2025 Vol. 7, No. 25
This study aimed to characterize the genetic diversity and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Campylobacter isolates collected throughout China from 2020 to 2023.
Campylobacter isolates analyzed in this study were obtained from the National Pathogen Identification Network Center database, maintained by the National Institute for Infectious Disease Control and Prevention of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) was performed against eleven antimicrobial agents. Genomic characteristics were analyzed through comprehensive genome sequence analysis.
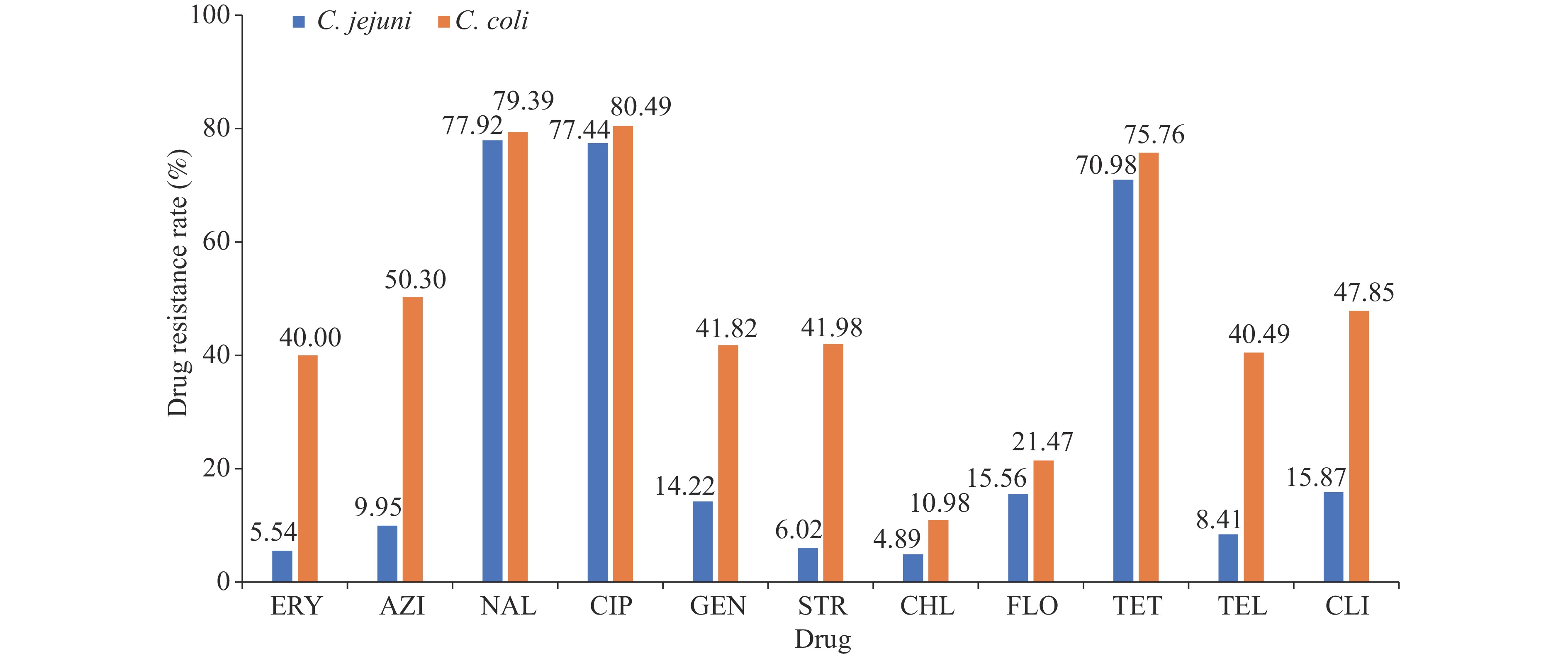
Between 2020 and 2023, the National Pathogen Identification Network documented 1,077 Campylobacter jejuni (C. jejuni) and 221 Campylobacter coli (C. coli) isolates. Most isolates originated from patients presenting with diarrhea. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was conducted on 634 C. jejuni and 165 C. coli isolates. The tested isolates demonstrated high resistance rates to nalidixic acid (78.22%), ciprofloxacin (78.07%), and tetracycline (71.96%). Longitudinal analysis of antimicrobial susceptibility testing results revealed a declining resistance trend from 2020 to 2023. Whole genome sequences were obtained for 540 C. jejuni and 125 C. coli isolates within the database. Virulence factors and antibiotic resistance determinants were identified using the VFDB and CARD databases, respectively. Phylogenetic relationships were established through Snippy 4.0 software analysis based on core genome comparisons.
This comprehensive analysis describes the antibiotic resistance profiles and genetic characteristics of Campylobacter isolates collected through the Identification Network Database from 2020 to 2023, establishing a foundational framework for campylobacteriosis control and prevention strategies in China.
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) caused by hantavirus remains a significant threat to human health in China. The incidence of HFRS, distribution, and evolution dynamics of hantavirus are influenced by factors such as ecological environment, climate, and rapid development; therefore, timely evaluation is essential for the prevention and control of HFRS.
The spatial, seasonal, temporal distributions, and spatiotemporal analysis of reported HFRS cases in China from 2014 to 2023 were performed using Excel 2019, ArcGIS, and SaTScan software. Rodents were trapped at national surveillance sites for HFRS. Genomic sequences of hantaviruses were obtained from lung tissues and aligned with reference genomic sequences using MAFFT. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using MEGA11.0.
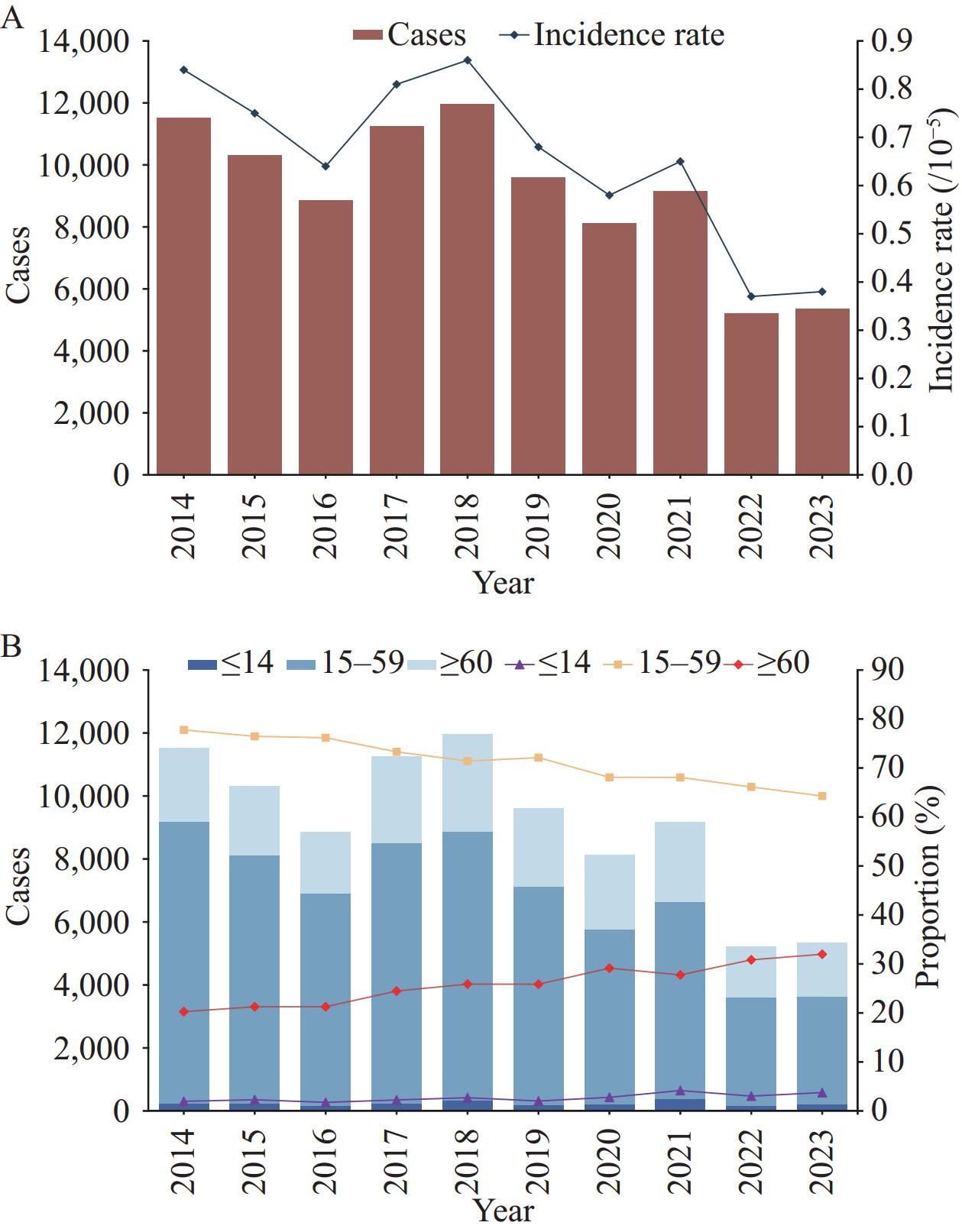
In the past decade, the incidence rate decreased from 1.01/100,000 to below 0.4/100,000; however, areas with hantavirus transmission were expanding. Diversity and distribution of hantaviruses were documented across 22 provincial-level administrative divisions, with 12 genotypes of Hantaan virus and 9 genotypes of Seoul virus identified circulating in China.
Significant progress has been made in HFRS control and prevention in China, with declining incidence rates. However, affected areas are expanding, and diverse hantaviruses are widely distributed, creating a risk of incidence rebounding that should not be ignored. More targeted strategies are needed to address potential new and complex challenges that lie ahead.
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) share significant genomic similarity, enabling NTM to induce protective immune responses against MTB infection. This characteristic has led to their increasing application in tuberculosis (TB) vaccine development.
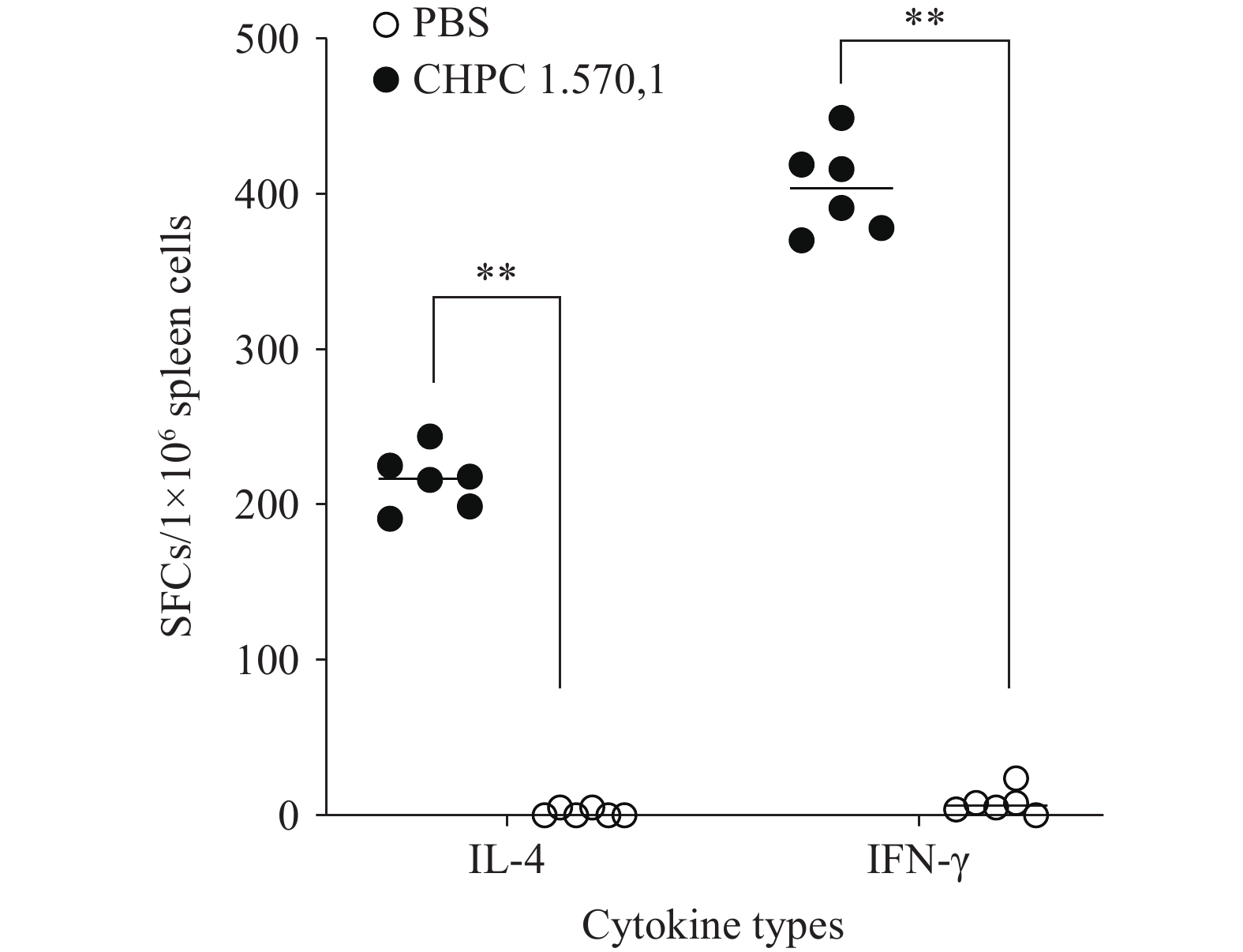
This study found mice in the experimental group developed high IgG antibody titers (1:921,600±446,351.3) and demonstrated a Th1-type immune response. Post-immunization serum antibodies exhibited cross-reactivity with MTB whole-cell proteins. Substantial neutrophil was recruited following antigen challenge. Mycobacterium intracellulare (Mit) whole-cell proteins demonstrate potent immunogenicity and cross-reactivity with MTB whole-cell proteins.
These findings suggest that potential applications in the immunoprevention and treatment of tuberculosis, and the Mit strain CHPC 1.5701 is identified as a promising candidate for tuberculosis vaccine development.
Burkholderia gladioli (B. gladioli) pathovar cocovenenans (BGC), a foodborne pathogen, can cause lethal poisoning. Most cases have been reported in China, primarily originating from fermented cereal products.
This study investigated the prevalence of BGC contamination in commercially available fungi and analyzed the environmental conditions for bongkrekic acid (BA) production in Shanghai. The overall detection rate of B. gladioli in the 85 samples was 44.7% . The highest detection rate was 94.4%, in dried black fungus, followed by fresh Tremella fuciformis (T. fuciformis) with 16.6%, fresh black fungus with 9.1%, and dried T. fuciformis with 3.8%. BGC was detected only in dried black fungus, with a detection rate of 39% . The results of this study demonstrate that all BGC strains carry the bon gene cluster encoding BA, indicating that bonABCDFGHIJKLM plays an essential role in the biosynthesis of BA.
Diagnostic polymerase chain reaction methods could enable rapid identification of BA-producing BGC, providing a potential clinical risk marker. People should avoid eating fungi products soaked 24 hours or more, no matter the temperature.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed