2024 Vol. 6, No. 23
Antimony (Sb) has been identified as a new neurotoxicant that impacts neurological functions in animal studies. However, its effects on the human population remain unknown.
The study reveals that there is an association between exposure to Sb and a higher incidence of cognitive impairment in older adults. The dose-response curve demonstrates that the risk of cognitive impairment consistently increased with higher levels of Sb exposure without a discernible threshold.
Reducing exposure to Sb may have a beneficial effect in delaying or preventing the onset of cognitive impairment. This intervention has the potential to significantly decrease the disease burden associated with cognitive impairment, ultimately contributing to social development.
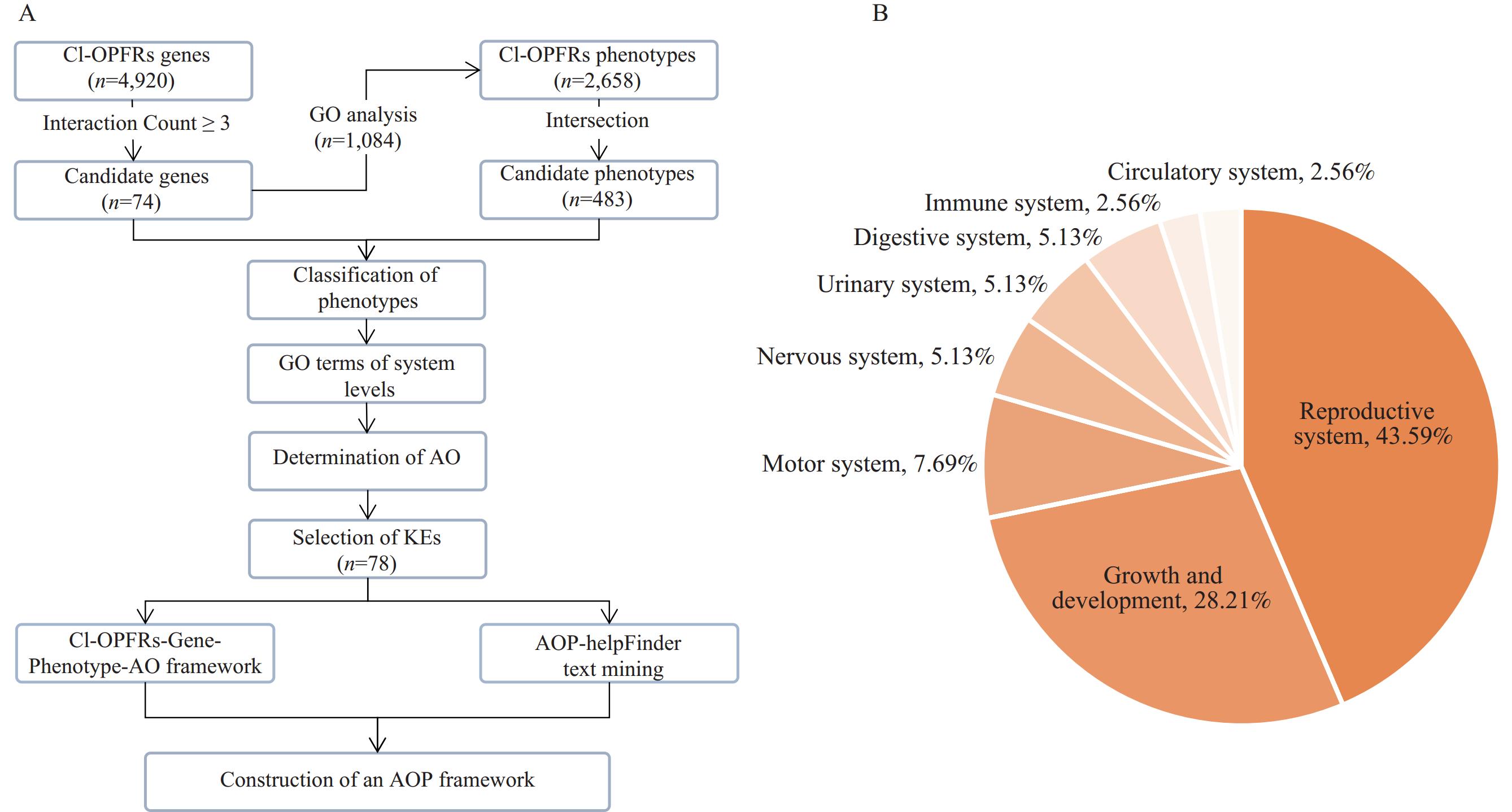
Chlorinated organophosphate flame retardants (Cl-OPFRs) are frequently detected chemicals in the environment and biological samples, yet there is a lack of systematic evaluation regarding the adverse effects and toxicological mechanisms of Cl-OPFRs.
This study utilizes the adverse outcome pathway (AOP) framework to assess the health implications and mechanisms of Cl-OPFRs, identifying multi-system toxicity, with a particular emphasis on reproductive issues and the possible toxic mechanisms.
These results enhance knowledge of the health hazards linked to Cl-OPFRs, supporting the creation of focused risk evaluations and suitable regulatory actions.
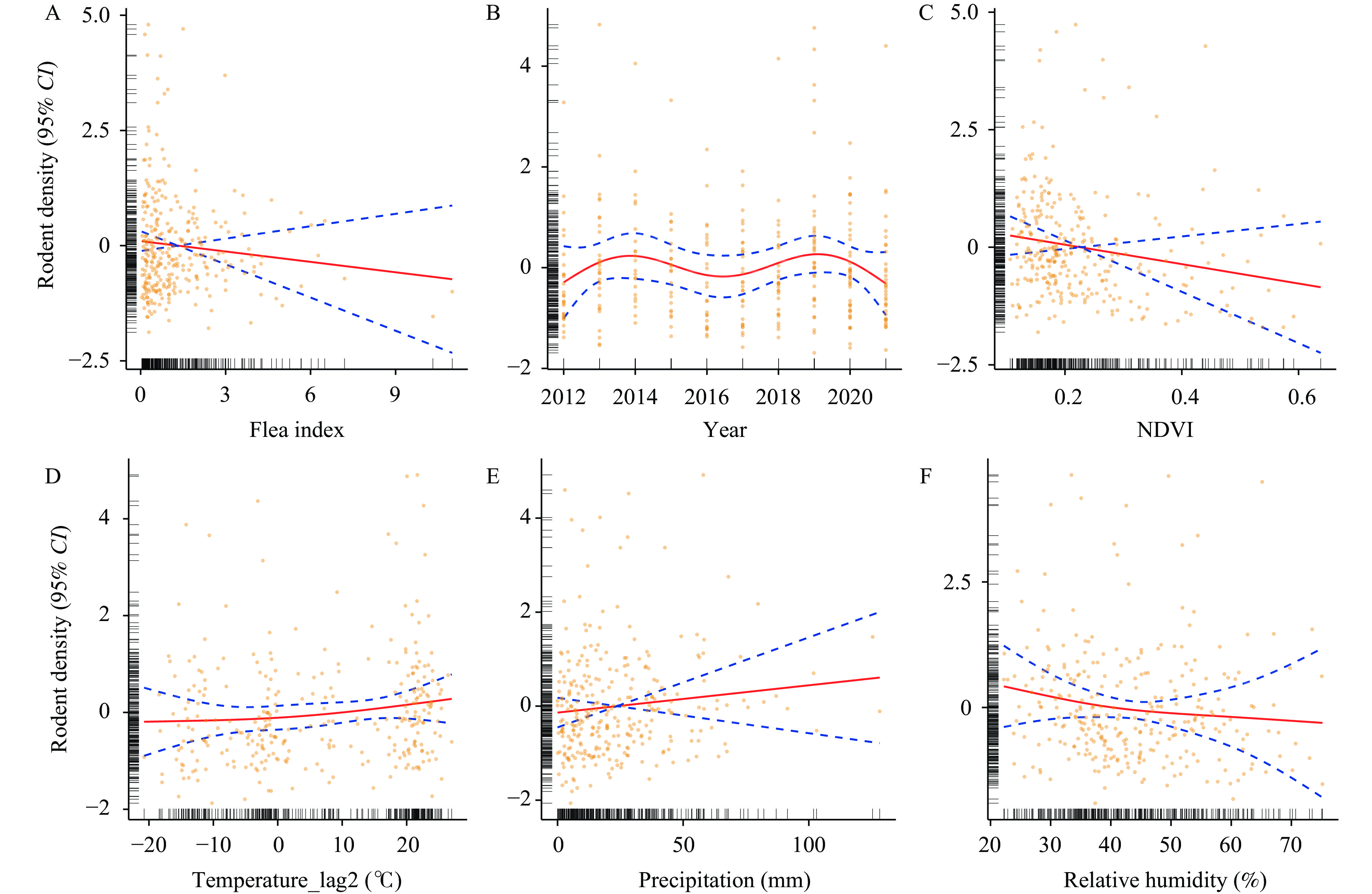
Plague is a significant global infectious disease, its spread is linked to host and flea populations. Meteorological conditions can impact flea populations and host densities, hence influencing plague outbreaks. Investigating the connection between meteorological factors, flea populations, and rodent densities in Inner Mongolia’s natural plague foci can aid in predicting and managing plague outbreaks.
Monthly data on flea index, rodent density, meteorological factors, and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) were collected for the study area. Generalized additive modeling (GAM) was used to analyze the non-linear and lag effects of meteorological factors on flea index and rodent density. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was employed to investigate the relationships among meteorological factors, NDVI, flea index, and rodent density.
GAM analysis revealed that temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, and NDVI had significant linear, non-linear, and time-lagged impacts on the density of Mongolian gerbils and the flea index. SEM analysis indicated that meteorological factors could directly influence the density and flea index of Mongolian gerbils, or indirectly impact NDVI, subsequently influencing gerbil density and the flea index.
Meteorological factors primarily influence gerbil density and flea index indirectly by affecting NDVI and the relationship between flea index and gerbil density. This study offers additional support for the significance of meteorological factors and NDVI in influencing the vector-rodent system, offering valuable insights for predicting and managing plague outbreaks.
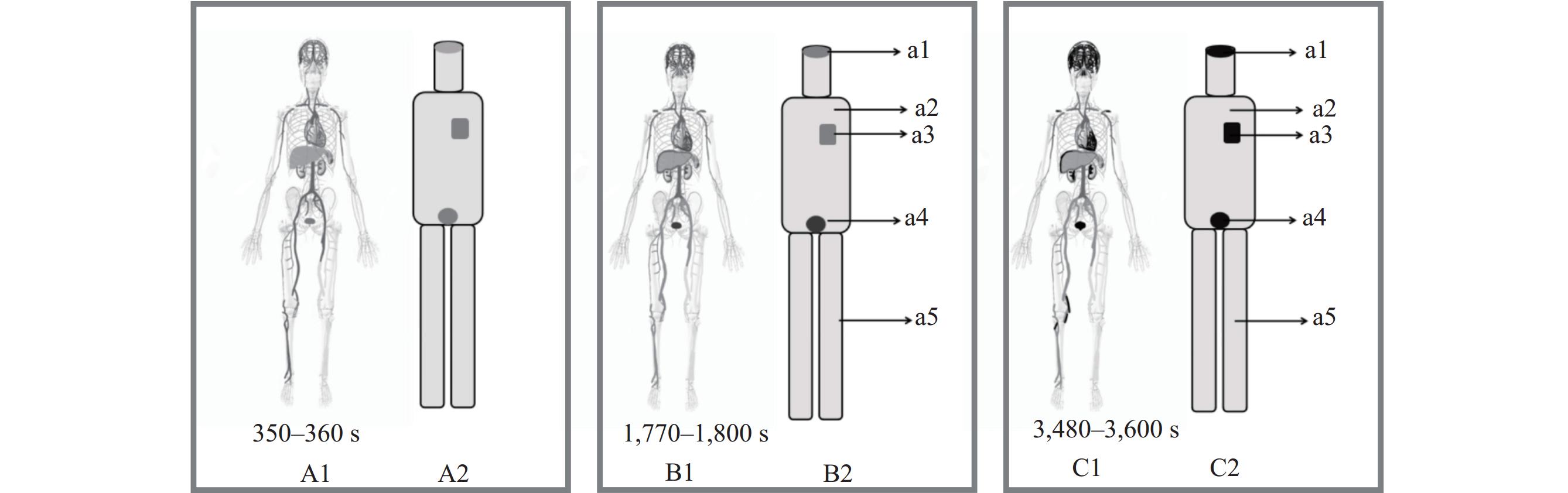
Traditional methods for determining radiation dose in nuclear medicine include the Monte Carlo method, the discrete ordinate method, and the point kernel integration method. This study presents a new mathematical model for predicting the radiation dose rate in the vicinity of nuclear medicine patients.
A new algorithm was created by combining the physical model of “cylinder superposition” of the human body with integral analysis to assess the radiation dose rate in the vicinity of nuclear medicine patients.
The model accurately predicted radiation dose rates within distances of 0.1–3.0 m, with a deviation of less than 11% compared to observed rates. The model demonstrated greater accuracy at shorter distances from the radiation source, with a deviation of only 1.55% from observed values at 0.1 m.
The model proposed in this study effectively represents the spatial and temporal distribution of the radiation field around nuclear medicine patients and demonstrates good agreement with actual measurements. This model has the potential to serve as a radiation dose rate alert system in hospital environments.
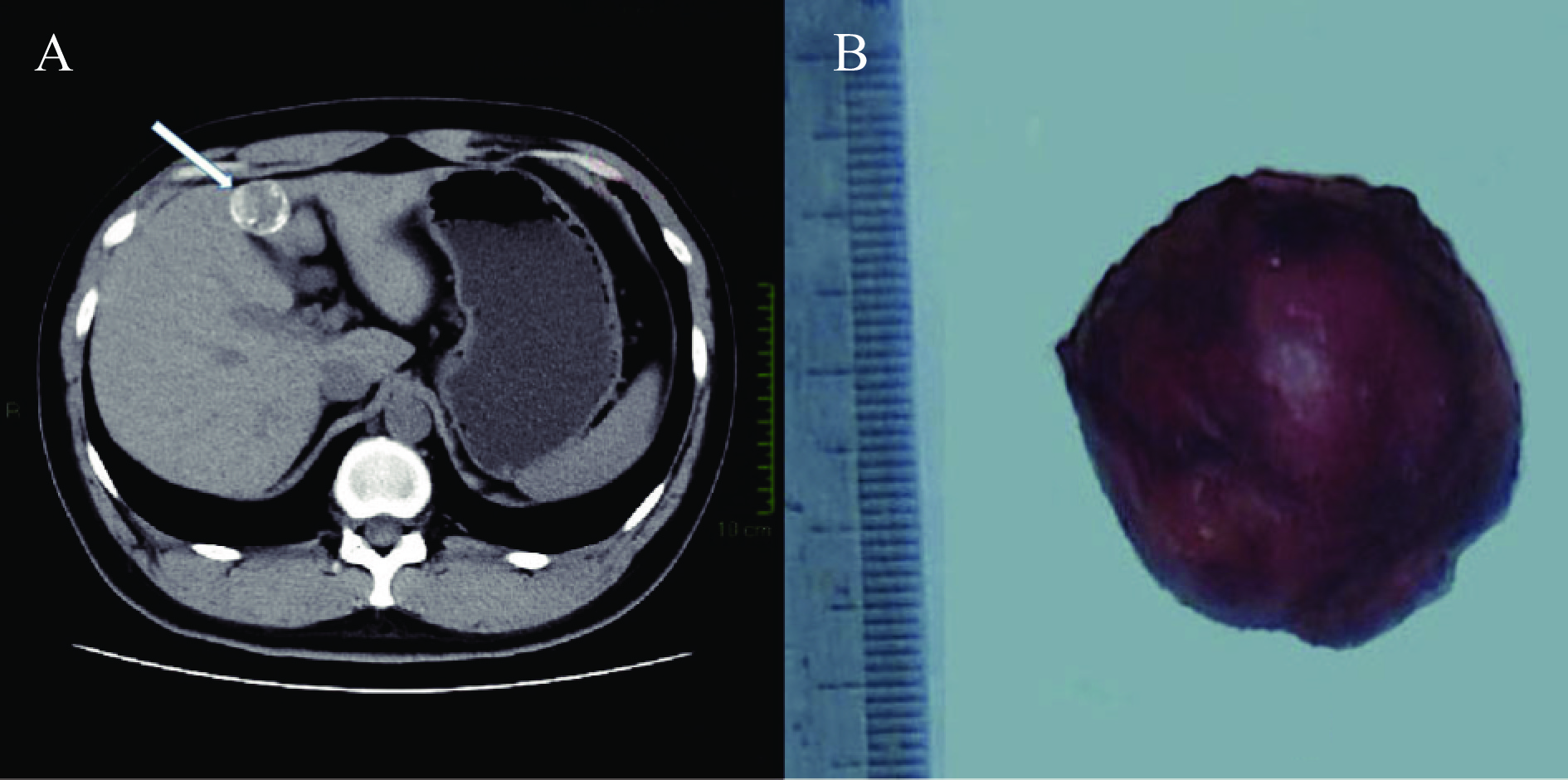
Echinococcosis exhibits a global distribution. In China, the primary endemic area is the northwest region. In December 2023, we documented a case of echinococcosis in an individual lacking any travel or residential history in endemic regions.
This is the first laboratory-confirmed case of hepatic echinococcosis reported in Guangdong Province, associated with the G7 genotype of Echinococcus granulosus (E. granulosus). The most probable mode of transmission is a local infection resulting from E. granulosus introduced from endemic regions.
As the circulation of agricultural products increases, it is essential to enhance the quarantine and management of livestock from epidemic areas to prevent and control the spread of echinococcosis to non-epidemic regions.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed