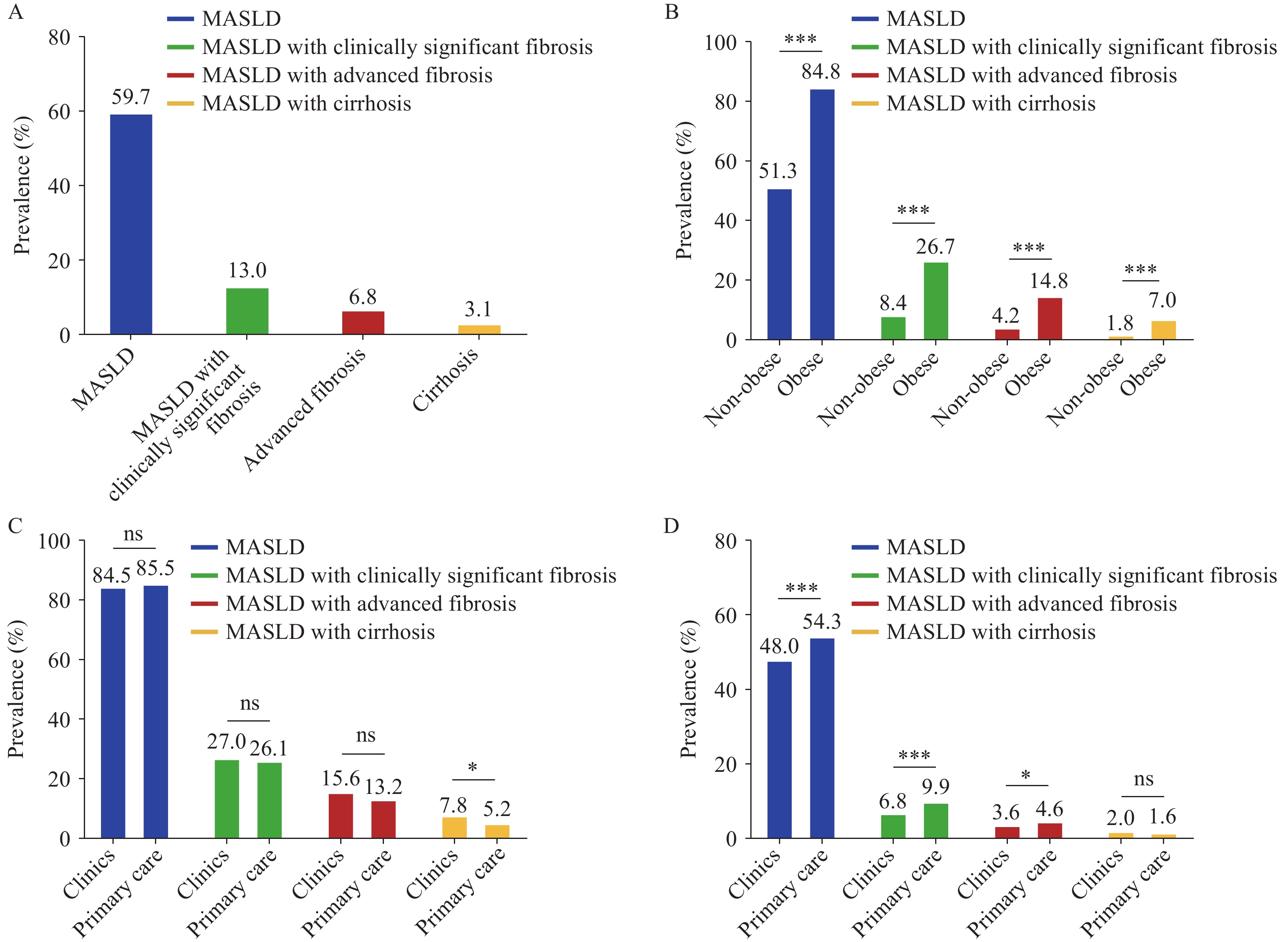
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) with clinically significant fibrosis substantially elevates the risk of liver-related complications and mortality. The American Diabetes Association consensus report specifically recommends systematic risk stratification for MASLD and hepatic fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), with particular emphasis on those presenting with obesity.
This multicenter study demonstrates that obese patients with T2DM exhibit a substantially elevated prevalence of MASLD with clinically significant fibrosis compared to their non-obese counterparts (26.7% vs. 8.4%). Furthermore, the prevalence escalates progressively with the accumulation of cardiometabolic risk factors, highlighting the synergistic impact of multiple metabolic abnormalities on hepatic fibrosis development.
Our findings underscore the critical need for routine screening and integrated management of MASLD with clinically significant fibrosis in patients with T2DM, particularly those presenting with obesity and multiple cardiometabolic risk factors.
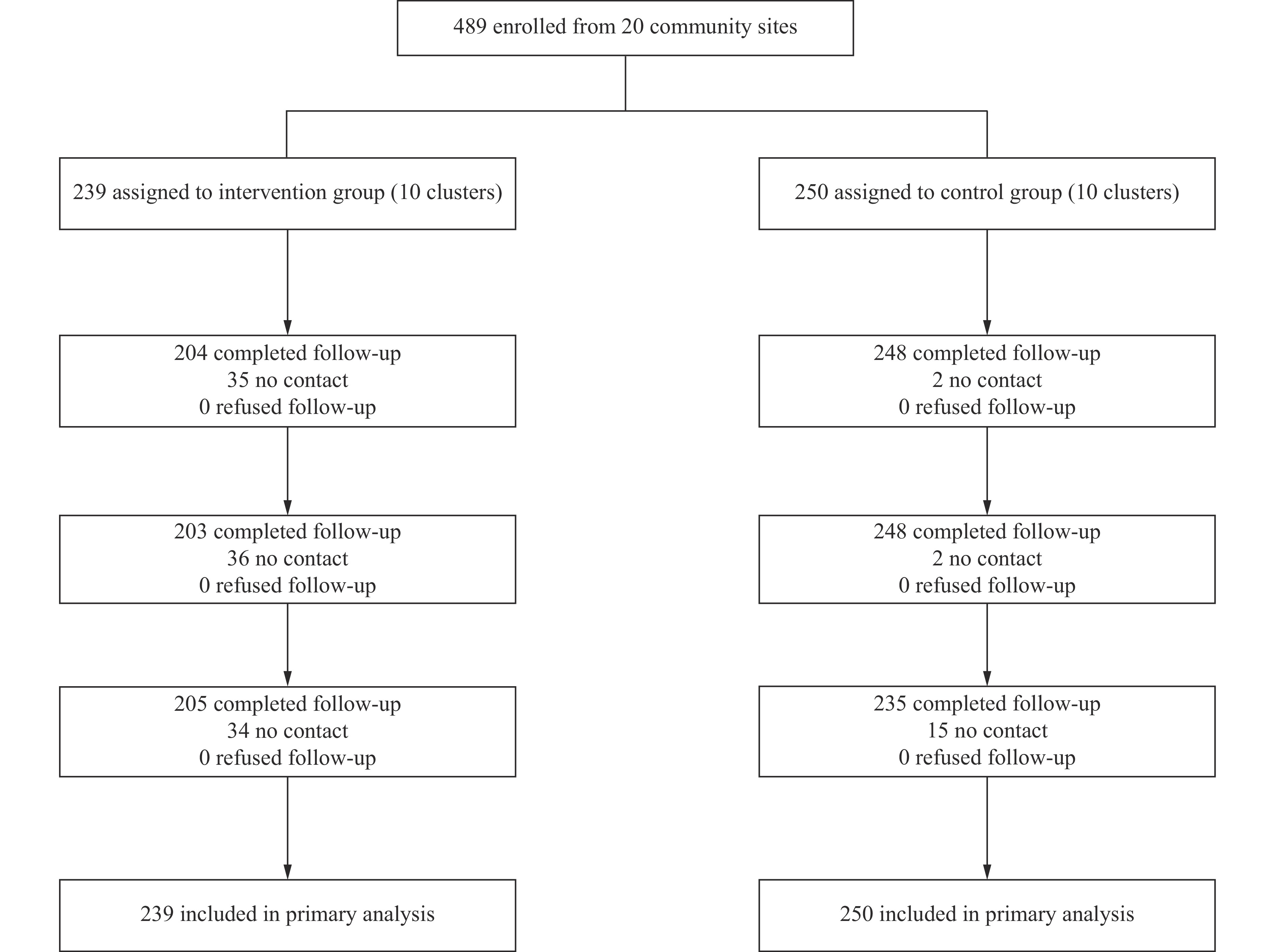
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) acupuncture represents a feasible, low-risk smoking cessation intervention, yet evidence supporting its integration into community-based programs in China remains limited.
The intervention group demonstrated substantially higher self-reported sustained abstinence rates compared to the control group at each follow-up assessment (23.85% vs. 7.60%, 19.25% vs. 4.40%, and 17.57% vs. 4.00%; P<0.05). Participants receiving the intervention were 2.44 times more likely to achieve sustained smoking cessation at 6 months compared to controls [adjusted odds ratio (aOR)=2.44, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.08, 5.50].
This study establishes a precedent for integrating comprehensive TCM approaches into existing community smoking cessation services. Our findings provide innovative perspectives and empirical evidence to advance the development of smoking cessation intervention models.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed