2024 Vol. 6, No. 25
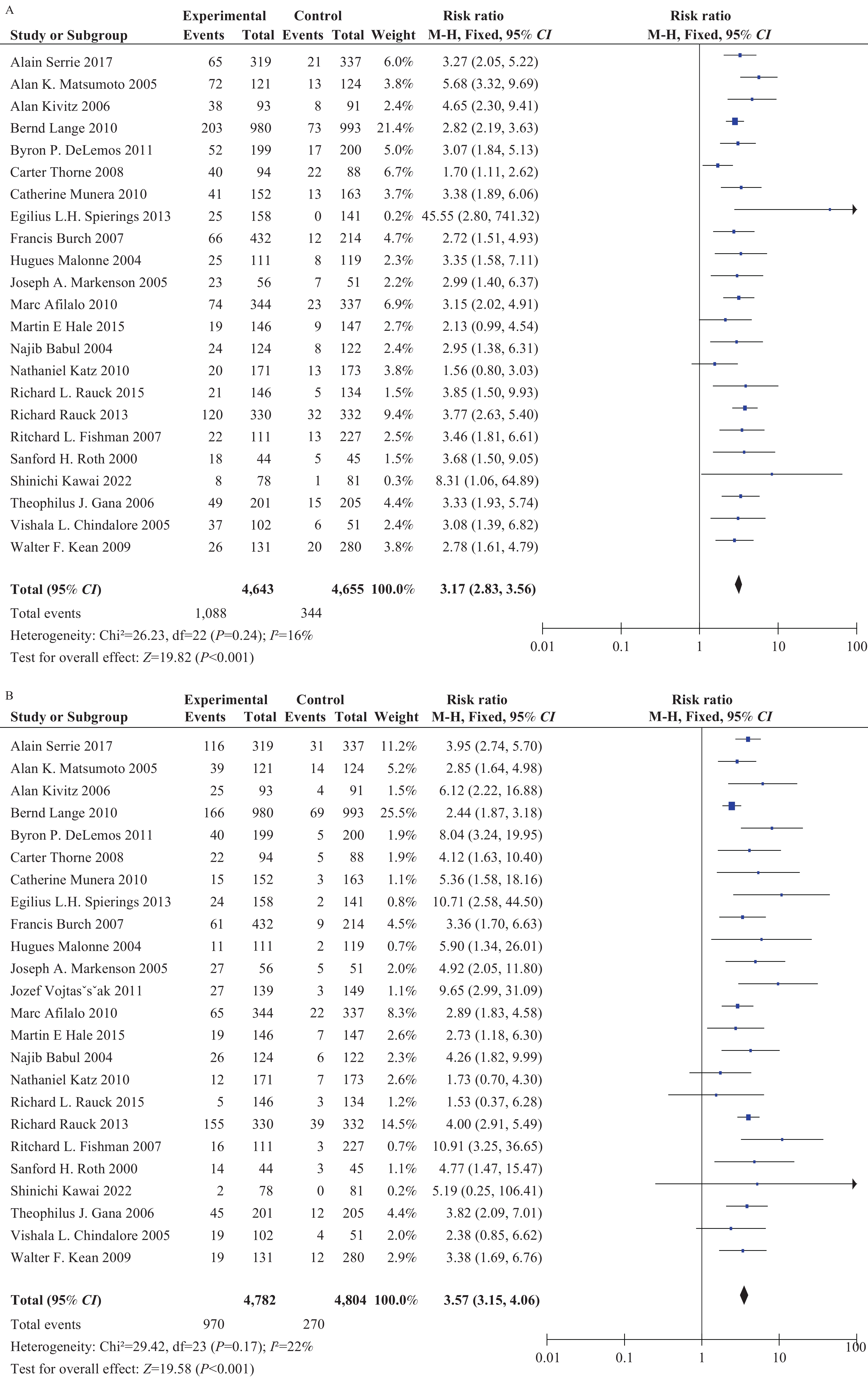
Osteoarthritis (OA) treatment commonly depends on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opioid medications. Nevertheless, the clinical use of opioids is controversial due to their adverse effects and addiction potential. This study, drawing on 24 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with a total of 9,586 patients, thoroughly explored the various side effects associated with opioid use in OA treatment. The results provide additional insight into the non-addictive risks of opioids and may assist clinicians in their judicious use, potentially fostering the advancement of safer treatment options. By reducing the risks of misuse and addiction, public health and safety can be enhanced.
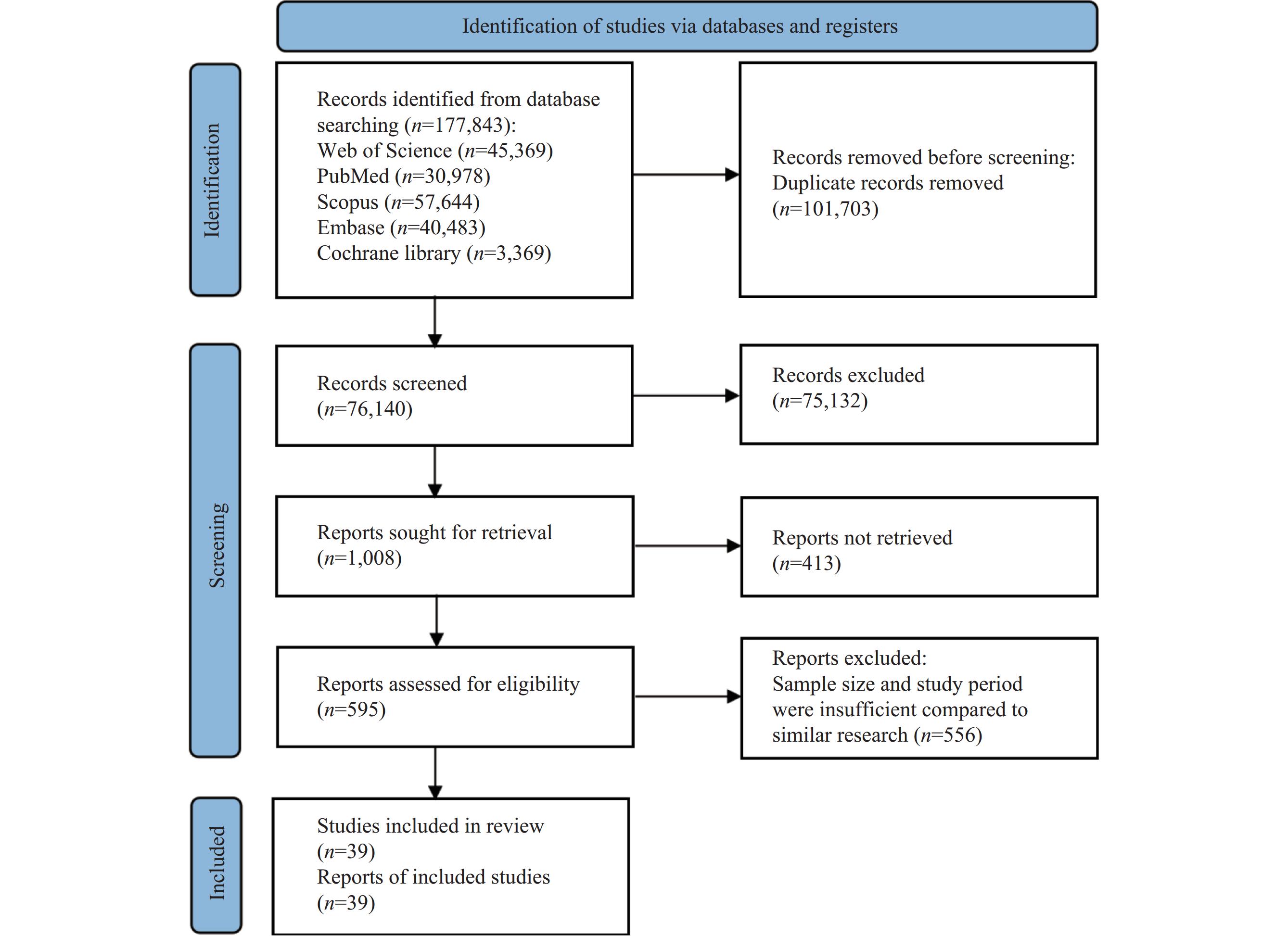
This study aims to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis on the global prevalence of cannabis use to inform drug prevention strategies, policy-making, and resource allocation. This study initially screened 177,843 studies published between January 1, 2000, and January 15, 2024, using peer-reviewed databases including Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Cochrane Library. Ultimately, 595 studies were identified for data extraction, and 39 of these were selected as country-representative studies. Heterogeneity among the selected studies was assessed using the chi-squared test and I2 statistic, while sensitivity analysis was conducted to evaluate the robustness of the results. The prevalence of cannabis use varied between 0.42% and 43.90% across 33 European countries, 1.40% to 38.12% across 15 North and South American countries, 0.30% to 19.10% across 16 Asian countries, and 1.30% to 48.70% across 18 Oceania and African countries. The pooled prevalence of cannabis use was 12.0% [95% confidence interval (CI): 10.0, 14.3] in countries where cannabis is legalized, compared to 5.4% (95% CI: 4.3, 6.9) in non-legalized countries. Our findings indicate that the prevalence of cannabis use has disproportionately increased in most countries with the implementation of medical or recreational cannabis legalization policies and relevant geographic proximity. Increased efforts are needed to monitor newly cannabis-legalized countries and prevent initial use.
H10 avian influenza viruses circulate in wild birds and can reassort with other subtypes. H10N8 and H10N3 have previously caused sporadic human infections in China.
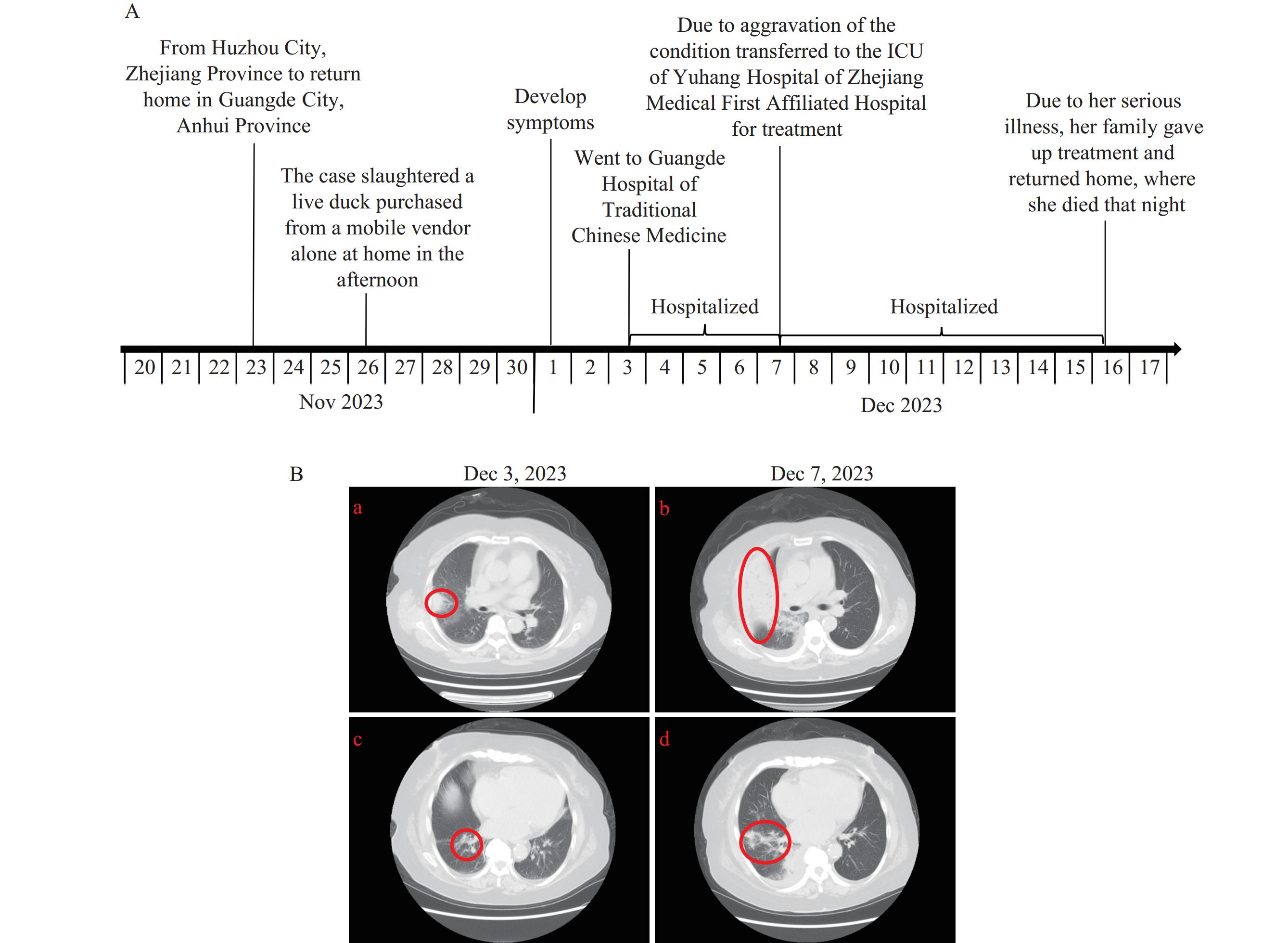
This report documents the first human case of co-infection with avian-origin H10N5 and seasonal H3N2 influenza viruses. Epidemiological investigations identified H10N5 in environmental samples linked to the patient, but no transmission to close contacts occurred.
Enhanced surveillance of avian influenza in live poultry markets and poultry populations is crucial for thoroughly characterizing the epidemiology, transmission, and pathogenesis of H10N5 viruses. Strengthening assessments of outbreak control measures is essential to guide effective management.
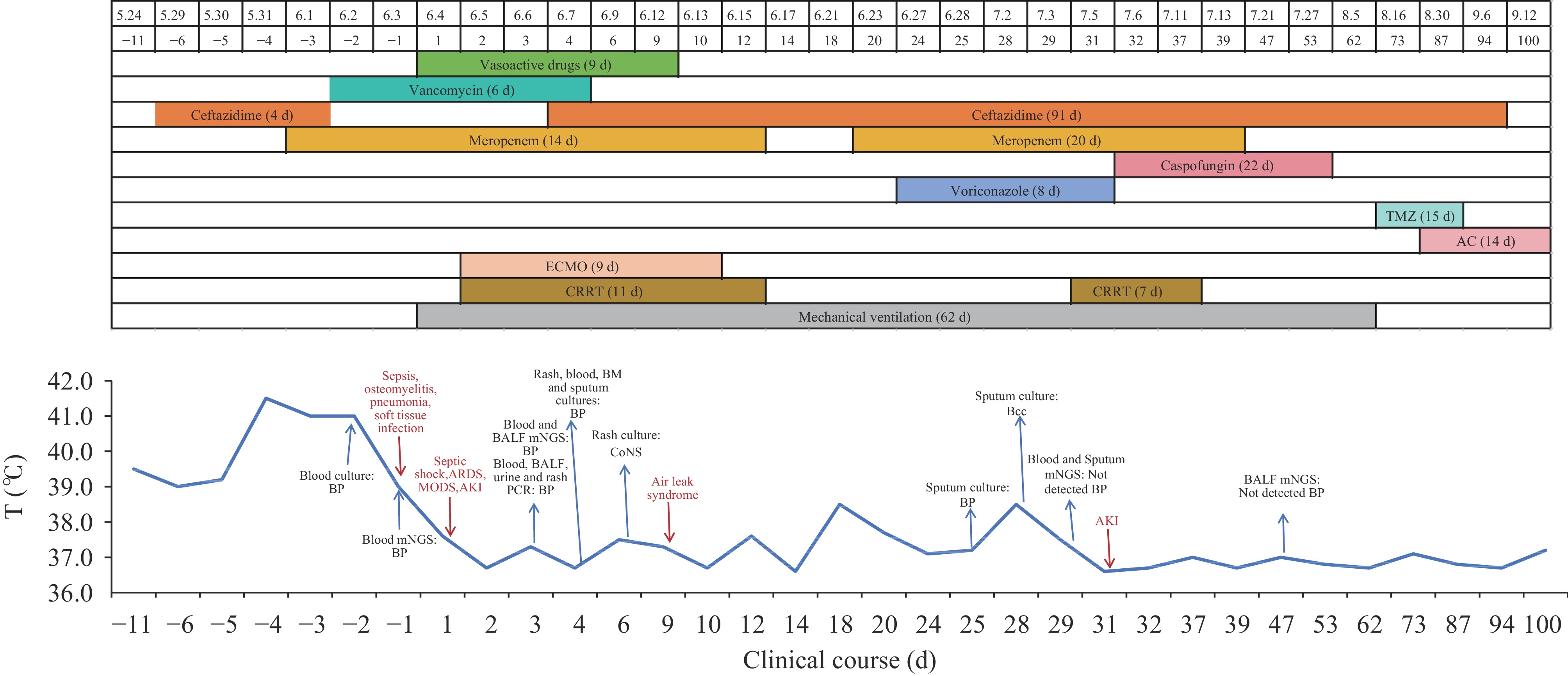
Burkholderia pseudomallei (BP) infection leads to melioidosis, a tropical disease endemic to coastal provinces of southern China. Physicians in non-endemic areas, do not commonly consider this disease as a primary differential diagnosis for febrile patients.
This article discusses a case of melioidosis in Northern China. The patient, who had recently visited a Southeast Asian region with high melioidosis prevalence, fell ill after exposure to contaminated water. The disease progressed quickly and with severity.
Healthcare workers need to remain vigilant regarding travel-related diseases for accurate differential diagnosis and to provide timely and effective treatment, especially for patients with recent travel history or symptoms during travel.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed