2024 Vol. 6, No. 52
Suspected occupational noise-induced deafness (ONID) represents the most prevalent suspected occupational disease in Guangdong Province and is among the most frequently reported nationwide. Given its public health significance, we conducted a systematic investigation of suspected ONID cases in Guangdong from 2014 to 2023, analyzing their epidemiological characteristics and diagnostic outcomes to inform evidence-based policies for ONID prevention and management.
Data on suspected ONID cases reported in Guangdong Province from 2014 to 2023 were extracted from the “Occupational Diseases and Health Hazard Factors Monitoring Information System.” Cases were analyzed using descriptive epidemiological methods, with joinpoint regression analysis employed to assess long-term trends.
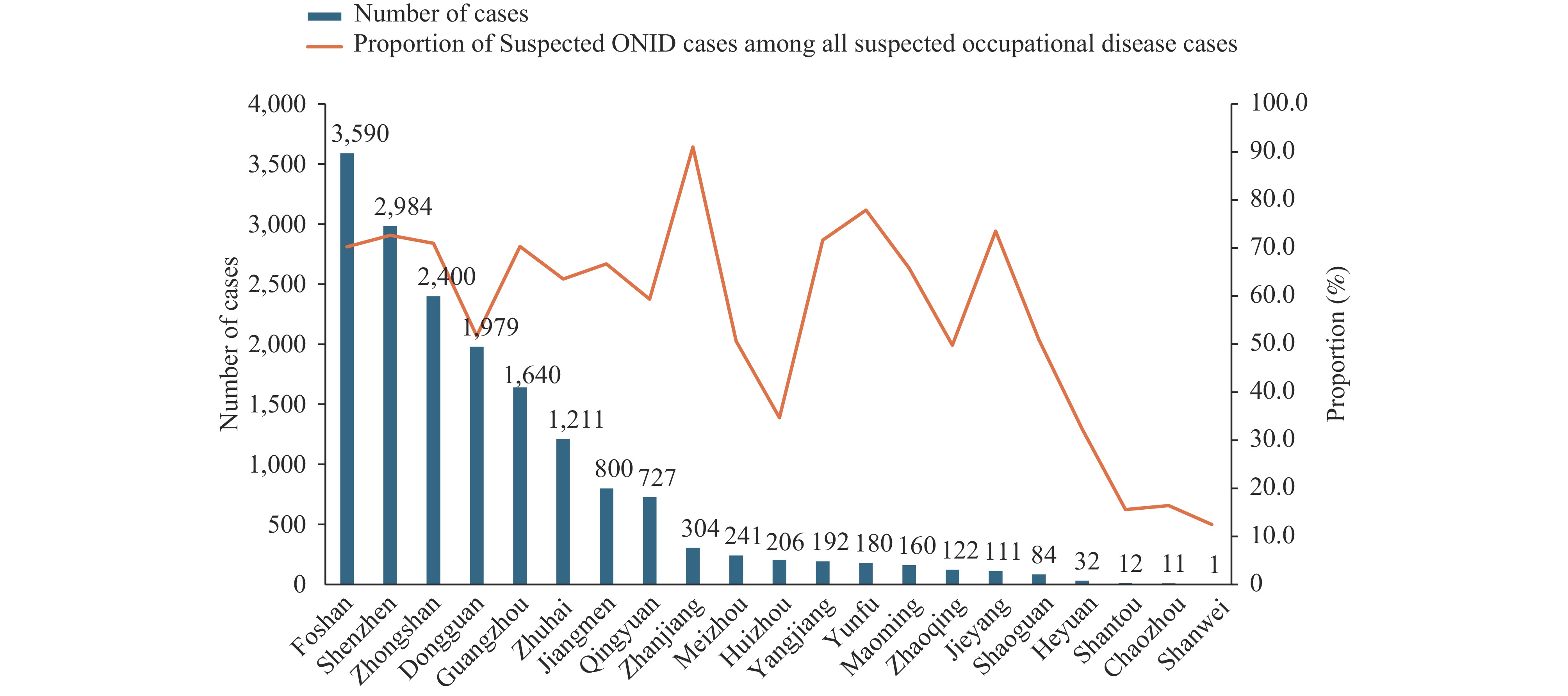
From 2014 to 2023, 16,987 suspected ONID cases were reported in Guangdong Province, comprising 65.22% of all suspected occupational disease cases (26,044). Cases exhibited a significant increasing trend (Average annual percentage change: 11.8%, 95% CI: 2.9%–22.3%, P = 0.013). The Pearl River Delta region accounted for 87.9% of all cases, with manufacturing being the predominant industry (90.1%). Within manufacturing, the metal products industry represented the highest proportion (15.2%). Males constituted 87.7% (14,905/16,987) of cases. Analysis of diagnostic outcomes from 2020 to 2023 revealed an overall diagnostic procedure initiation rate of 45.1%, with a subsequent confirmation rate of 48.9%.
Guangdong Province demonstrates high occurrence patterns of suspected ONID cases, particularly concentrated in the Pearl River Delta region and manufacturing sectors. The low rates of diagnostic procedure initiation and confirmation highlight the urgent need for enhanced regulatory oversight of diagnostic procedures and the development of expert consensus on suspected ONID identification criteria to improve diagnostic confirmation rates.
Lower extremity musculoskeletal diseases (LE-MSDs) have emerged as a significant contributor to the global disease economic burden and worker absenteeism, becoming a global public health concern. However, the epidemic characteristics of LE-MSDs among occupational populations in China are unknown.
This report finds that the LE-MSDs prevalence rate among key occupational groups in China is 17.7%, with the top 5 being toy manufacturing, medical personnel, automobile manufacturing, nonferrous metal smelting and rolling processing, and coal mining and washing.
This study investigated the occurrence of LE-MSDs in key industries in China and its possible risk factors to provide big data support for preventing and controlling such diseases in these industries.
Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) is a widely used industrial polymerization material. Current occupational exposure limits (OELs) for GMA in China show significant disparities compared to those established by international regulatory bodies, including the United States, the European Union, and Japan. A comprehensive revision of GMA exposure limits is crucial for ensuring optimal worker protection.
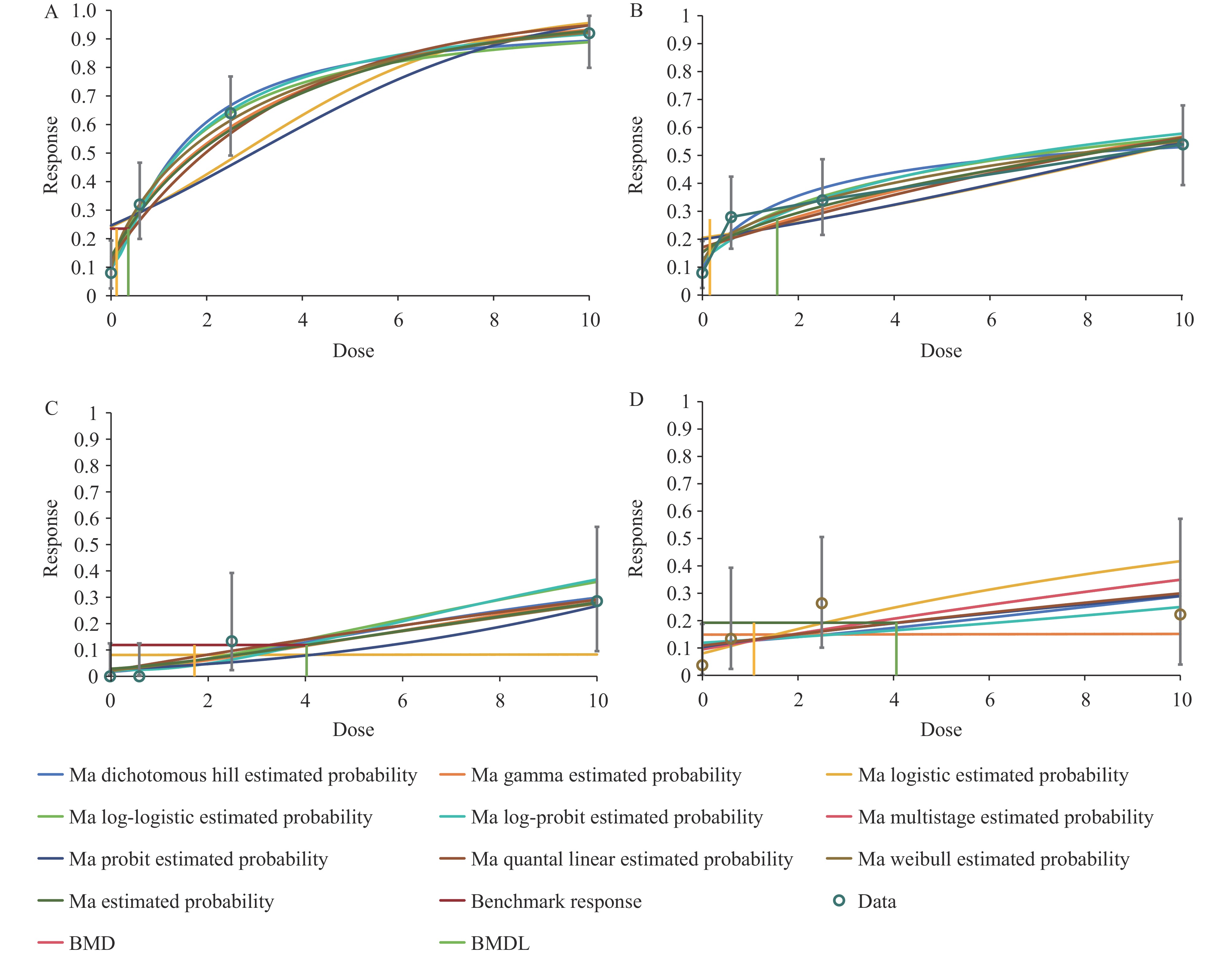
This investigation analyzed data from a 104-week inhalation carcinogenicity study of GMA in mice conducted in Japan. This study identified statistically significant pathological endpoints and employed benchmark dose (BMD) analysis to evaluate meaningful endpoints, focusing on those with the lowest benchmark dose lower bound values. The final recommendations were optimized using Bayesian model averaging (BMA) methodology to establish appropriate OELs.
Our analysis recommends a time-weighted average allowable concentration of 0.01 ppm for GMA, which aligns with international standards established by the European Chemicals Agency (0.016 ppm), Japan Society for Occupational Health (0.012 ppm), and American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (0.01 ppm).
The combined application of BMD and BMA methodologies represents a scientifically robust approach for deriving points of departure in risk assessment. These evidence-based OELs are essential for effective occupational hazard management and worker health protection.
Pneumoconiosis represents the most prevalent occupational disease in China, with coal workers’ pneumoconiosis (CWP) showing the highest incidence. Analysis of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the exhaled breath of CWP patients may provide novel insights into its pathogenesis.
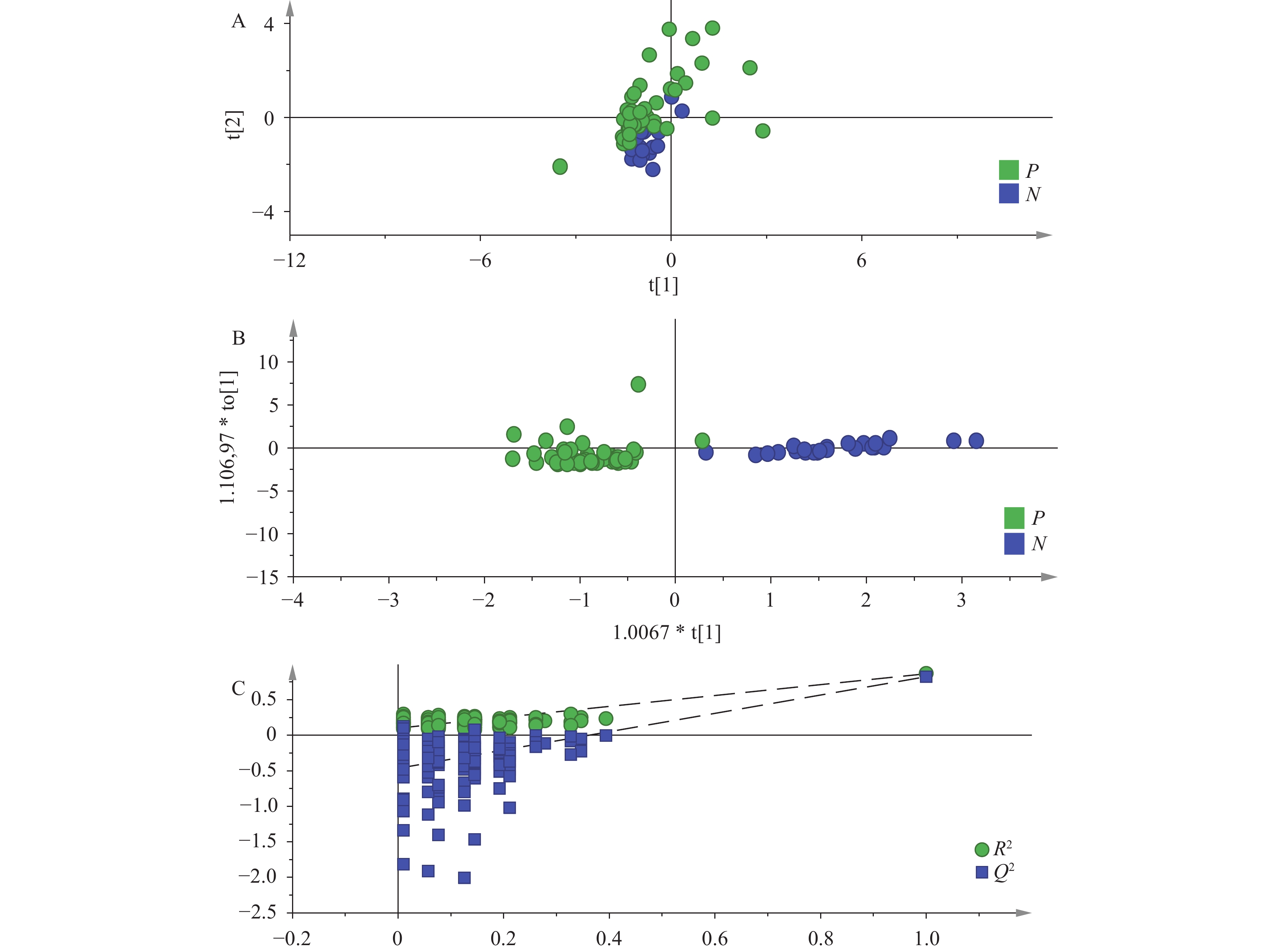
Study data were collected through questionnaires and medical examinations. Thermal desorption-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry was employed for targeted VOC analysis. Differential VOCs were identified using OPLS-DA, the Mann-Whitney U test, and fold change analysis. The discriminatory efficacy of differential VOCs was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Spearman correlation analysis explored relationships between differential VOCs, lung function indices, and blood cell levels.
The pneumoconiosis group showed elevated concentrations of 10 compounds, including isopentane, n-pentane, and isoprene, while four compounds, including 2,4-dimethylpentane, methylcyclohexane, 2,3,4-trimethylpentane, and 2-methylheptane showed decreased concentrations. Combined univariate and multivariate statistical analyses identified six significant VOCs, including isopentane and pentane. Notably, isopentane and n-pentane demonstrated negative correlations with forced vital capacity and levels, while 2-methylheptane showed positive correlations.
Clear metabolic differences in VOCs exist between CWP patients and non-dust-exposed healthy controls. Six compounds — isopentane, n-pentane, 3-methylpentane, n-hexane, cyclohexane, and 2-methylheptane — in exhaled breath demonstrate potential as biomarkers for CWP.
Pneumoconiosis is the most prevalent occupational disease in China, with coal worker pneumoconiosis (CWP) demonstrating the highest incidence. Studies have indicated that phospholipids may be associated with CWP.
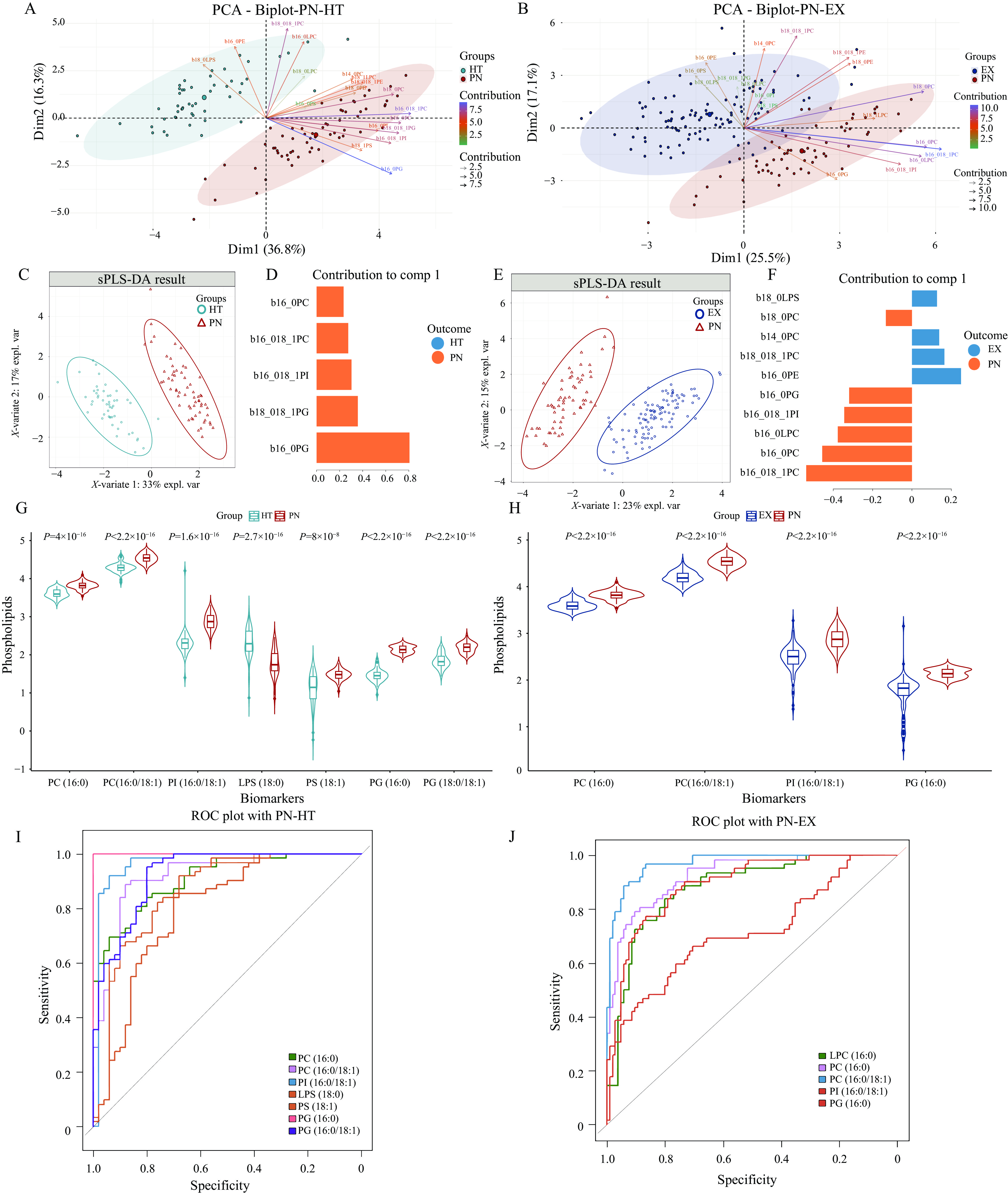
In this study, serum was obtained from 62 patients with pneumoconiosis, 105 coal dust-exposed workers, and 50 healthy individuals and analyzed via targeted lipidomics using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). After initially identifying phospholipids with significant differences through univariate and multivariate statistical analyses, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed. The differential phospholipids identified in patient samples were then integrated to assess their diagnostic potential for CWP using a support vector machine (SVM).
Compared with healthy subjects, the levels of Lyso-PS (18:0) were decreased, while PC (16:0), PC (18:0), PC (16:0/18:1), PI (16:0/18:1), PS (18:1), PG (16:0), and PG (18:0/18:1) were significantly increased in the pneumoconiosis group, with an area under the curve (AUC)>0.7. Moreover, compared with the dust-exposed group, Lyso-PC (16:0), PC (16:0), PC (16:0/18:1), PI (16:0/18:1), and PG (16:0) were significantly elevated in the pneumoconiosis group, with an AUC>0.7. The diagnostic model, including PC (16:0), PC (16:0/18:1), PI (16:0/18:1), and PG (16:0), demonstrated excellent performance with an AUC of 0.956.
The serum phospholipid profiles of patients with pneumoconiosis differed significantly from those of controls, including differences in PC, Lyso-PC, PI, PS, Lyso-PS, and PG. Among these, a diagnostic model incorporating PC (16:0), PC (16:0/18:1), PI (16:0/18:1), and PG (16:0) demonstrated superior screening efficiency.
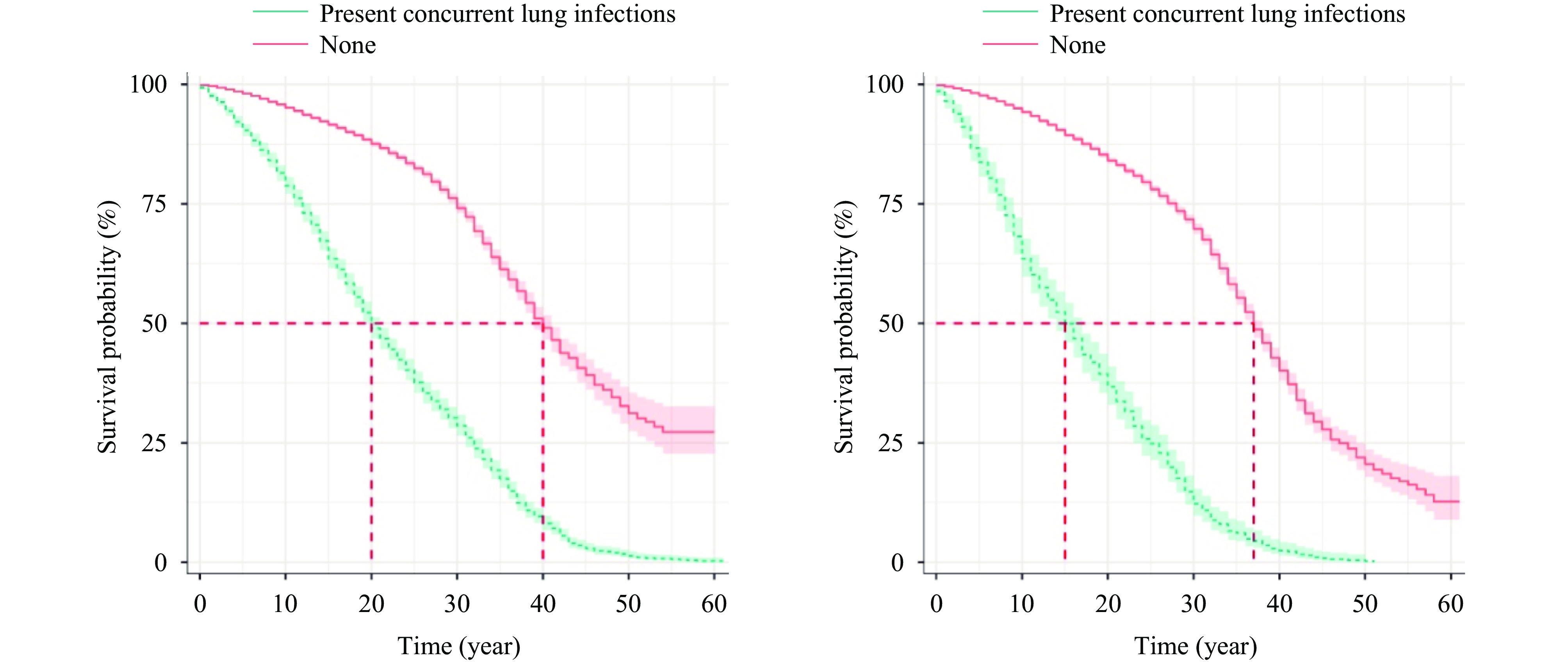
Pneumoconiosis is the occupational disease with the highest proportion in China. This study conducted a retrospective analysis of 5,791 deceased pneumoconiosis patients. In this study, males comprised 93.02% of cases, with primary affected industries being mining (58.47%), manufacturing (20.55%), and public management (16.42%). Silicosis (69.42%) and coal worker’s pneumoconiosis (20.57%) were the predominant diagnoses. Most patients (66.47%) were diagnosed at stage one. Significant differences were observed in both diagnosis age and post-diagnosis survival time across disease stages (P<0.05). The proportion of patients who died directly from lung infections was the highest (37.32%). The primary underlying causes of death in pneumoconiosis patients include pulmonary infections, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, and digestive tract and lung tumors. Life expectancy for patients aged 30–35 years was 15.83 years. After excluding the effects of pulmonary infections, cardiovascular diseases, digestive tract tumors, and lung tumors, life expectancy increased by 3.75, 1.11, 1.31, and 0.63 years, respectively. Pneumoconiosis patients with concurrent lung tumors showed a 7.797-fold increased mortality risk, while pulmonary infections elevated mortality risk by 3.030-fold. Management strategies for pneumoconiosis should emphasize both primary disease treatment and comprehensive care for complications, particularly pulmonary infections, cardiovascular diseases, and malignancies. This integrated approach could extend survival time and enhance quality of life for affected patients.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed