2025 Vol. 7, No. 24
Transfusion-transmitted infections (TTIs) pose significant public health challenges. Screening potential blood donors for hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and Treponema pallidum (TP), along with ongoing monitoring of epidemiological data on TTIs among donors, is essential to ensure blood safety.
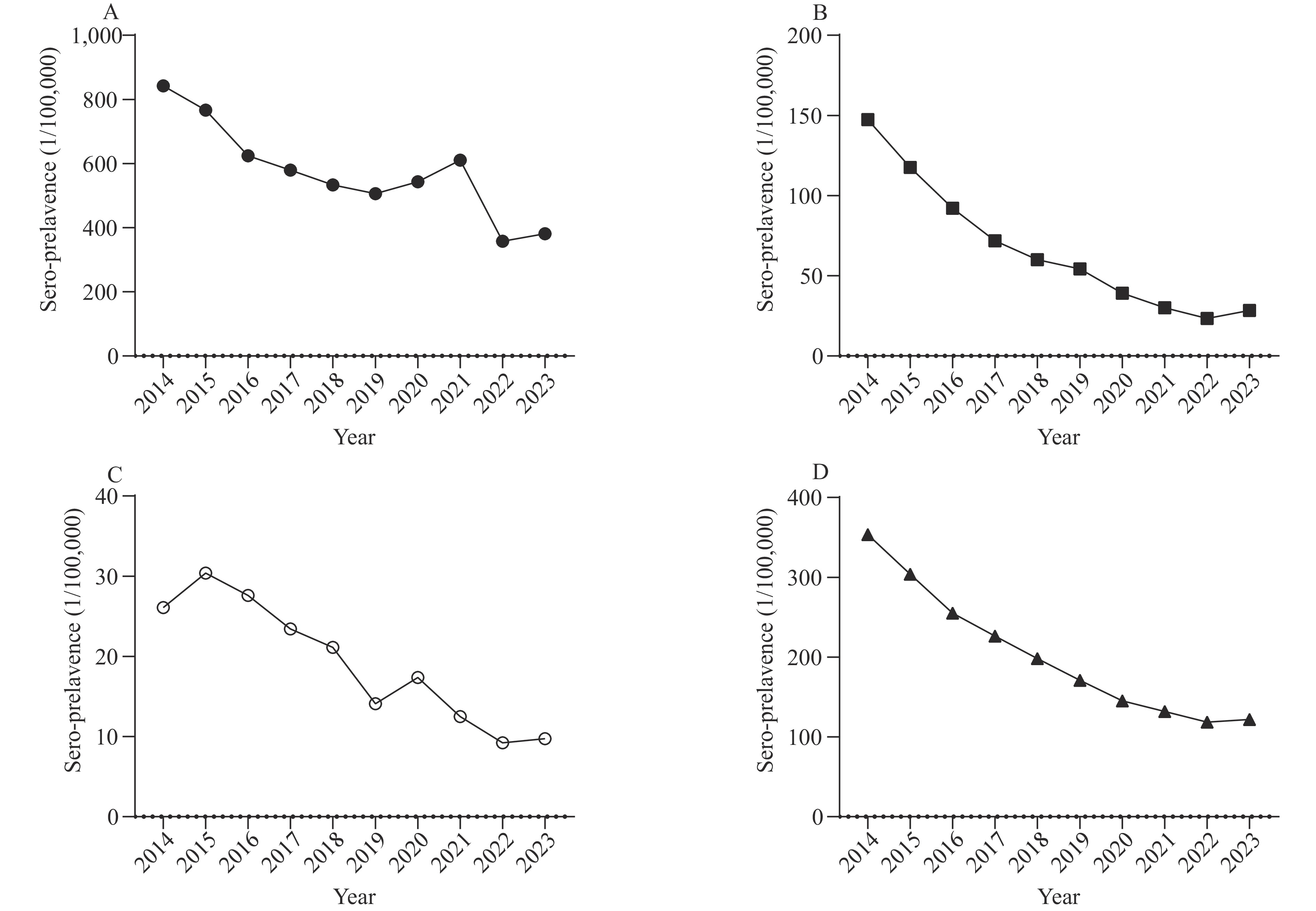
This study conducted a retrospective analysis of the seroprevalence of HBsAg, anti-HCV, anti-HIV, and anti-TP among 3,111,265 blood donation events in Guangzhou from 2014 to 2023, investigating their relationships with demographic characteristics such as gender, age, and donation status.
The findings indicated that the overall seroprevalence of TTIs among blood donations was 866.21 per 100,000, demonstrating a declining trend over the ten-year period. Seroprevalence rates of transfusion-transmissible infections also exhibited a downward trend across various demographic groups. Notably, male donors, first-time donors, and older donors demonstrated higher seroprevalence rates for TTIs.
While the overall seroprevalence rate of transfusion-transmissible infections among blood donors remains relatively low, significant disparities exist among different demographic groups. It is necessary of sustained TTIs monitoring among blood donors to guide public health interventions and donor screening practices.
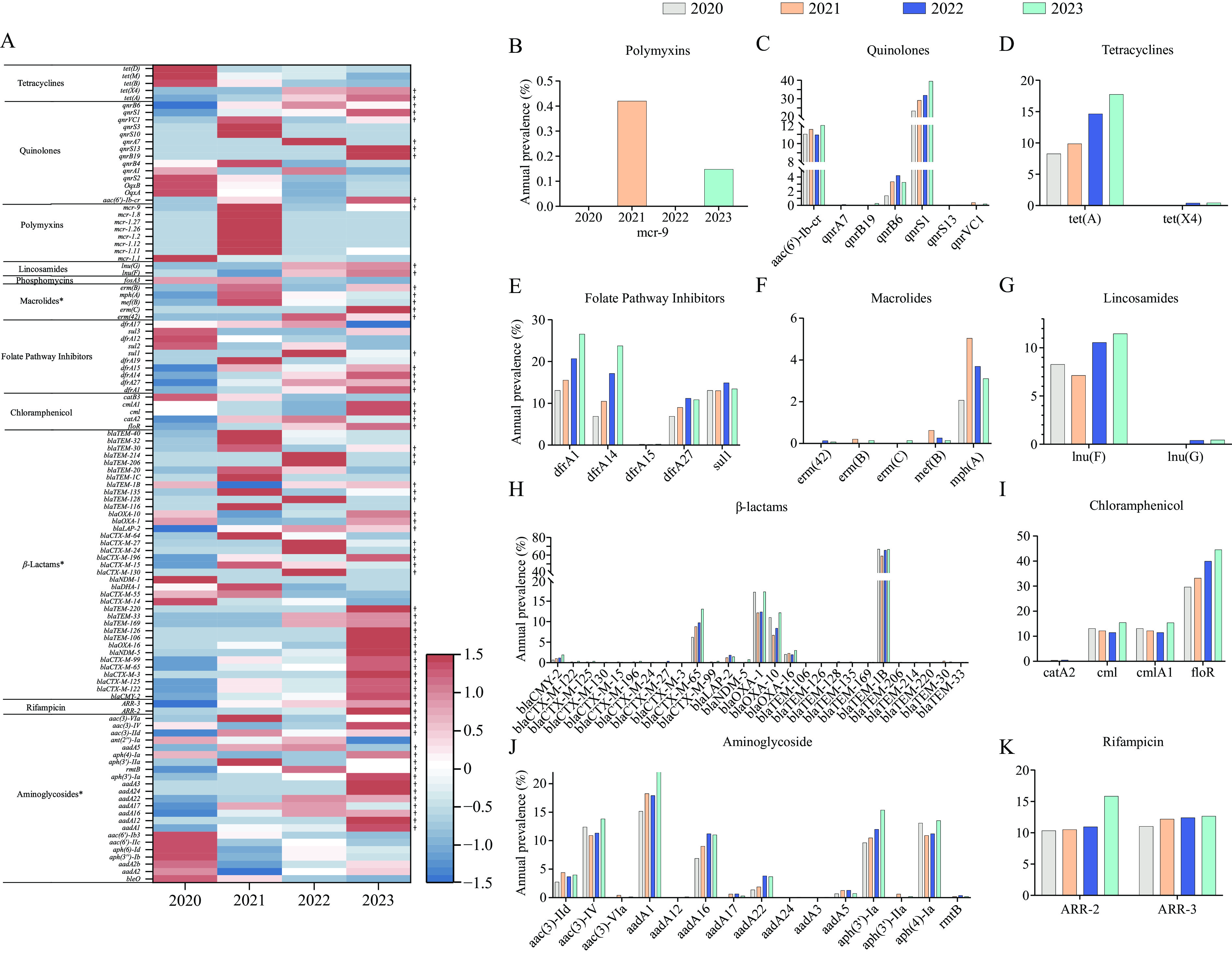
Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:-, a globally emerging pathogen with multidrug resistance (MDR), is spreading in China. Nationwide data on the antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and genomic characteristics of Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- from human sources in China are scarce. This study aimed to characterize the prevalence, genetic diversity, and AMR profiles of Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- in China.
All information, including geographical data, antimicrobial susceptibility test results, and whole-genome sequences, was extracted from the Chinese Pathogen Identification Network database from 2017 to 2023. Antimicrobial resistance phenotypes of 2,736 human-derived isolates were determined, and genomic analysis was applied to assess their genetic heterogeneity. Additionally, resistance genes were detected.
Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- strains exhibited varying levels of resistance to the tested antibiotics, with an overall resistance rate of 98.83%, MDR rate of 87.98%, and cefotaxime resistance of 25.91%. An increasing trend was observed for resistance to key antibiotics and AMR determinants from 2020–2023. Whole-genome analysis revealed five clades with high genetic diversity (A–E), with 97.33% belonging to ST34. Clade D carried a significant proportion of ESBL genes. Moreover, we identified 15 meropenem-resistant isolates primarily harboring widely distributed plasmids containing multiple resistance genes, including blaNDM-5 and blaOXA-10.
Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- is highly sporadic in China but remains phylogenetically linked to the prevalent MDR clone with a distinct resistance profile worldwide. The emergence of elevated resistance to third-generation cephalosporins and sharp rise in carbapenem resistance, coupled with the detection of plasmid-mediated resistance determinants, suggests the evolution of endemic MDR clones circulating within China. These findings emphasize the need for enhanced surveillance, stricter regulations on antibiotic use in agriculture, comprehensive risk factor surveys, and targeted interventions to prevent outbreaks.
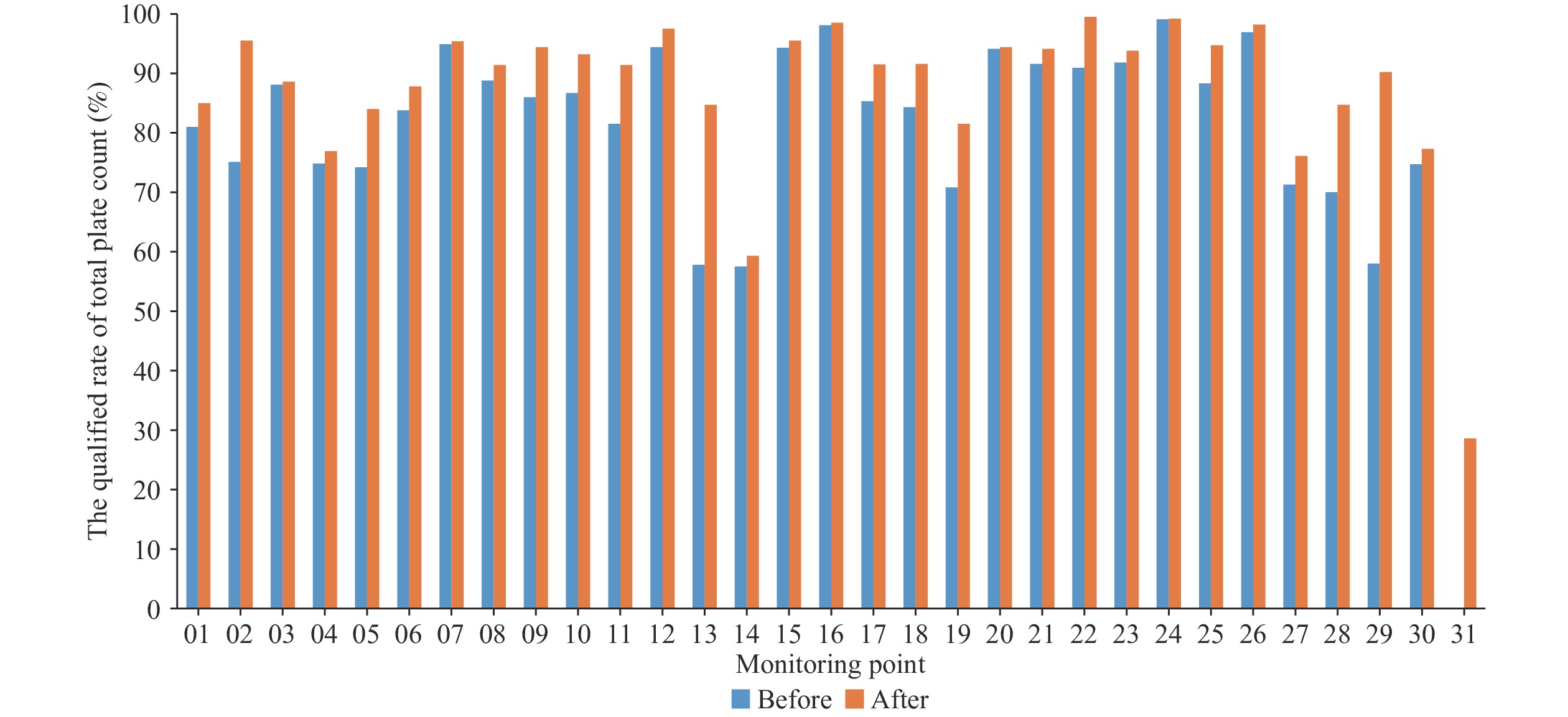
The study aims to monitor the dynamics of bacterial contamination on hospital surfaces and assess the effectiveness of disinfection procedures for controlling bacterial contamination in hospitals and protecting patient safety.
This survey was conducted in sentinel hospitals across 31 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) in China from 2007 to 2022. Surface samples were collected from each site before and after disinfection. Bacterial concentrations were measured using the pour plate method, while pathogenic bacteria were isolated and identified using selective media.
The overall qualified rate for total plate count was 85.7% (41,474/48,367). Pathogenic bacteria were detected in 577 (5.2%) of the 14,665 samples. Significant differences were observed in the qualified rate of total plate count (χ2=14.627, P<0.05) and the positive rate of pathogenic bacteria (χ2=266.700, P<0.05) among primary, secondary, and tertiary hospitals. Significant differences were also found in the qualified rate of total plate count among four environmental classes (χ2=775.700, P<0.05) and seventeen departments (χ2=1606.000, P<0.05). The qualified rate of total plate count after disinfection (89.5%) was higher than before disinfection (81.8%), while the positive rate of pathogenic bacteria after disinfection (3.8%) was lower than before disinfection (4.3%).
Routine disinfection significantly reduces microbial contamination levels on hospital surfaces. Microbiological monitoring of hospital surfaces is a valuable tool for assessing environmental contamination and the effectiveness of disinfection procedures.
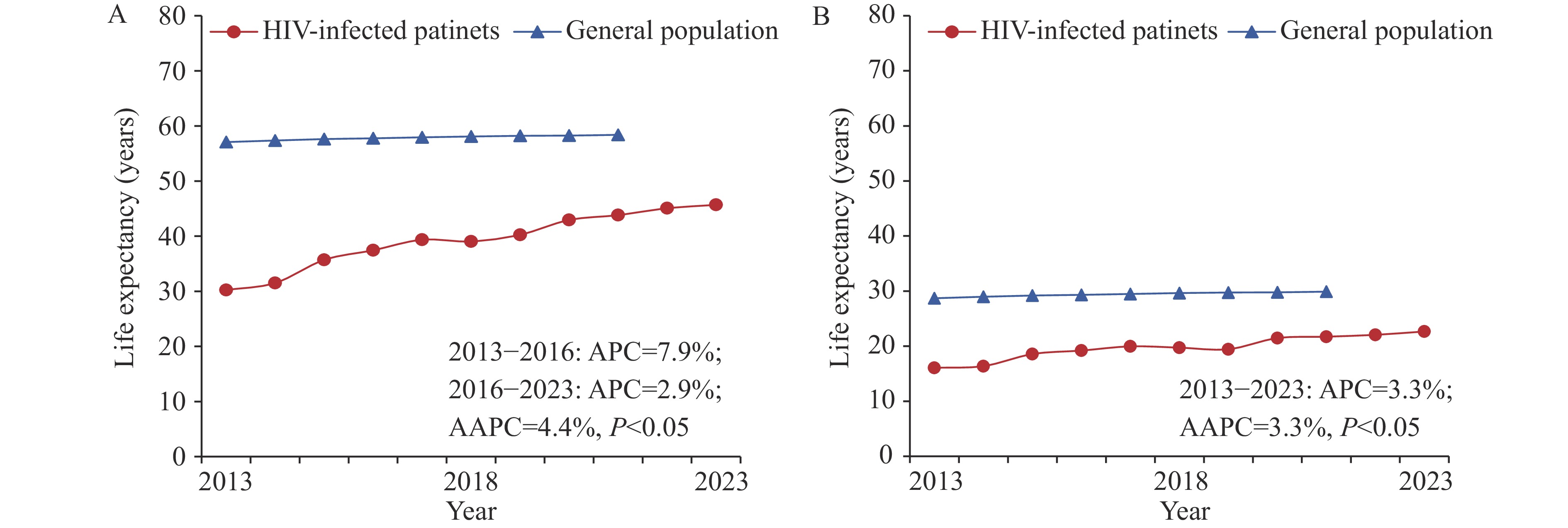
With the expanding coverage of antiretroviral therapy (ART), life expectancy among people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has increased significantly. However, relevant research evidence in China remains very limited.
From 2013 to 2023, China witnessed a remarkable improvement in life expectancy among HIV-infected patients receiving ART, with the disparity compared to the general population narrowing annually.
Our findings recognize the remarkable progress made in ART implementation in China over the past decade, providing timely evidence for improving the health status of HIV population and addressing the emerging challenges of an aging HIV population.
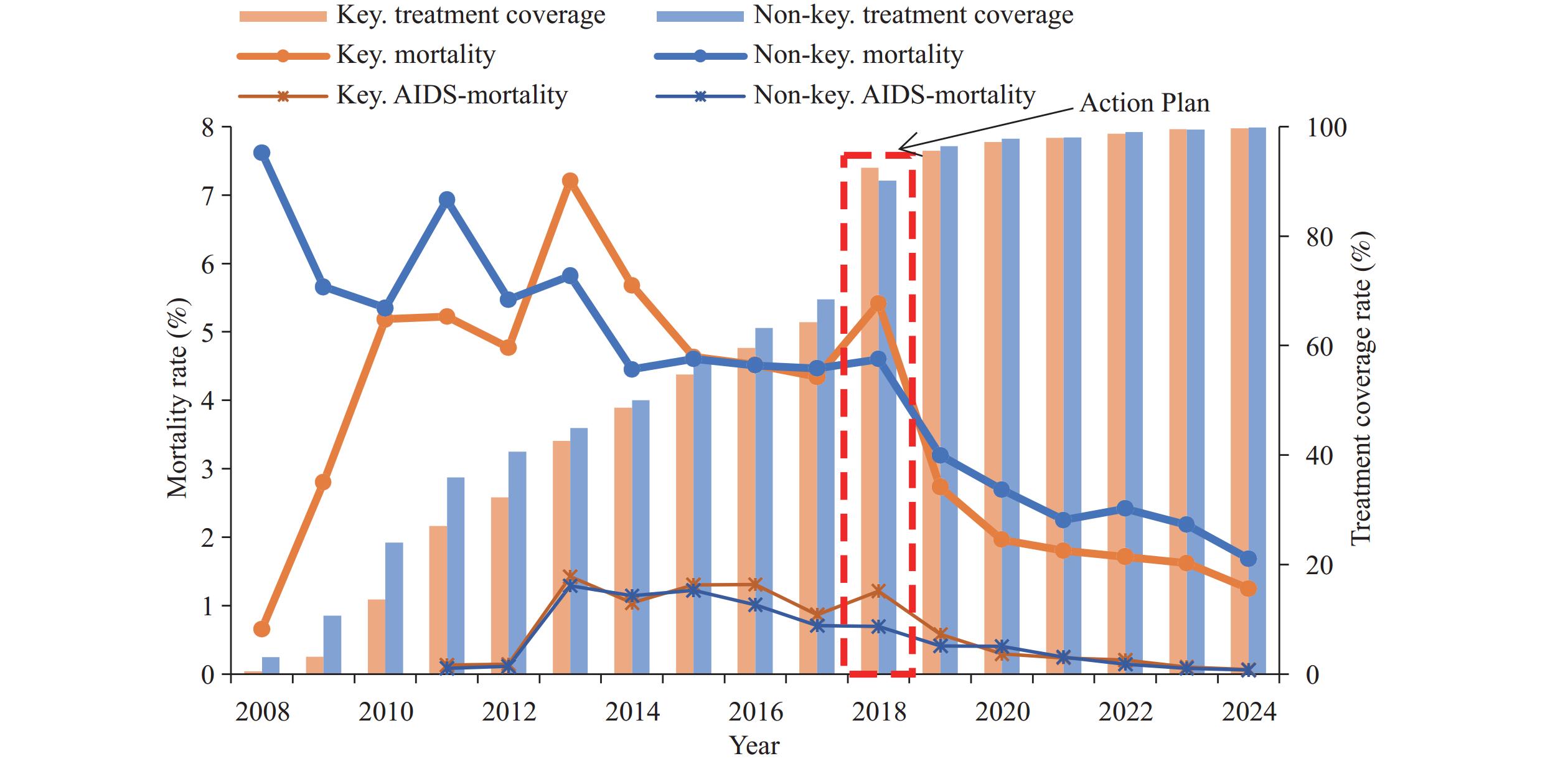
A comprehensive strategy integrating universal human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) testing, real-time patient tracking, and enhanced antiretroviral therapy (ART) within a poverty-alleviation framework was implemented to curb the HIV epidemic in Liangshan Prefecture. This study aimed to quantify its impact on HIV treatment coverage and mortality among heterosexually transmitted HIV-infected individuals. Data on heterosexually transmitted HIV infections in Liangshan from 2008 to 2024 were extracted from China’s HIV/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) Comprehensive Response Information Management System (CRIMS) database. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate the effectiveness of the comprehensive strategy on mortality. Interrupted time series analysis examined trends and changes in treatment coverage and mortality before and after implementation. Subgroup analysis investigated outcomes variations across different populations. Among 37,034 eligible HIV-infected individuals, 7,302 deaths occurred. Not receiving ART was the strongest risk factor for mortality [hazard ratio (HR): 17.74]. The comprehensive strategy led to a 21.62% immediate increase and a 1.48% annual increase in treatment coverage, accompanied by a 0.47% decline in mortality per year [95% confidence interval (CI): −0.73, −0.21]. By 2024, the mortality rate was 4.89% lower than the expected level (95% CI: −8.02, −1.75), representing an 81.2% reduction. Reductions were greatest among males, residents of key counties, and patients at the HIV infection stage. The comprehensive strategy in Liangshan significantly improved treatment coverage and reduced mortality among heterosexually infected individuals. Further efforts are needed to promote early diagnosis, rapid ART initiation, and tailored care support for advanced disease. This comprehensive model offers an adaptable template for high-burden, resource-limited settings.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed