2024 Vol. 6, No. 24
Chloropropanols, along with their fatty acid esters and glycidyl fatty acid esters (GEs), are prevalent contaminants in a variety of processed foods, posing potential health risks to humans.
In the Sixth China Total Diet Study (TDS), 3-monochloropropane-1,2-diol esters (3-MCPD esters) and GEs were identified as the predominant chloropropanols and their esters in composite food samples. Vegetables (47.0%) and cereals (15.4%) were the major contributors to exposure among the 12 food categories evaluated.
The Sixth China TDS highlighted concerns regarding potential health risks associated with dietary exposure to GEs. This study underscores the need for further attention in devising practical strategies to mitigate dietary exposure to GEs.
Foodborne diseases present a significant public health concern, particularly in China, where they represent a significant food safety challenge. Currently, there is a need for a thorough and systematic analysis of the extended epidemiological patterns of foodborne diseases in Beijing Municipality.
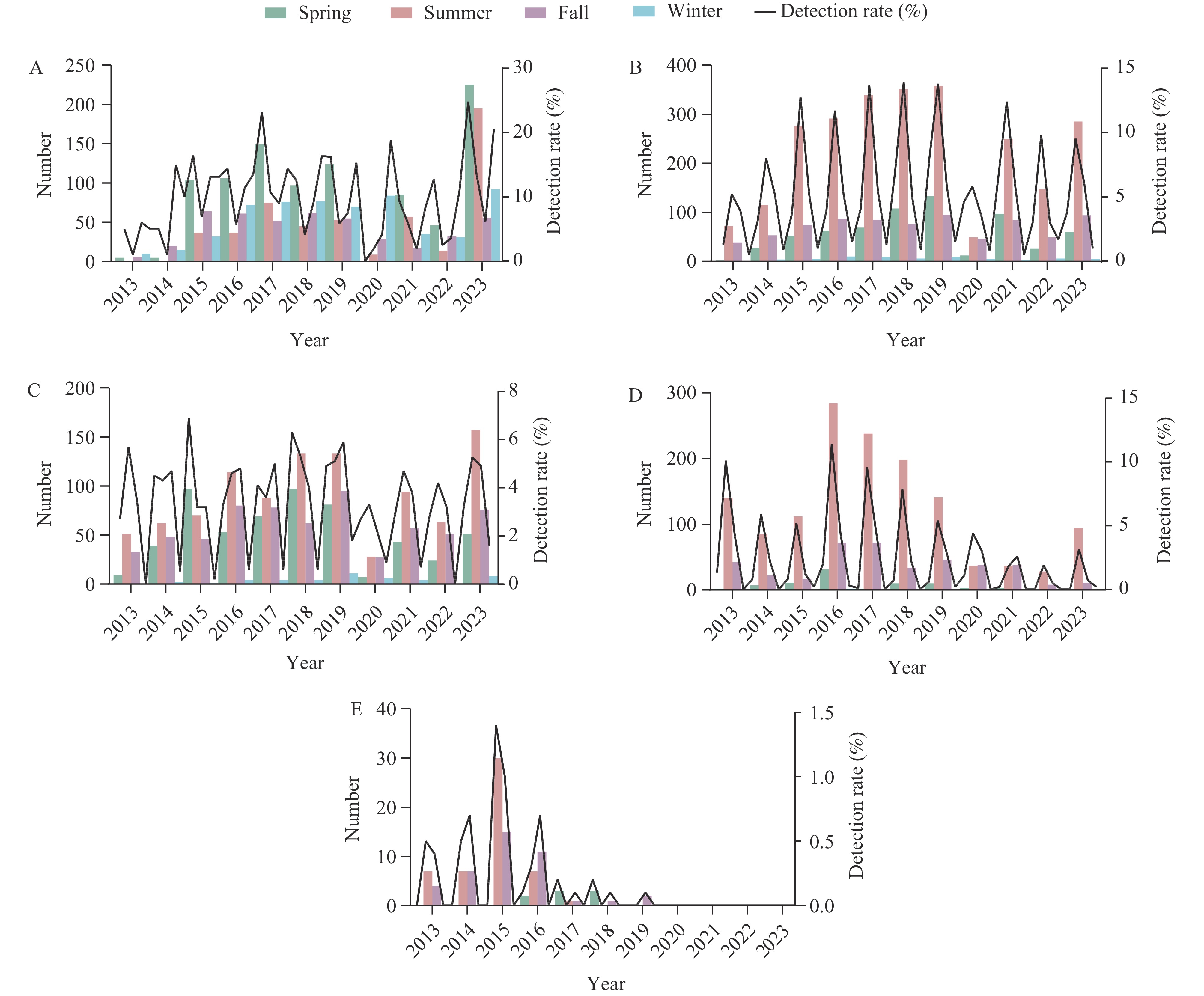
Monitoring results show that Norovirus and diarrheagenic Escherichia coli (DEC) are the most commonly identified foodborne diarrheal pathogens. Individuals aged 19–30 are at a higher risk of foodborne diarrhea in Beijing, with Salmonella infection being associated with fever symptoms.
This study analyzes 11 years of consecutive monitoring data to enhance understanding of the epidemiological and clinical features of foodborne diarrhea in Beijing. It aims to identify high-risk populations, assist in clinical pathogen identification and treatment, and support the development of tailored preventive strategies.
Foodborne diseases, representing significant food safety and public health challenges globally, are not well-documented in terms of incidence, particularly for cases characterized by acute gastroenteritis (AGI) in China.
This study developed a pyramid model to estimate the incidence of five pathogens, stratified by gender and age. The estimated incidences per 100,000 people with 95% uncertainty intervals (UI) are as follows: Norovirus, 3,188.28 (95% UI: 2,518.03, 7,296.96); Salmonella spp., 1,295.59 (95% UI: 1,002.62, 1,573.11); diarrheagenic E. coli (DEC), 782.62 (95% UI: 651.19, 932.05); Vibrio parahaemolyticus, 404.06 (95% UI: 342.19, 468.93); and Shigella spp., 26.73 (95% UI: 21.05, 33.46).
This study elucidates the incidence rates across various gender and age groups, thereby identifying priority populations for targeted preventive interventions aimed at reducing disease burden. These insights are crucial for the development of public health policies and management of food safety risks.
Cordierites frondosus (C. frondosus) is a species of toxic mushroom known to induce symptoms of photosensitive dermatitis.
In the months of May and June 2023, a total of four patients in Chuxiong Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan Province, were affected by C. frondosus poisoning, occurring over two distinct incidents. The condition of two patients deteriorated after they were re-exposed to sunlight on the seventh day following the initial poisoning. Separately, an additional two patients reported experiencing a mild, needle-like sensation on areas of their skin exposed to the sun, recorded on the twelfth day subsequent to the poisoning.
Given that symptoms of photosensitive dermatitis, a potential severe consequence of C. frondosus poisoning, can manifest up to a week post-sun exposure, it is advisable to avoid sunlight for a minimum of two weeks following poisoning.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed