-
On July 26, 2023, a patient exhibiting an unexplained fever was admitted to Yidu Central Hospital of Weifang. The diagnosis of brucellosis was confirmed based on clinical symptoms, epidemiological history, the Brucella Rose Bengal test, and the serum agglutination test. Despite receiving treatment, the patient's platelet counts continued to decline. Subsequent testing using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) led to an additional diagnosis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS), indicating a co-infection with Brucella and SFTS virus (SFTSV). To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of simultaneous brucellosis and SFTS, underscoring the necessity of integrated prevention strategies for multiple zoonotic diseases. Medical practitioners should maintain vigilance for local endemic diseases and consider the potential for concurrent infections to prevent treatment delays.
-
A 52-year-old female was referred to Yidu Central Hospital of Weifang presenting with fever, generalized muscle and joint pain, chills, severe fatigue, and diminished appetite. The patient, a farmer resident in Changle County, Weifang City, Shandong Province, reported extensive contact with sheep and other livestock.
On July 17, 2023, the patient developed a fever, registering a temperature of 38.9 ℃. Despite receiving treatment at a local hospital for three days, her temperature continued to fluctuate. She reported experiencing a worsening of symptoms.
On July 26, 2023, a patient presented at Yidu Central Hospital of Weifang for evaluation; initial blood tests conducted prior to admission indicated leukopenia. She was assessed in the outpatient clinic with a primary diagnosis of unexplained fever. The findings from the physical examination at the time of admission included a temperature of 38.5 °C, a respiratory rate of 22 breaths per minute, a pulse rate of 86 beats per minute, and a blood pressure of 123/78 mmHg. The patient was alert but appeared lethargic and was minimally responsive. Examination revealed slight yellowing of the skin and sclera, with no accompanying rash. A tender lymph node approximately the size of a peanut was palpable in the right groin. Examination of the heart and lungs did not disclose any significant abnormalities. Laboratory tests showed decreased leukocyte and platelet counts, while elevations were noted in ferritin, procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, and interleukin-6 levels (Table 1). The Rose Bengal test for Brucella and the serum agglutination test at a titer of 1∶200 were both positive, confirming an infection with Brucella. Antibiotic therapy was subsequently initiated.
Test items Days after onset (date) Normal range 8 (7.25) 9 (7.26) 10 (7.27) 15 (8.1) 17 (8.3) White blood cell count (109/L) 2.34 2.67 3.78 7.69 6.07 3.5–9.5 Neutrophil percentage (%) 46.3 48.4 53.6 − − 40–75 Red blood cell (1012/L) 4.56 4.15 4.26 − − 3.8–5.1 Hemoglobin (g/L) 119 124 109 − − 115–150 Platelet (109/L) 100 93 80 82 108 125–350 Ferritin (ng/mL) − 929 − − 300 15–200 Procalcitonin (ng/mL) − 0.253 − − 0.031 <0.15 C-reactive protein (mg/mL) − 68 − − 21 0–10 Interleukin-6 (pg/mL) − 149.3 − − 18.34 <7 Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) − − 484 92 42 7–40 Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) − − 839 44 33 13–35 Total bile acids (μmol/L) − − 92.9 2.3 − 0.1–10.0 Total protein (g/L) − − 53.9 64.6 − 55–80 Albumin (g/L) − − 33.7 34.6 − 35–55 Total bilirubin (μmol/L) − − 44.8 13.6 21 1.71–21.00 Direct bilirubin (μmol/L) − − 39.9 9.1 13 0–6.8 Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) − − 407 282 57 35–100 Lactate dehydrogenase (U/L) − − 690 329 248 313–618 Creatine kinase (U/L) − − 1261 498 65 40–200 Creatine kinase isoenzyme (U/L) − − 342 201 23 <5.0 Sodium (mmol/L) − − 126 142 − 135–145 Note: “−” indicates that this test was not performed on that day.
Abbreviation: SFTS=severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome.Table 1. Laboratory test results of a case with brucellosis and SFTS in Yidu Central Hospital of Weifang in 2023.
On July 27, 2023, the patient exhibited a significant drop in platelet count to 80×109/L. Although renal function, blood glucose, and lipid levels remained within normal limits, elevated levels were noted in several liver function markers — including alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, total bile acids, alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase — as well as in creatine kinase and its isoenzymes (Table 1). Electrolyte concentrations were overall stable, with the exception of a decreased sodium level (Table 1). Imaging using superficial lymph node B-ultrasound identified a lymph node measuring 2cm by 1cm with distinct borders in the right groin. Further laboratory analysis using RT-PCR detected SFTSV nucleic acids in the serum at a concentration of 5.52×104 copies/mL. Based on these clinical findings and laboratory data, the patient was diagnosed with SFTS and subsequently received symptomatic treatment.
On July 28, 2023, the patient’s blood culture tested positive for Brucella melitensis biovar 3, confirming an infection with brucellosis.
On August 1, 2023, the patient’s condition and laboratory indicators stabilized. By August 3, 2023, the patient was discharged following the resolution of her symptoms and the normalization of all laboratory test indicators.
Following a series of diagnostic tests, the patient was confirmed to have SFTS and brucellosis on the tenth day after disease onset and was subsequently discharged on the seventeenth day. Treatment initiated post-diagnosis included rest, doxycycline (100 mg twice daily) and levofloxacin (500 mg once daily) for brucellosis, along with caffeic acid (0.2 g three times daily) to boost white blood cells and platelet counts. Nutritional support was provided through supplements of vitamin C and vitamin B6. No similar cases were identified upon interviewing her family, neighboring villagers, and the hospital staff involved in her care.
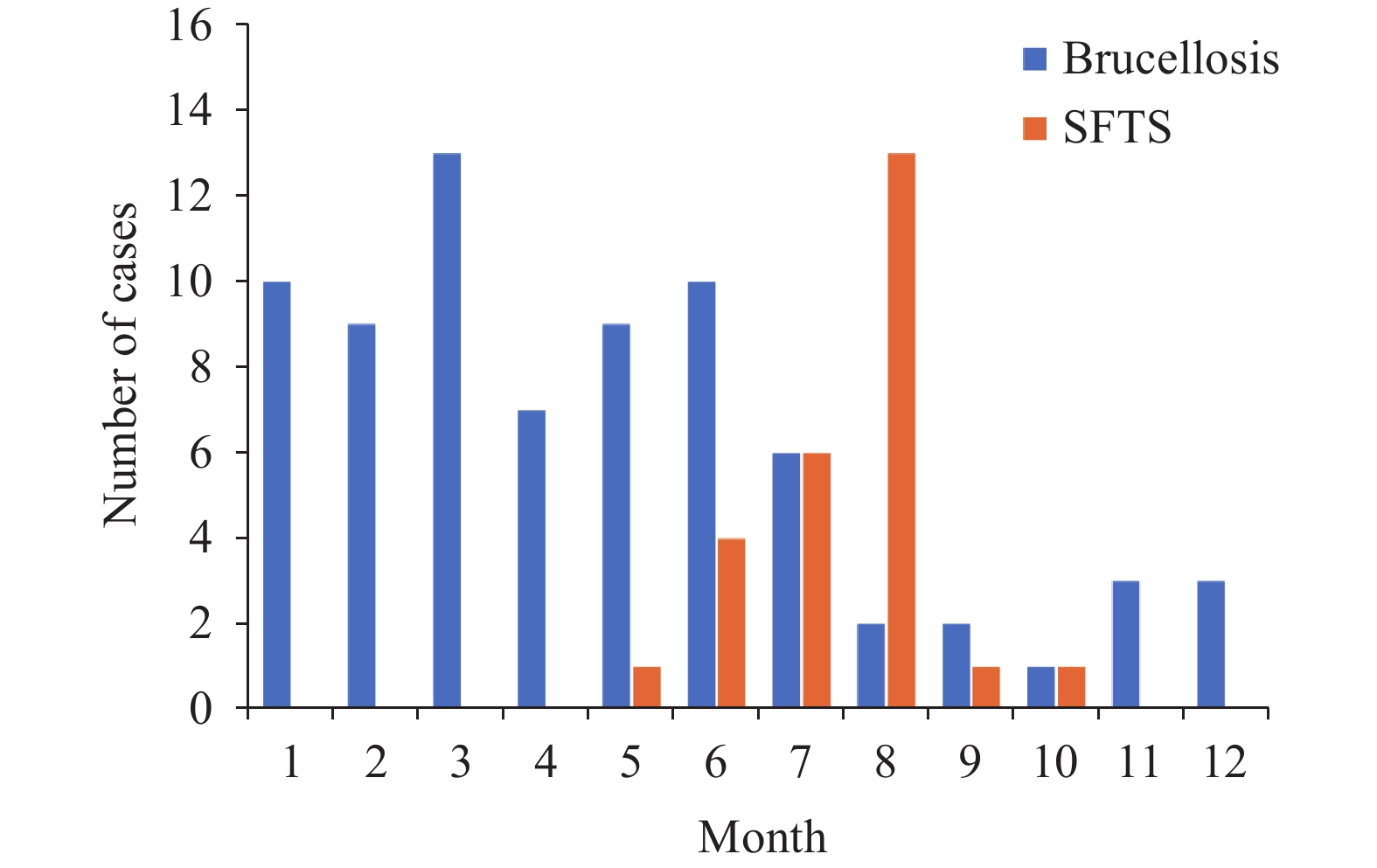
In this study of co-infection, we examined patients diagnosed with two distinct diseases at Yidu Central Hospital of Weifang in 2023. The analysis included 75 cases of brucellosis and 26 cases of SFTS. Both the incidence and distribution of these infectious diseases exhibited temporal and spatial overlap. Brucellosis cases occurred throughout the year, peaking between January and July, whereas SFTS cases were confined to the months of May through October, as shown in Figure 1. Geographically, brucellosis cases were more broadly spread, with the majority (72%) originating from Linqu County and Qingzhou county-level City, Weifang City. In contrast, all reported cases of SFTS were from these same locations.
-
While co-infections involving various zoonotic infectious diseases have been documented (1), cases involving simultaneous infections with SFTSV and Brucella are yet unreported. To the best of our knowledge, this report describes the first rare instance of a patient co-infected with brucellosis and SFTS. Managing and treating this co-infection proved challenging. Despite the eventual discharge of the patient free of symptoms and laboratory abnormalities, the journey from detection to definitive diagnosis was protracted. This extended diagnostic timeline poses a significant risk to health. It is crucial for the management of both brucellosis and SFTS to focus on early detection, diagnosis, and treatment (2-3). Delayed treatment of these conditions can lead to severe outcomes, including chronic infection from Brucella and potentially fatal complications from SFTS (4). In summary, prompt and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and recovery.
This case illustrates that brucellosis should be a primary consideration in patients presenting with fever, fatigue, joint pain, and a history of contact with sheep. Conversely, SFTS should be suspected in patients who report tick bites and exhibit thrombocytopenia, tender lymphadenopathy, and elevated levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase, and creatine kinase. The occurrence of such symptoms suggests the need to evaluate for potential co-infections with multiple pathogens.
Brucellosis and SFTS are neglected zoonotic diseases that have demonstrated a rising incidence in recent years (5-6). A spatiotemporal analysis of the occurrence of these diseases among patients at the Yidu Central Hospital of Weifang revealed concurrent spatial and temporal patterns of infection. We hypothesize that an increasing number of similar cases may be identified in the future. Consequently, heightened vigilance is essential to timely detect co-infected patients, thereby preventing misdiagnosis and underdiagnosis. First, healthcare institutions must assume greater responsibility by analyzing disease patterns among local and nearby populations, offering free consultations, and enhancing health education in areas at high risk. These measures will improve awareness and diagnosis of these diseases and ensure the availability of necessary diagnostic reagents. Second, to facilitate early detection, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment — thereby reducing chronicity and mortality — we recommend the implementation of a joint-examination strategy in regions where both brucellosis and SFTS are prevalent, such as Linqu County and Qingzhou county-level City. Lastly, considering the interconnected nature of human, animal, and environmental health in the transmission of brucellosis and SFTS, it is imperative to adopt a “One Health” approach. This strategy will promote comprehensive health and well-being across these interconnected domains.
In this paper, we present a rare case of co-infection involving brucellosis and SFTS, which contributes to the sparse body of knowledge on the simultaneous presence of multiple zoonotic diseases. This report aims to enhance the recognition and diagnosis of such co-infections among healthcare professionals. The insights gleaned from our study are crucial for the early diagnosis and treatment of these diseases, and they also inform preventive and control strategies. To improve the prevention, control, diagnosis, and treatment of these diseases, we propose several recommendations. First, it is imperative to conduct public education campaigns for local farmers, emphasizing preventive measures against brucellosis and SFTS. Second, medical practitioners in endemic regions must possess a thorough understanding of local infectious diseases and engage in comprehensive consultations with patients presenting with fever to ensure accurate diagnoses. Third, the development and implementation of rapid and precise methods for detecting multiple pathogens are essential to minimize the risks of misdiagnosis and underdiagnosis.
-
No conflicts of interest.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:




