-
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) continues to pose a significant public health threat, particularly among men who have sex with men (MSM). In 2022 (1), the global tally of new HIV infections approximated at 1.3 million, with HIV incidence among MSM reportedly nearly five per 100 person-years (PYs), 27 to 150 times higher than that in the general adult male population (2). Alarmingly, China has observed an uptick in HIV instances among MSM (3). Concurrently, syphilis resurfaced as a major public health concern, predominantly affecting the MSM community (4). Despite this pronounced escalation, insight into the extent and trajectory of HIV and syphilis incidence among MSM in China remains inadequate. In Tianjin Municipality, for instance, case reports suggest MSM constitute approximately 80% of HIV/acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) instances (5), mirrored by a high prevalence of syphilis within the demographic (6). Comprehending the dynamics behind these incidence rates is critical in monitoring and appraising public health approaches. To that end, a cohort study involving 2,110 participants for HIV and 1,927 for syphilis was conducted among the MSM population in Tianjin from 2013 to 2022. The study revealed a declining trend in HIV incidence of an average rate of 2.3 per 100 PYs over the study period, contrasted by a rising trend in syphilis incidence of an average rate of 4.8 per 100 PYs. These findings, via multivariate analysis, pinpointed several factors linked to HIV and syphilis incidence, emphasizing the imperative to amplify intervention initiatives for MSM to mitigate HIV and syphilis transmission.
From April 2013 to March 2022, an open cohort study was conducted focusing on MSM based in Tianjin. Inclusion criteria for participants were: biological male , being at least 16 years old, engaging in oral or anal intercourse with males in the past year, voluntary completion of questionnaires and registration with fingerprints, submission to blood sampling for HIV and syphilis testing, a negative or unknown HIV/syphilis status at the initial survey, and having at least two HIV/syphilis test records during the study period. Exclusion criteria included inability to participate independently in the survey, and pre-existing HIV/syphilis infection prior to the initial survey. Between April 2013 and March 2022, MSM were recruited via online and offline methods through community-based organizations, creating an open cohort. All participants were required to provide baseline data relating to demographics, behavioral factors, and HIV/syphilis status, with information collected through structured questionnaires administered by trained interviewers. Participants were then followed up every six months for serological testing for HIV and syphilis. HIV testing used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA; Wantai Biotech Inc., China and Lizhu Biotech Inc., Beijing, China) and any positive results were confirmed by western blotting (HIV Blot 2.2; MP Diagnostics, Singapore). Syphilis testing also used an ELISA test (Yingke-xinchuang Biotech Inc., China), but positive results were confirmed using a toluidine red unheated serum test (TRUST; Wantai Biotech Inc., China). Syphilis was diagnosed only when both ELISA and TRUST tests were positive (7). After excluding participants who tested HIV positive at the baseline (n=123), or lacked follow-up records (n=557), 2,110 MSM were included in the final data analysis to estimate HIV incidence (Figure 1). Of those 2,110 participants, 183 tested positive for syphilis at baseline; hence, the remaining 1,927 MSM who tested syphilis-negative were included in the final data analysis for syphilis incidence estimation. Follow-up PYs were calculated from the date of the baseline survey to the last HIV/syphilis test, date of death, loss to follow-up, or March 31, 2022 — whichever occurred first. Incidence rates for HIV and syphilis were then calculated based on seroconversions and observed PYs.
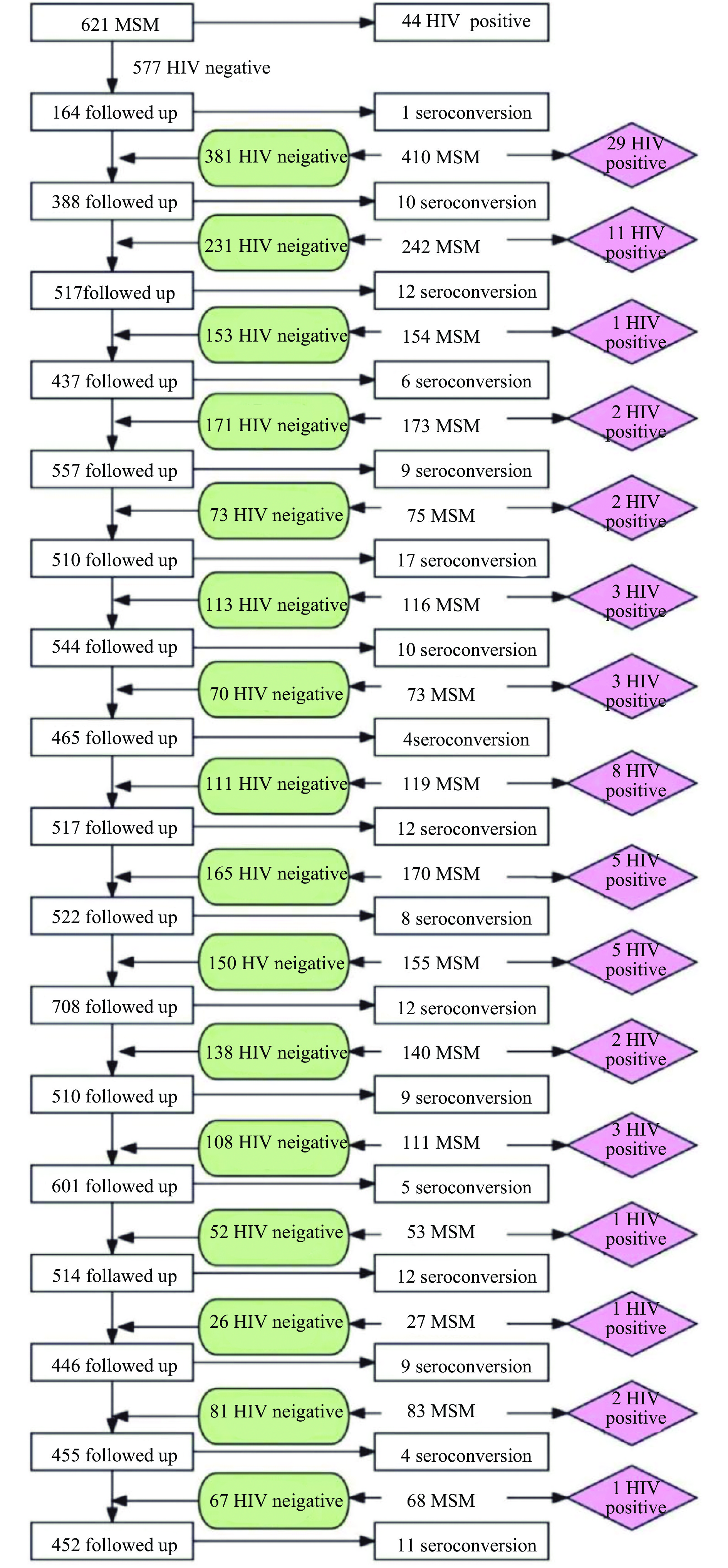 Figure 1.
Figure 1.Process of the retrospective cohort study among MSM in Tianjin Municipality, China.
Abbreviation: HIV=human immunodeficiency virus; MSM=men who have sex with men.Categorical variables were delineated in terms of frequencies and percentages, whereas continuous variables were displayed as “Median (lower quartile, upper quartile)”. To estimate the hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for HIV and syphilis incidences, Cox proportional hazards (PH) models were utilized. All statistical analyses, including two-sided tests with a significance level of P<0.05, were carried out using SPSS software (version 24.0; Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.). The study received ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of the Center for STD and AIDS Prevention and Control of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (X130419285).
The median age for the 2,110 participating MSM was determined to be 27.5 years, with an interquartile range (IQR) of 24.0 to 34.0 years. Demographic analysis revealed that 60.5% of the participants were local residents, 74.7% were single, and 88.9% had acquired at least a high school level education. In terms of sexual orientation, 84.5% identified themselves as homosexual.
During the observation period, there were 151 reported HIV seroconversions within 6,486.0 PYs, establishing an HIV incidence rate of 2.3 per 100 PYs (95% CI: 2.0, 2.7). To minimize the effects of random errors and facilitate a comprehensive assessment of incidence trends, the 2-year incidence rate was utilized. HIV incidence rates varied over time, reaching a peak of 5.2 (95% CI: 3.2, 7.2) in 2013–2014, before dropping to 4.2 (95% CI: 3.0, 5.4) in 2015–2016, 2.4 (95% CI: 1.7, 3.1) in 2017–2018, 2.2 (95% CI: 1.5, 2.9) in 2019–2020, and 1.9 (95% CI: 0.9, 2.9) per 100 PYs in 2021–2022 (Figure 2). The PH assumption for the Cox models was validated by examining the interaction terms between the variables included in the model and the log of follow-up time, with no violations observed. Therefore, Cox PH models were employed to estimate the associations between various factors and HIV/syphilis incidence. The multivariate analysis demonstrated that MSM identifying as heterosexual or bisexual had a lower risk of HIV incidence than those identifying as homosexual [adjusted hazard ratio (aHR)=0.597, 95% CI: 0.358, 0.996]. MSM who engaged in unprotected anal sex during the previous six months had a 43.6% increased risk of HIV incidence (aHR=1.436, 95% CI: 1.014, 2.033) compared to those who did not. Furthermore, MSM who experienced their first homosexual intercourse at 20 years old or later were found to be at a 46.7% higher risk of HIV incidence (aHR=1.467, 95% CI: 1.023, 2.104) compared to those who first engaged in homosexual intercourse at a younger age. The risk of HIV incidence was also higher among MSM who used psychoactive substances within the last six months (aHR=1.584, 95% CI: 1.137, 2.207). Conversely, regular follow-up visits (more than thrice) seemed to serve as a protective factor against HIV incidence (aHR=0.216, 95% CI: 0.152, 0.308) in comparison to those with two or fewer follow-ups during the study period. Syphilis infection proved to be a significant risk factor for HIV incidence among MSM (aHR=1.795, 95% CI: 1.131, 2.849) (Table 1).
 Figure 2.
Figure 2.Trends in the incidence of HIV and syphilis among MSM in Tianjin Municipality, China, from 2013 to 2022.
Abbreviation: HIV=human immunodeficiency virus; MSM=men who have sex with men.Variables HIV
conversionsPYs Incidence rate
(/100 PYs)Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis HR (95% CI) P value HR (95% CI) P value Age group (years) <20 8 260.4 3.1 1.000 1.000 20–29 89 3,468.0 2.6 0.835 (0.405, 1.722) 0.625 0.808 (0.381, 1.712) 0.577 30–39 30 1,669.1 1.8 0.587 (0.269, 1.281) 0.181 0.491 (0.211, 1.146) 0.491 ≥40 24 1,088.5 2.2 0.726 (0.326, 1.616) 0.433 0.566 (0.229, 1.398) 0.566 Household registration Tianjin 68 2,376.8 2.9 1.000 1.000 Other city 83 4,109.2 2.0 0.712 (0.517, 0.982) 0.038 0.750 (0.530, 1.060) 0.104 Ethnicity Ethnic minorities 3 65.1 4.6 1.000 1.000 Han 148 6,420.9 2.3 0.509 (0.161, 1.604) 0.249 0.649 (0.204, 2.067) 0.464 Marital Status Unmarried 111 4,600.6 2.4 1.000 1.000 Married/cohabiting 31 1,602.7 1.9 0.809 (0.543, 1.206) 0.299 0.974 (0.583, 1.627) 0.920 Divorced/widowed 9 282.7 3.2 1.325 (0.671, 2.614) 0.417 1.378 (0.647, 2.933) 0.405 Education Junior high school and below 20 831.2 2.4 1.000 1.000 High school and above 131 5,654.8 2.3 0.958 (0.598, 1.535) 0.859 0.995 (0.602, 1.646) 0.985 Sexual orientation Homosexual 131 5,216.6 2.5 1.000 1.000 Bisexual/heterosexual 20 1,269.4 1.6 0.633 (0.395, 1.015) 0.058 0.597 (0.358, 0.996) 0.048 Having unprotected anal sex in the last six months No 48 2,686.1 1.8 1.000 1.000 Yes 103 3,799.9 2.7 1.518 (1.078, 2.139) 0.017 1.436 (1.014, 2.033) 0.041 Number of anal intercourse in the last one week ≤1 131 5,683.8 2.3 1.000 1.000 ≥2 20 802.2 2.5 1.074 (0.671, 1.720) 0.766 1.064 (0.661, 1.713) 0.798 Having commercial homosexual intercourse in the last six months No 146 6,124.5 2.4 1.000 1.000 Yes 5 361.5 1.4 0.585 (0.240, 1.426) 0.238 0.777 (0.314, 1.924) 0.586 Age of first homosexual intercourse (years) ≤19 61 3,012.0 2.0 1.000 1.000 ≥20 90 3,474.0 2.6 1.282 (0.926, 1.775) 0.134 1.467 (1.023, 2.104) 0.037 Main places to find homosexual partners Internet dating software 117 5,041.7 2.3 1.000 1.000 Other locations 34 1,444.3 2.4 1.019 (0.694, 1.495) 0.923 1.221 (0.817, 1.824) 0.330 Psychoactive substances use No 62 3,198.0 1.9 1.000 1.000 Yes 89 3,288.0 2.7 1.410 (1.019, 1.953) 0.038 1.584 (1.137, 2.207) 0.007 Number of follow-up visits ≤2 81 1,475.0 5.5 1.000 1.000 ≥3 70 5,011.0 1.4 0.218 (0.154, 0.308) 0.000 0.216 (0.152, 0.308) 0.000 Syphilis infection No 129 5,935.3 2.2 1.000 1.000 Yes 22 550.7 4.0 1.828 (1.163, 2.873) 0.009 1.795 (1.131, 2.849) 0.013 Abbreviation: PYs=person-years; HR=hazard ratio. Table 1. Factors associated with HIV incidence among MSM in Tianjin Municipality, China.
In the study, 1,927 participants contributed to syphilis incidence evaluation by providing 5,469.3 PYs of follow-up data. Throughout this period, 260 new syphilis cases were identified, which yielded an incidence rate of 4.8 per 100 PYs (95% CI: 4.2, 5.3). A pattern of escalating syphilis incidence rates was witnessed over the years, increasing from 3.6 (95% CI: 1.9, 5.3) in 2013–2014, 2.7 (95% CI: 1.9, 3.6) in 2015–2016, 4.8 (95% CI: 3.8, 5.8) in 2017–2018, 5.9 (95% CI: 4.8, 7.1) in 2019–2020, and reaching 7.2 (95% CI: 4.5, 9.8) per 100 PYs in 2021–2022 (Figure 2). Results from multivariate analysis indicated certain patterns of syphilis risk among MSM. Divorced or widowed MSM had a lower risk compared to those who were unmarried (aHR=0.335, 95% CI: 0.142, 0.792). Furthermore, MSM identifying as heterosexual or bisexual exhibited lower risks compared to those identifying as homosexual (aHR=0.605, 95% CI: 0.459, 0.964). A rather alarming observation was that MSM who reported using psychoactive substances in the last six months had a 50.4% higher syphilis incidence risk compared to those who reported no use of such substances (aHR=1.504, 95% CI: 1.169, 1.934) (Table 2).
Variables Syphilis
conversionsPYs Incidence rate
(/100 PYs)Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis HR (95% CI) P value HR (95% CI) P value Age group (years) <20 12 202.5 5.9 1.000 1.000 20–29 134 3,062.7 4.4 0.737 (0.408, 1.330) 0.310 0.716 (0.391, 1.313) 0.280 30–39 60 1,391.9 4.3 0.733 (0.394, 1.362) 0.326 0.826 (0.424, 1.607) 0.573 ≥40 54 812.2 6.6 1.121 (0.600, 2.096) 0.721 1.628 (0.810, 3.271) 0.171 Household registration Tianjin 102 2,019.9 5.0 1.000 1.000 Other city 158 3,449.4 4.6 0.909 (0.709, 1.167) 0.455 0.837 (0.638, 1.098) 0.199 Ethnicity Ethnic minorities 3 54.7 5.5 1.000 1.000 Han 257 5,414.6 4.7 0.840 (0.268, 2.632) 0.765 0.971 (0.308, 3.058) 0.959 Marital Status Unmarried 189 3,926.8 4.8 1.000 1.000 Married/cohabiting 65 1,299.6 5.0 1.048 (0.790, 1.390) 0.744 0.867 (0.603, 1.248) 0.443 Divorced/widowed 6 242.9 2.5 0.522 (0.231, 1.176) 0.117 0.335 (0.142, 0.792) 0.013 Education Junior high school and below 36 660.9 5.4 1.000 1.000 High school and above 224 4,808.4 4.7 0.855(0.601, 1.217) 0.385 0.770 (0.525, 1.129) 0.181 Sexual orientation Homosexuality 221 4,380.9 5.0 1.000 1.000 Bisexual/heterosexual 39 1,088.4 3.6 0.722 (0.513, 1.017) 0.062 0.605 (0.459, 0.964) 0.031 Had unprotected anal sex in the last six months No 112 2,282.8 4.9 1.000 1.000 Yes 148 3,186.5 4.6 0.954 (0.746, 1.219) 0.705 0.952 (0.742, 1.220) 0.697 Number of anal intercourse in the last 1 week ≤1 222 4,755.2 4.7 1.000 1.000 ≥2 38 714.2 5.3 1.145 (0.811, 1.615) 0.441 1.100 (0.774, 1.562) 0.596 Having commercial homosexual intercourse in the last six months No 222 5,199.6 4.3 1.000 1.000 Yes 38 269.8 14.1 1.195 (0.709, 2.013) 0.504 1.217 (0.711, 2.083) 0.473 Age of first homosexual intercourse (years) ≤19 126 2,566.6 4.9 1.000 1.000 ≥20 134 2,902.7 4.6 0.939(0.736, 1.198) 0.612 0.964 (0.735, 1.265) 0.793 Main places to find homosexual partners Internet dating software 209 4,218.9 5.0 1.000 1.000 Other locations 51 1,250.5 4.1 0.831 (0.611, 1.130) 0.238 0.787 (0.568, 1.089) 0.148 Psychoactive substances use No 108 2,728.7 4.0 1.000 1.000 Yes 152 2,740.7 5.5 1.414 (1.104, 1.811) 0.006 1.504 (1.169, 1.934) 0.001 Abbreviation: PYs=person-years; HR=hazard ratio. Table 2. Factors associated with the incidence of syphilis among MSM in Tianjin, China.
-
Our research presents the results of the inaugural long-term cohort study investigating the incidence rate of HIV/syphilis and contributing factors within Tianjin’s population. We documented an HIV incidence rate of 2.3 per 100 PYs among MSM in Tianjin. This rate surpasses the one reported in Australia (8) yet remains lower than the incidence rate identified in Chengdu city(9). Interestingly, the syphilis incidence rate among Tianjin’s MSM population (4.75 per 100 PYs) exceeded the rates noted in Australian studies (10).
Our study observed a declining incidence of HIV among MSM in Tianjin, contrasting with an upward trend in syphilis incidence. This divergence may be attributed to the comprehensive preventative interventions for MSM that have been in place over recent years. First, mRNA surveillance for acute HIV infection among MSM has been conducted since 2015. Additionally, pooled nucleic acid testing has been employed since 2015 for MSM who initially tested HIV-negative, with the goal of identifying early-stage infections and promptly starting treatment. Measures such as post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), increased HIV testing coverage through self-testing, volunteer promotion, and advocating for herpes testing before homosexual intercourse have all been introduced. Given that instances of HIV/AIDS transmission via homosexual contact frequently commence antiretroviral treatment punctually (5), these efforts have fostered a reduction in HIV incidence. Contrastingly, while the Undetectable equals Untransmittable (U=U) theory has spurred increased emphasis on HIV testing and treatment, it has also prompted a surge in syphilis incidence, attributed to the persistence of unregulated unsafe sexual behaviors. Notably, syphilis is known to heighten the risk of HIV infection (11), and our findings suggest that MSM infected with syphilis are more likely to seroconvert to HIV. Thus, the higher incidence of syphilis signals an elevated future potential for HIV transmission. Moreover, there is a substantial overlap of HIV and syphilis infection among Asian MSM (12). This underlines the need to prioritize screening for and treating sexually transmitted infections (STIs), especially syphilis, as a key strategy for controlling the HIV epidemic. Standardized treatment for those testing positive for syphilis is of paramount importance in preventing its spread and carries broader implications for HIV control. The routine detection of syphilis among HIV/AIDS cases is therefore critical for containing its spread. Consequently, it is vital to integrate HIV and syphilis prevention efforts, and enhance the diagnostic and preventative aspects of syphilis treatment to ensure standardized care.
The use of psychoactive substances, prevalent in 43.5% of MSM in Tianjin (6), has been identified as a risk factor contributing to the incidence rates of both HIV and syphilis. It is critical to pay particular attention to MSM who utilize internet dating applications, as the consumption of psychoactive substances is more widespread among this group (6). Interestingly, participants identifying as bisexual or heterosexual exhibited lower incidence rates of HIV and syphilis compared to those identifying as homosexual. This variation may be due to a reduced frequency of sexual interactions with other men and differences in sexual roles compared to their homosexual peers. Existing research indicates that homosexual participants are more likely to assume the passive role during anal sex than their bisexual or heterosexual counterparts (13), a role that carries an increased susceptibility to contracting HIV/syphilis. Moreover, individuals from this group are more likely to be married to women, and societal and familial pressure may discourage engagement in risky behaviors.
Our findings also revealed that increased age at the time of first homosexual intercourse was linked to a higher risk of HIV, underscoring the significance of implementing targeted education initiatives for older MSM demographics. Regular health check-ups seemed to diminish the risk of HIV, likely due to the heightened healthcare awareness among these individuals.
This study is subject to some limitations. First, tracking the HIV and syphilis status of participants who didn’t join the cohort was not possible. Second, our restriction to a cohort of MSM with HIV incidence negated further observation post-HIV conversion, potentially introducing bias into the syphilis incidence data. Yet, despite these constraints, the longevity of the study — spanning a decade — and its exhaustive data set on MSM, offer essential insights into strategies for HIV and syphilis prevention in China’s major cities.
In summary, our research points to a steady decline in the incidence of HIV, juxtaposed with a surge in syphilis cases among MSM in Tianjin from 2013 to 2022. We noted sexual orientation and the use of psychoactive substances as shared risk factors for both HIV and syphilis. Our study highlights the difficulties in curbing HIV transmission, largely attributed to the high prevalence of syphilis. This study is of significant value to public health practices intending to prevent HIV and syphilis, underlining the urgency for more robust intervention measures amongst MSM to limit the spread of both HIV and syphilis.
-
No conflicts of interest.
-
The study participants, data collectors, and the staff from Tianjin Shenlan CBO for their contributions towards quality control.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:




