2024 Vol. 6, No. 26
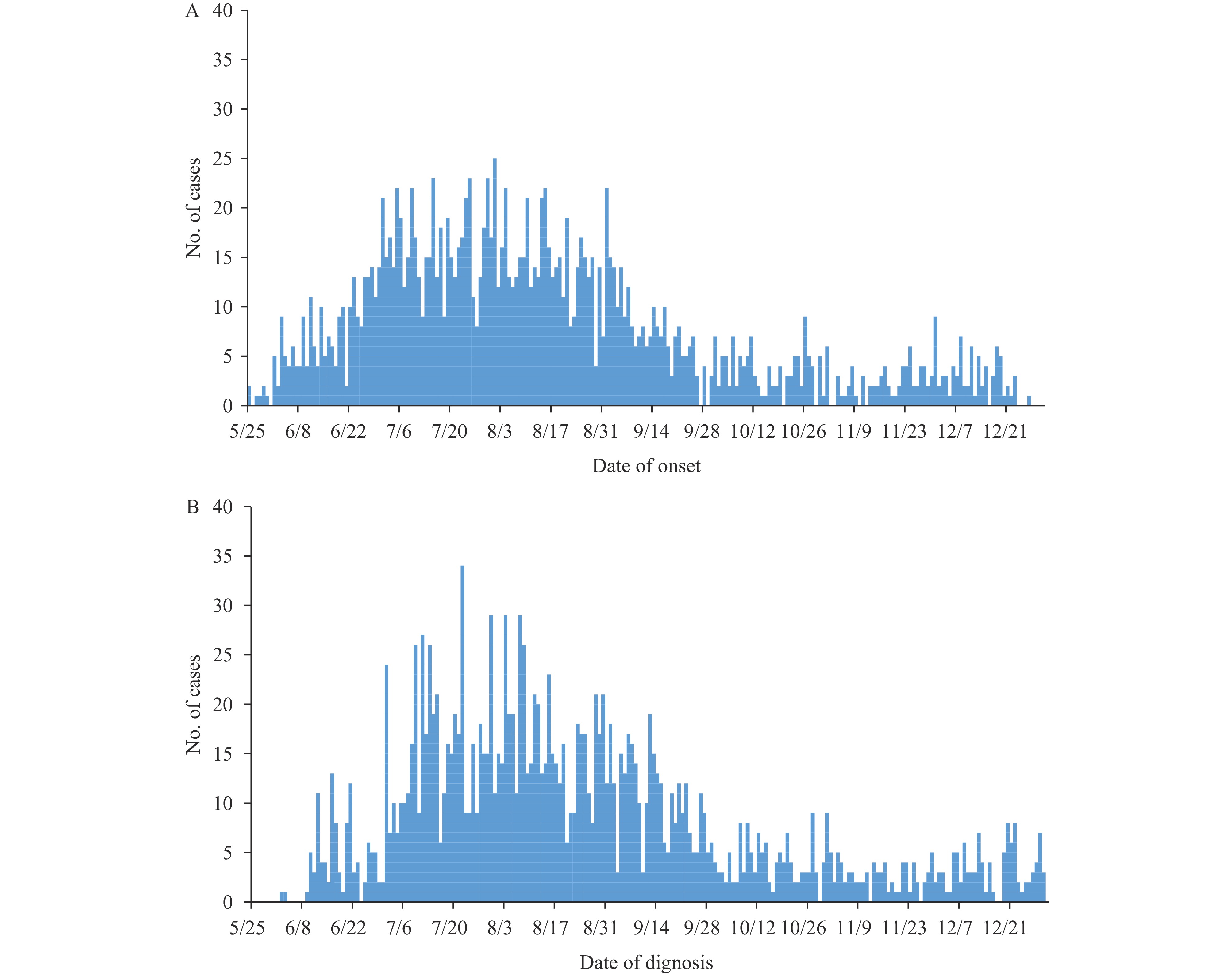
Since May 2022, a global outbreak of mpox has emerged in more than 100 non-endemic countries. As of December 2023, over 90,000 cases had been reported. The outbreak has predominantly affected men who have sex with men (MSM), with sexual contact identified as the principal mode of transmission.
Since June 2023, China has faced an occurrence of mpox, predominantly affecting the MSM population. Approximately 90% of those affected reported engaging in homosexual behavior within 21 days prior to symptom onset, a trend that aligns with the global outbreak pattern. The prompt identification of cases, diligent tracing of close contacts, and the implementation of appropriate management strategies have successfully mitigated the spread of mpox virus in China.
We propose that mpox is transmitted locally within China. Drawing from our experiences in controlling the virus spread, it is crucial to investigate and formulate effective surveillance and educational strategies. Importantly, we must encourage high-risk populations to promptly seek medical care upon the onset of symptoms.
Both the decline in immunity over time and the evolution of the virus play a role in the level of protection offered by a prior infection.
Point estimates indicated variations in protection levels based on the initial infecting variant and the reinfecting variant. There was a consistent correlation between real-world protection, antigenic distance, and humoral immunity levels. Specifically, shorter antigenic distances and higher humoral immunity levels corresponded to enhanced real-world protection.
Our findings suggest that virological and immunological studies could help identify and assess the epidemic risk posed by new variants before they become dominant. Prompt incorporation of the latest variants into the antigen components of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines can significantly contribute to effective epidemic prevention and control measures.
This study investigated the lagged correlation between Baidu Index for influenza-related keywords and influenza-like illness percentage (ILI%) across regions in China. The aim is to establish a scientific foundation for utilizing Baidu Index as an early warning tool for influenza-like illness epidemics.
In this study, data on ILI% and Baidu Index were collected from 30 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) spanning April 2014 to March 2019. The Baidu Index was categorized into Overall Index, Ordinary Index, Prevention Index, Symptom Index, and Treatment Index based on search query themes. The lagged correlation between the Baidu Index and ILI% was examined through the cross-correlation function (CCF) method.
Correlating the Baidu Overall Index of 30 PLADs with ILI% revealed CCF values ranging from 0.46 to 0.86, with a median lag of 0.5 days. Subcategory analysis indicated that the Prevention Index and Symptom Index exhibited quicker responses to ILI%, with median lags of −9 and −0.5 days, respectively, compared to 0 and 3 days for the Ordinary and Treatment Indexes. The median lag days between the Baidu Index and the ILI% were earlier in the northern PLADs compared to the southern PLADs.
The Prevention and Symptom Indexes show promising predictive capabilities for influenza-like illness epidemics.
Respiratory infectious diseases, such as influenza and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), present significant global public health challenges. The emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and big data offers opportunities to improve traditional disease surveillance and early warning systems.
The study analyzed data from January 2020 to May 2023, comprising influenza-like illness (ILI) statistics, Baidu index, and clinical data from Weifang. Three methodologies were evaluated: the adaptive dynamic threshold method (ADTM) for dynamic threshold adjustments, the machine learning supervised method (MLSM), and the machine learning unsupervised method (MLUM) utilizing anomaly detection. The comparison focused on sensitivity, specificity, timeliness, and warning consistency.
ADTM issued 37 warnings with a sensitivity of 71% and a specificity of 85%. MLSM generated 35 warnings, with a sensitivity of 82% and a specificity of 87%. MLUM produced 63 warnings with a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 80%. The initial warnings from ADTM and MLUM preceded those from MLSM by five days. The Kappa coefficient indicated moderate agreement between the methods, with values ranging from 0.52 to 0.62 (P<0.05).
The study explores the comparison between traditional methods and two machine learning approaches for early warning systems. It emphasizes the validation of machine learning’s reliability and underscores the unique advantages of each method. Furthermore, it stresses the significance of integrating machine learning models with various data sources to enhance public health preparedness and response, alongside acknowledging limitations and the need for broader validation.
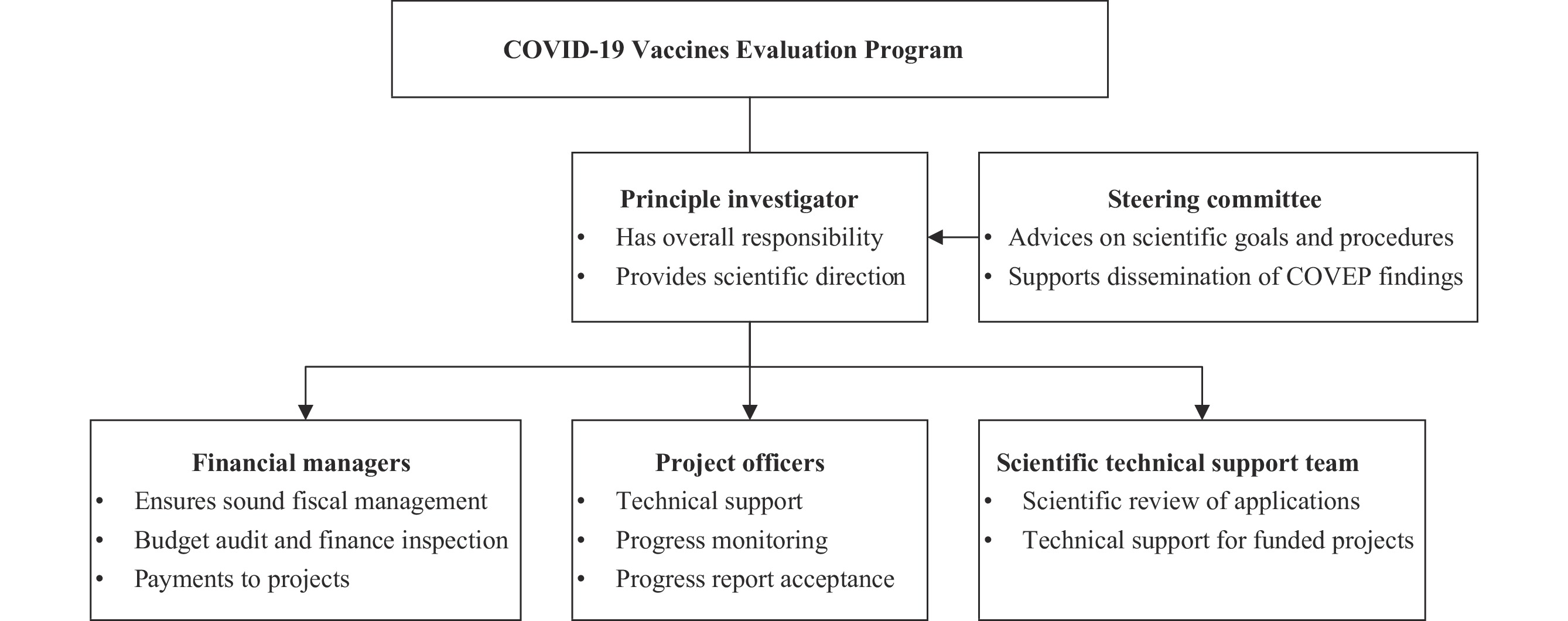
In 2021, China’s domestically produced coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines received approval from regulatory bodies and were administered worldwide. Due to a low number of infections within China during that period, it became imperative to evaluate the vaccines’ real-world effectiveness through international studies. To facilitate this, China CDC launched the COVID-19 Vaccines Evaluation Program (COVEP). This program formed research collaboration agreements with health institutes across five World Health Organization regions, addressing key questions about vaccine performance through ten cooperative agreements. The findings from COVEP projects reinforced confidence, both domestically and globally, in the effectiveness of the vaccines produced in China. Moreover, the outcomes observed internationally were frequently mirrored by later studies conducted within China. COVEP thus pioneered a novel approach for fostering cross-national research collaborations, addressing significant public health issues and exemplifying a framework for international cooperation. This approach is in line with the strategic objectives and other development efforts of China CDC’s national disease control and prevention initiatives.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed