2024 Vol. 6, No. 27
Given the common modes of transmission, outbreaks of both human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and syphilis are primarily observed in men who have sex with men (MSM). However, minimal research has been conducted to concurrently evaluate the rates and trends of HIV and syphilis incidence within this community in China.
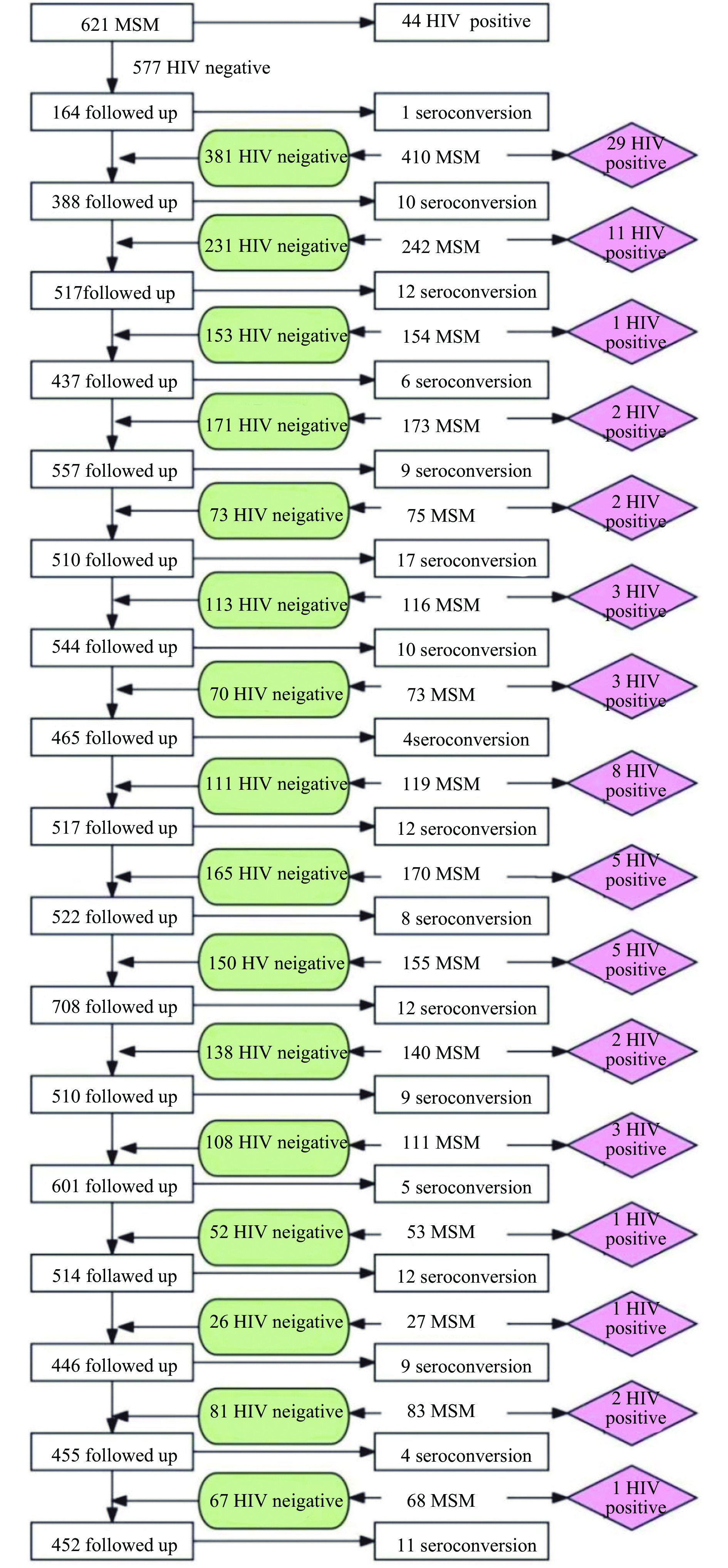
This manuscript presents the incidence rates and associated factors of HIV and syphilis in MSM in Tianjin based on data derived from a decade-long cohort study. Intriguingly, it depicts a decreasing trend in HIV incidence juxtaposed with an increasing incidence of syphilis among this population in Tianjin.
The interconnected risk factors for HIV and syphilis pose significant hindrances to disease control. Our study underscores the urgent need for improved intervention strategies specifically aimed at MSM to mitigate the propagation of both infections.
HIV transmission among serodiscordant couples remains a persistent issue in China. However, the practice of combining counseling with antiretroviral therapies (ART) to enhance ART adherence is not widely implemented or recommended in Chinese health guidelines.
This randomized controlled trial suggests that increased follow-up, counseling, and awareness of HIV risk can enhance ART compliance, thereby maximizing treatment efficacy.
Early testing and counseling of serodiscordant couples, following the identification of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positive spouse, is crucial for initiating ART and reducing the risk of seroconversion in the uninfected partner. Implementing a combination of ART and adjunct counseling in China is advisable.
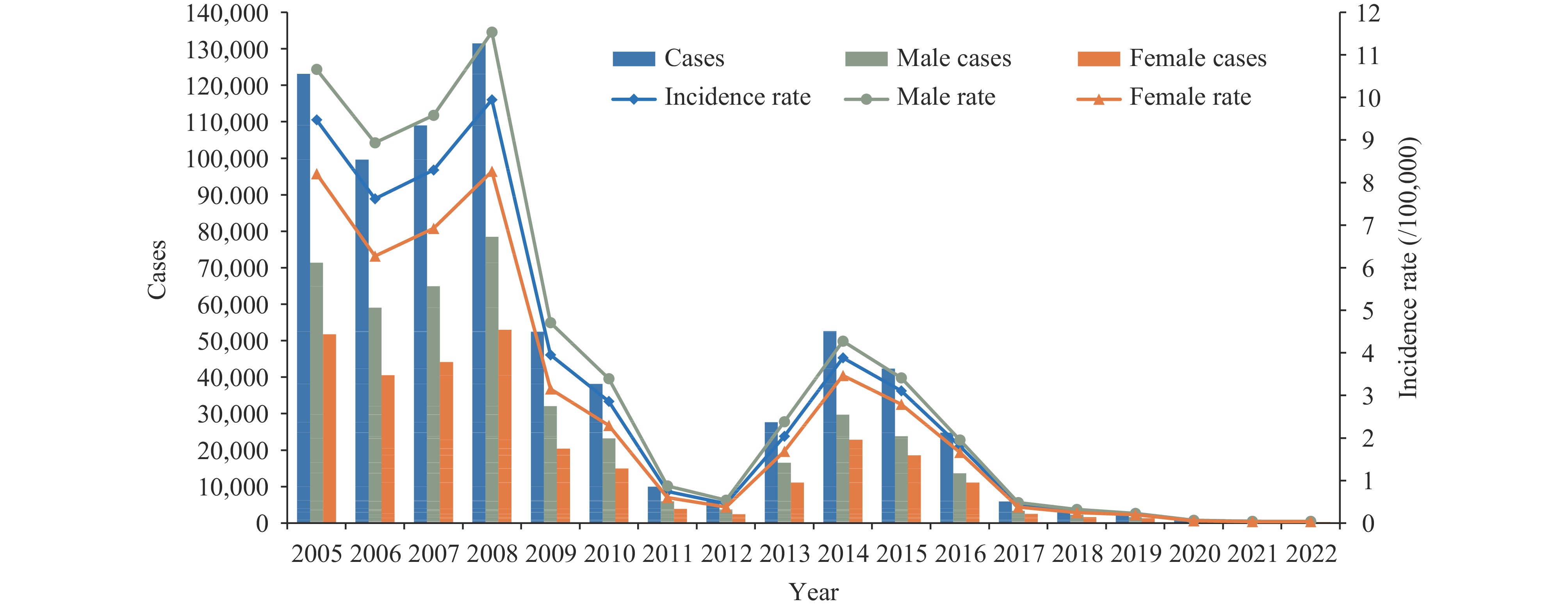
In recent years, the incidence of measles in China has consistently remained below 1 per 100,000 population, yet the disease has not been eliminated. This study aims to comprehensively analyze the epidemiological characteristics of measles from 2005 to 2022, identify high-risk populations and areas, and propose targeted interventions.
We utilized data from the China Disease Prevention and Control Information System for our comprehensive analysis. Spatial autocorrelation was employed to examine the spatial clustering of measles, while spatiotemporal scanning analysis was used to detect spatiotemporal clustering to describe measles epidemiology during the study period.
Between 2005 and 2022, 732,218 measles cases were reported in China. Overall, the incidence of measles exhibited a downward trend, particularly during the periods of 2008–2011 and 2015–2022. In 2022, the incidence rate reached its historical low at 0.039 per 100,000 population. Measles predominantly affects young children. Since 2017, global spatial clustering has diminished, although hotspot areas persist in the western provinces. Spatial-temporal scanning identified a high-incidence cluster from 2005 to 2008, comprising 15 provinces in the western, central, and northern regions of China. Conversely, from 2016 to 2022, a low-incidence cluster was detected in the southern and central provinces.
China has made significant progress in measles prevention and control. The recent low incidence and absence of substantial spatiotemporal clustering indicate that China is nearing measles elimination. However, there is a continuing need to enhance prevention and control efforts among very young children and in historic incidence hotspots in western provinces. Additionally, improving the diagnosis of vaccine-associated rash illnesses is essential.
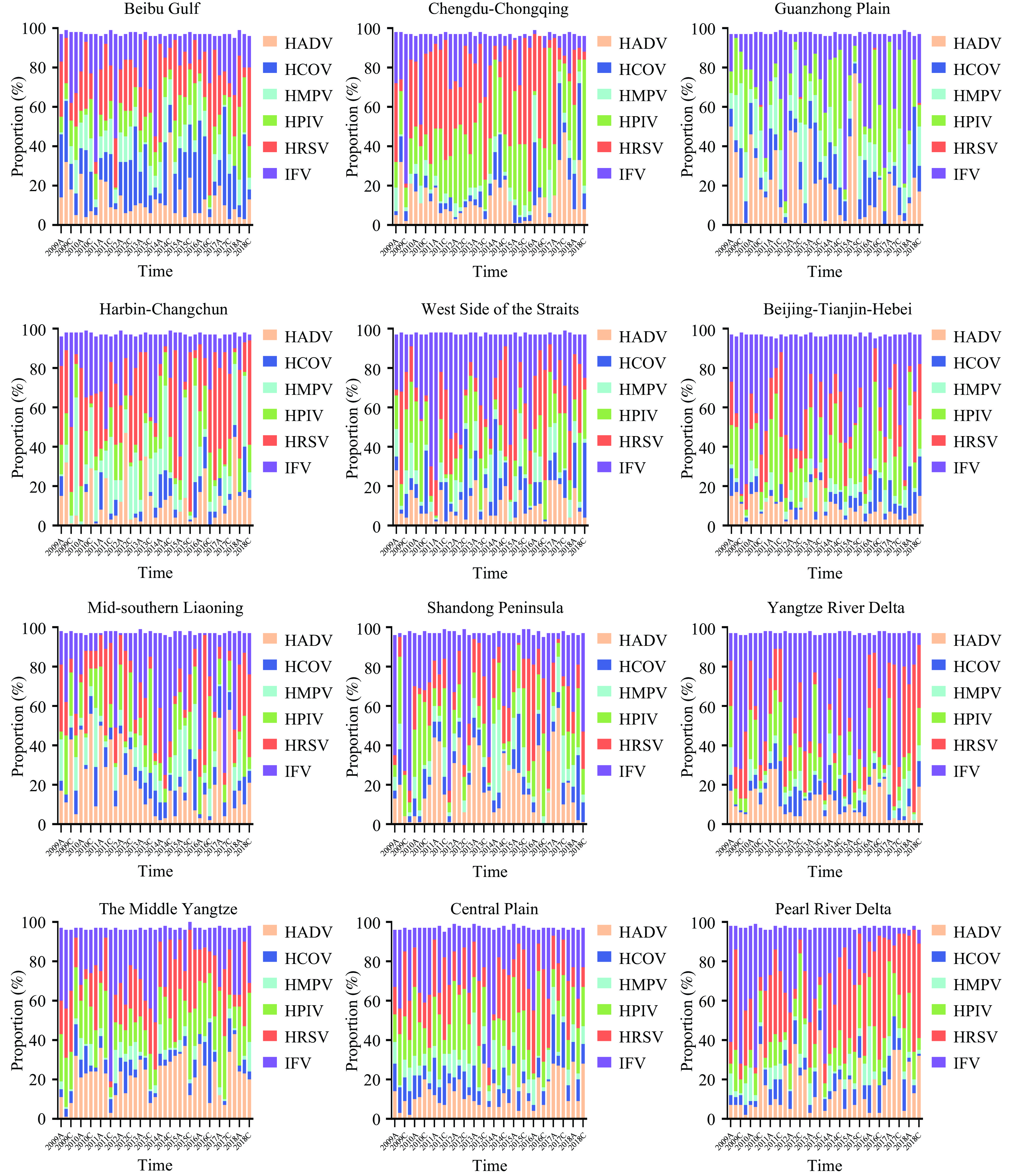
The prevalence of unstable and incomplete monitoring data significantly complicates syndromic analysis. Many data interpolation methods currently available demonstrate inadequate effectiveness in overcoming this issue.
To improve the accuracy of interpolation, we propose the integration of the SHapley Additive exPlanation model (SHAP) with the structural equation model (SEM), forming a combined SHAP-SEM approach. A case study is then performed to assess the enhanced performance of this novel model compared to traditional methods.
The SHAP-SEM model was utilized to develop an interpolation model employing data from the Chinese respiratory syndrome surveillance database. We executed three distinct experiments to establish the model datasets, comprising a total of 100 replicates. The performance of the model was evaluated using the root mean square error (RMSE), correlation coefficient (r), and F-score. The findings demonstrate that the SHAP-SEM model consistently achieves superior accuracy in data interpolation, which is evident across different seasons and in overall performance.
We conclude that the SHAP-SEM model demonstrates an exceptional capacity for accurately interpolating volatile and incomplete data. This capability is crucial for developing a comprehensive database that is essential for conducting risk assessments related to syndromes.
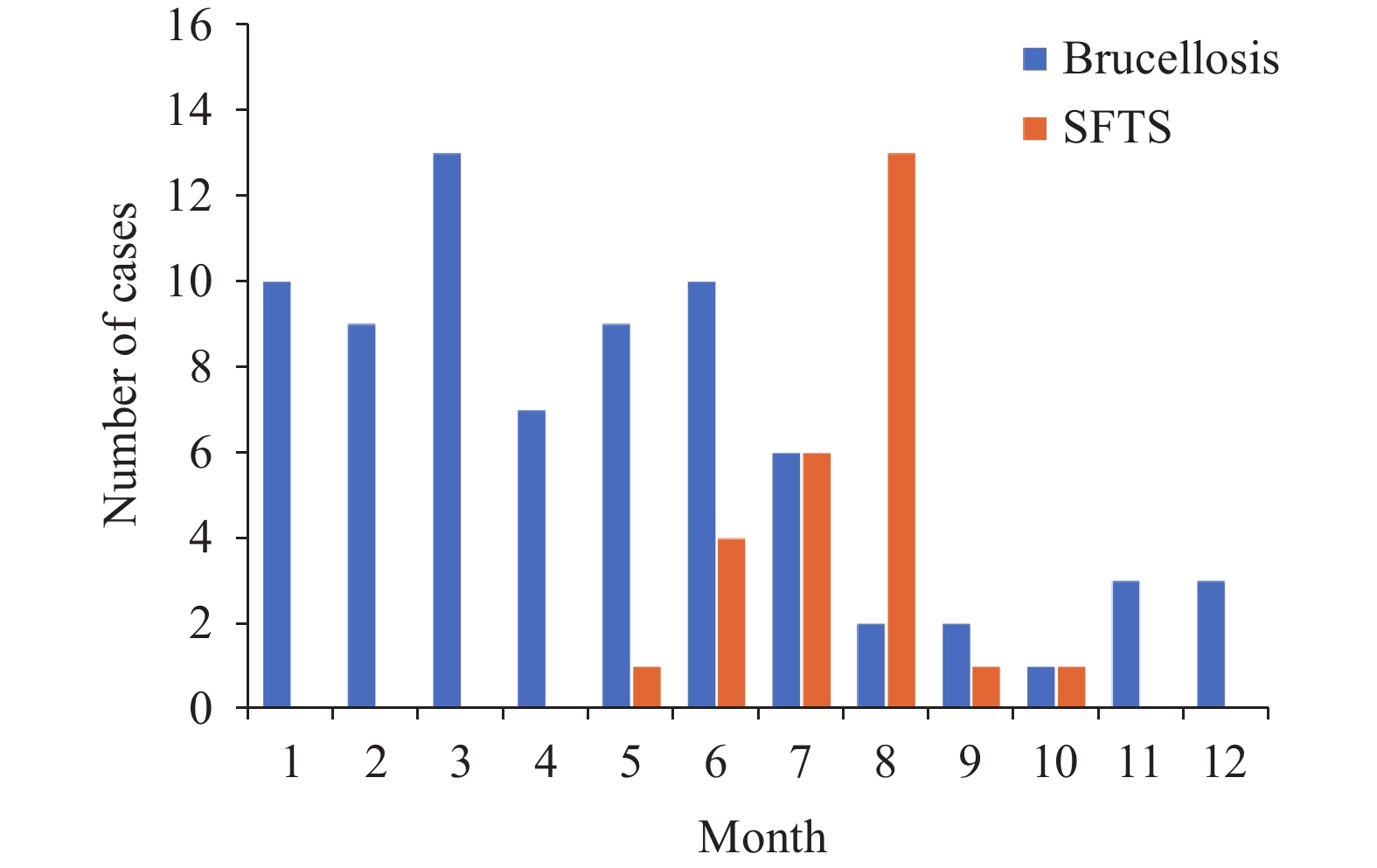
Brucellosis and severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) are neglected zoonoses, attributable respectively to Brucella and the SFTS virus (SFTSV). While the incidence of these diseases has been rising, instances of co-infection remain uncommon.
This represents the first documented case of a rare coinfection involving Brucella and SFTSV. We carried out an epidemiological analysis of patients diagnosed with brucellosis and those with SFTS at Yidu Central Hospital of Weifang. Our findings demonstrate a temporal and spatial overlap among the affected individuals.
Our findings suggest that co-infections arising from the spatiotemporal overlap of Brucella and SFTSV are plausible, necessitating heightened awareness and enhanced diagnostic measures.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed