2025 Vol. 7, No. 50
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination administered before viral exposure (i.e., prior to sexual debut) effectively prevents infection with vaccine-type HPV strains and associated diseases, including cervical cancer. To advance HPV vaccination efforts and cervical cancer prevention, China has incorporated the bivalent HPV vaccine (types 16/18) into its National Immunization Program (NIP) as a program vaccine. This Policy Note presents comprehensive technical and implementation guidelines for HPV vaccine deployment, encompassing guidance development methodology, target population definition, routine vaccination schedules, catch-up vaccination protocols, implementation strategies, vaccine coverage and adverse event monitoring plans, and anticipated implementation challenges with proposed mitigation measures. The Vaccine Technical Working Groups of the China CDC developed relevant technical recommendations and guidelines, which were officially issued in November 2025.
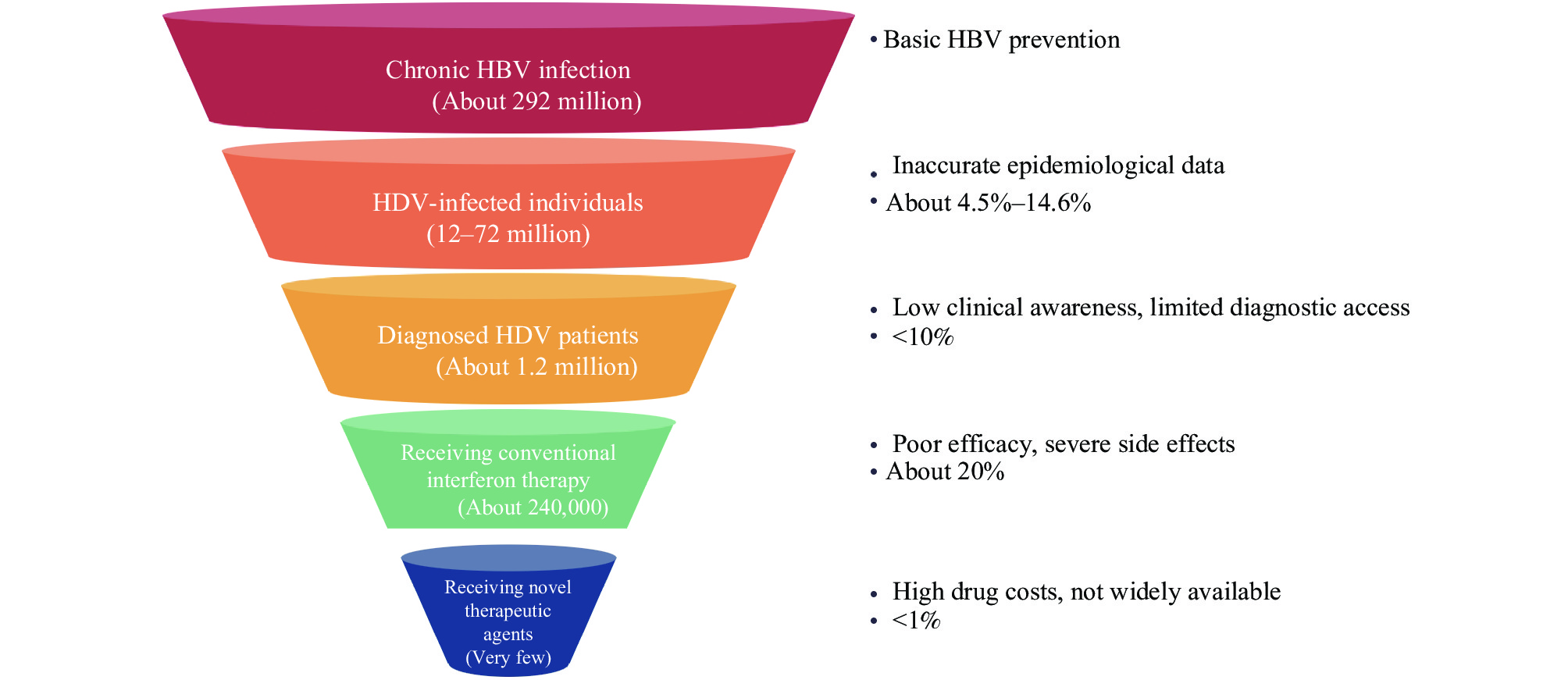
Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a defective virus whose replication depends on hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen (HBsAg). HBV/HDV coinfection represents the most severe form of viral hepatitis, substantially accelerating progression to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. In response to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) 2030 elimination target for viral hepatitis as a major public health threat, HDV elimination has emerged as one of the most formidable challenges, driven by its unique biological characteristics, widespread underdiagnosis, and historical absence of effective therapies. This article reviews key global advances in HDV epidemiology, screening and diagnosis, therapeutic development, and public health strategies. We provide an in-depth analysis of current barriers to elimination and offer strategic insights to guide future control efforts.
The global incidence of herpes zoster (HZ) in the general population is 3–5 cases per 1,000 person-years, with the Asia-Pacific region reporting 3–10 cases per 1,000 person-years. This rate has been rising annually by 2.5%–5.0% and is high among older adults.
In 2024, the China Family Panel Study — covering a nationwide sample of 21,750 adults (≥16 years) across 25 provincial-level administrative divisions and cities (PLADs) in China — identified 813 cases of HZ. Among these 813 patients, 28.78% reported unmet outpatient care needs, and 36.36% had unmet inpatient care needs. The main factors associated with unmet healthcare needs were age and place of residence. Older adults demonstrated significantly low unmet outpatient needs, whereas urban residents experienced higher levels of unmet inpatient needs.
These findings highlight the need to advance equity and effectiveness of healthcare services for HZ patients. Strategic investments in health literacy and workforce development are essential to ensure that provider competencies align with community health needs.
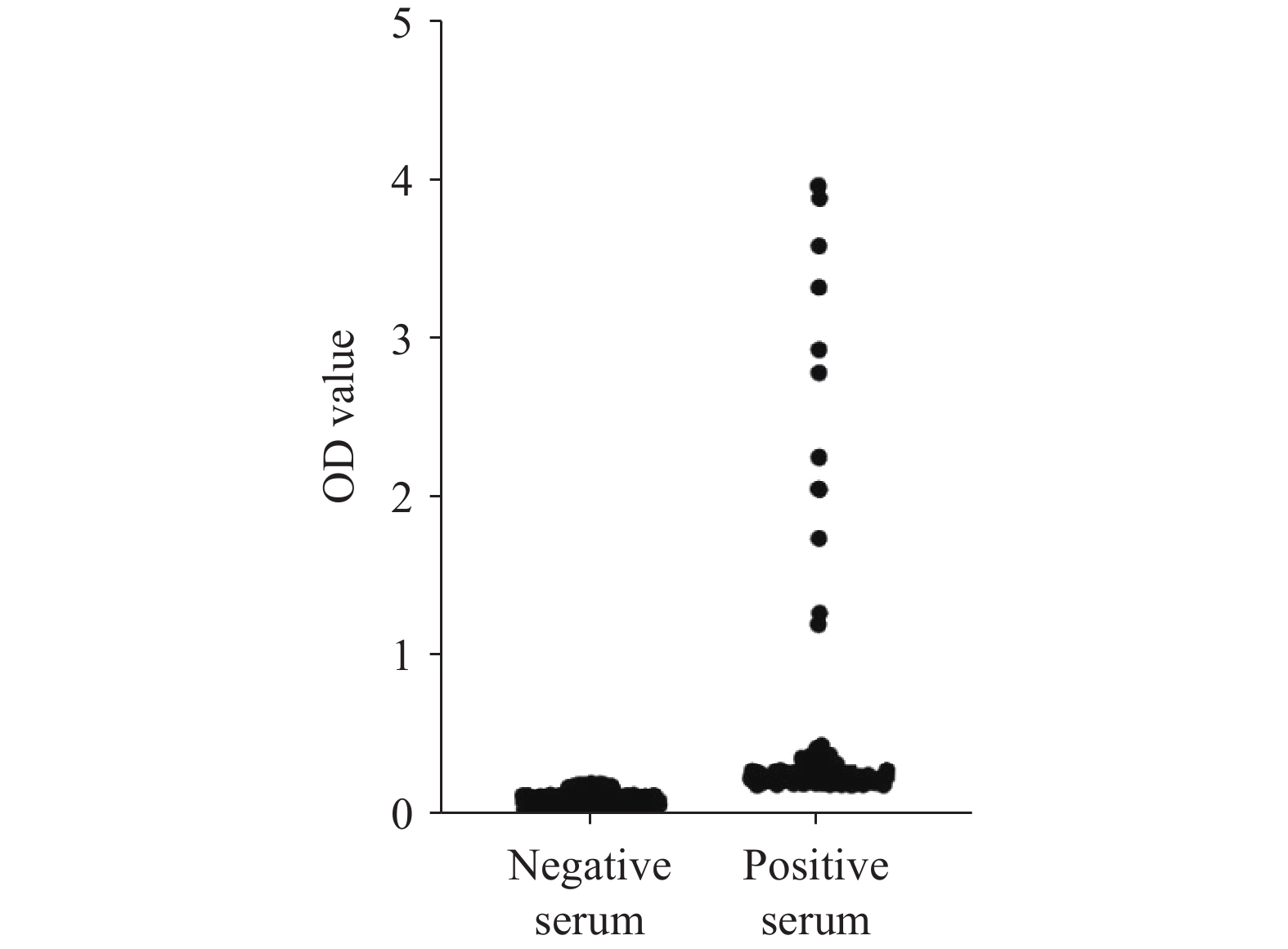
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) is transmitted primarily through rodent excreta, with humans being universally susceptible to infection. Transmission via organ transplantation occurs rarely. The predominantly nonspecific clinical presentation in humans has contributed to LCMV remaining an underrecognized zoonotic pathogen.
This study provides the first serological confirmation of past LCMV infection among the general population in Gansu Province, with seroprevalence rates of 18.31% by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and 1.97% by immunofluorescence analysis (IFA). Priority populations for targeted LCMV prevention and control interventions include rural residents, individuals with lower educational attainment, and agricultural workers.
LCMV clinical manifestations overlap with those of pathogens targeted by national sentinel surveillance systems; LCMV should be incorporated into future screening protocols for unidentified infectious agents.
Measles is a common infectious disease, and the global health community is working to eliminate it. However, recent measles outbreaks in several countries have posed challenges for China, which is close to eliminating the disease.
In Gansu Province, in 2024, the predominant measles virus (MeV) strains were found to be genotype D8, forming two distinct clusters. Notably, mutations within one of these clusters, at a critical diagnostic primer-binding site, could potentially affect the sensitivity of detection methods.
The findings suggest imported virus transmission. Sustaining vaccination programs in key areas and enhancing sensitive virus surveillance are critical for measles elimination efforts.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed