2025 Vol. 7, No. 38
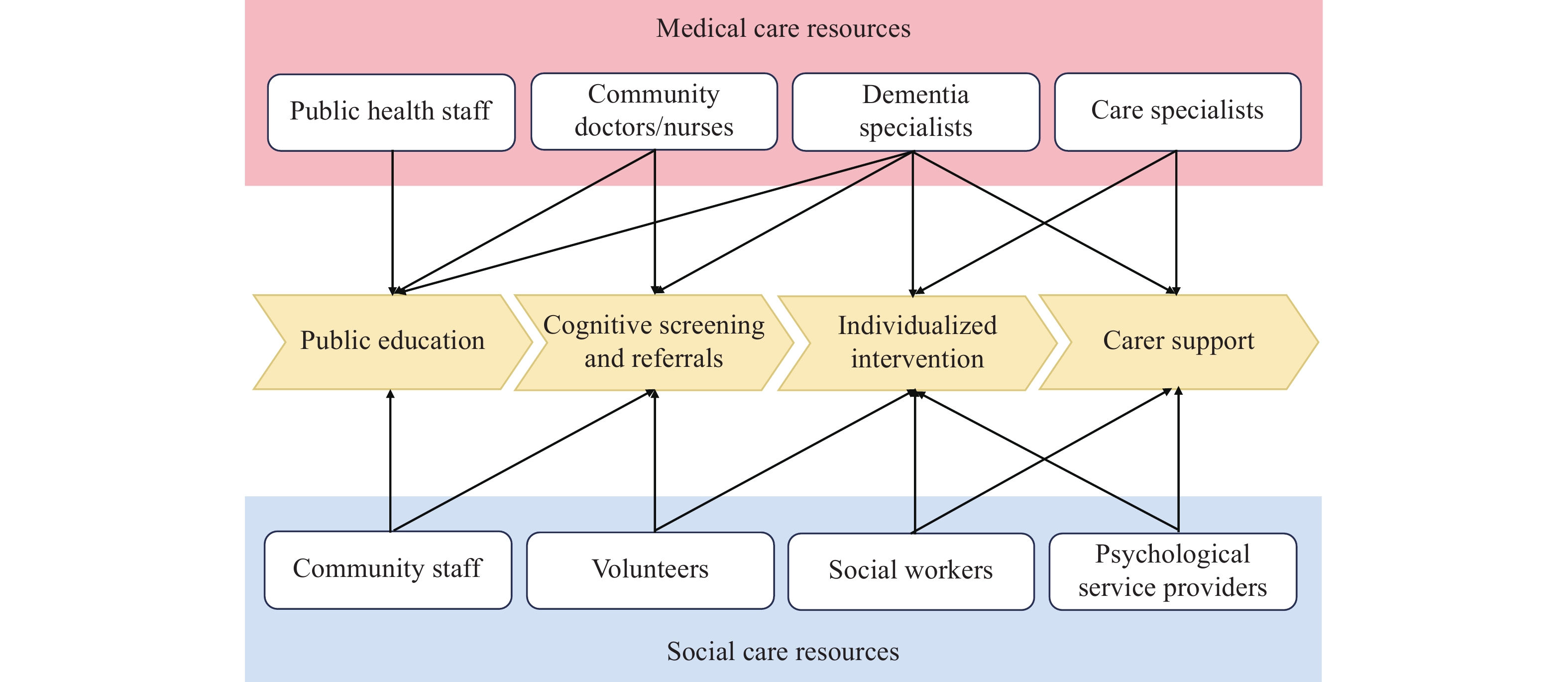
In the context of World Alzheimer’s Month 2025, this perspective article examines the current state of care continuity for people living with dementia in China and identifies critical gaps in this domain. The article further reviews existing global dementia action plans, highlighting the strategic approaches outlined in China’s National Action Plan on Response to Dementia (2024–2030). To transform knowledge into meaningful change, this perspective proposes the 3A approach — Awareness, Attitude, and Action — as a comprehensive guiding framework to strengthen and advance the continuum of care.
Nutrition knowledge (NK) is a key modifiable factor influencing the dietary behavior and nutritional status of children. Currently, nationally representative data assessing NK among Chinese junior high school students are unavailable. This study aimed to assess NK levels using recent, nationally representative data from China.
A multistage stratified random cluster sampling method was used to select 28,629 junior high school students from 195 survey sites across 31 provincial-level administrative divisions in China. Data were collected using a standardized questionnaire developed using rigorous scientific procedures. NK awareness rates were described as weighted prevalence rates with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Subgroup comparisons were performed using the Rao–Scott chi-square test.
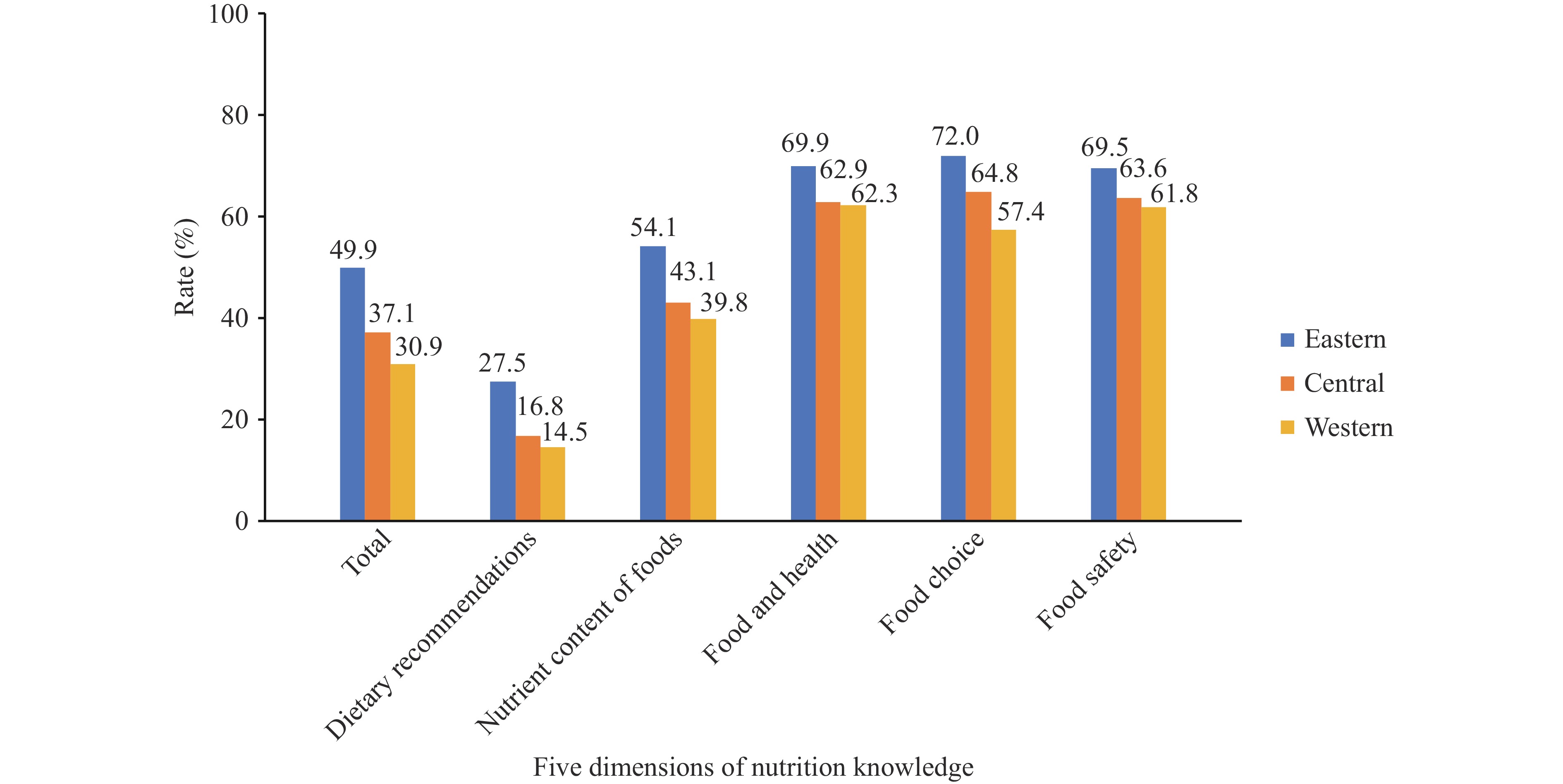
The overall NK awareness rate among Chinese junior high school students was 40.0% (95% CI: 36.5%–43.5%). The rates for the five dimensions, dietary recommendations, nutrient content of foods, food and health, food choices, and food safety, were 20.1%, 46.2%, 65.3%, 65.2%, and 65.2%, respectively. The analysis revealed significant variations in overall and dimension-specific awareness rates across groups. Boys, students from rural and western regions, and students from families with lower socioeconomic status had poorer NK levels than their counterparts. Among the 10 knowledge points with the lowest correct rates, seven belonged to dietary recommendations, two to food safety, and one to food and health.
NK awareness rates among junior high school students require improvement, especially regarding dietary recommendations, which remain a key component of students’ nutrition education. Boys, students from rural and western regions, and students from families with lower socioeconomic status should be the key populations for NK dissemination in the future.
Training laypersons can increase cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) attempts by bystanders by improving their intention to perform CPR. However, the association between curriculum content and post-training intention to perform CPR remains unclear.
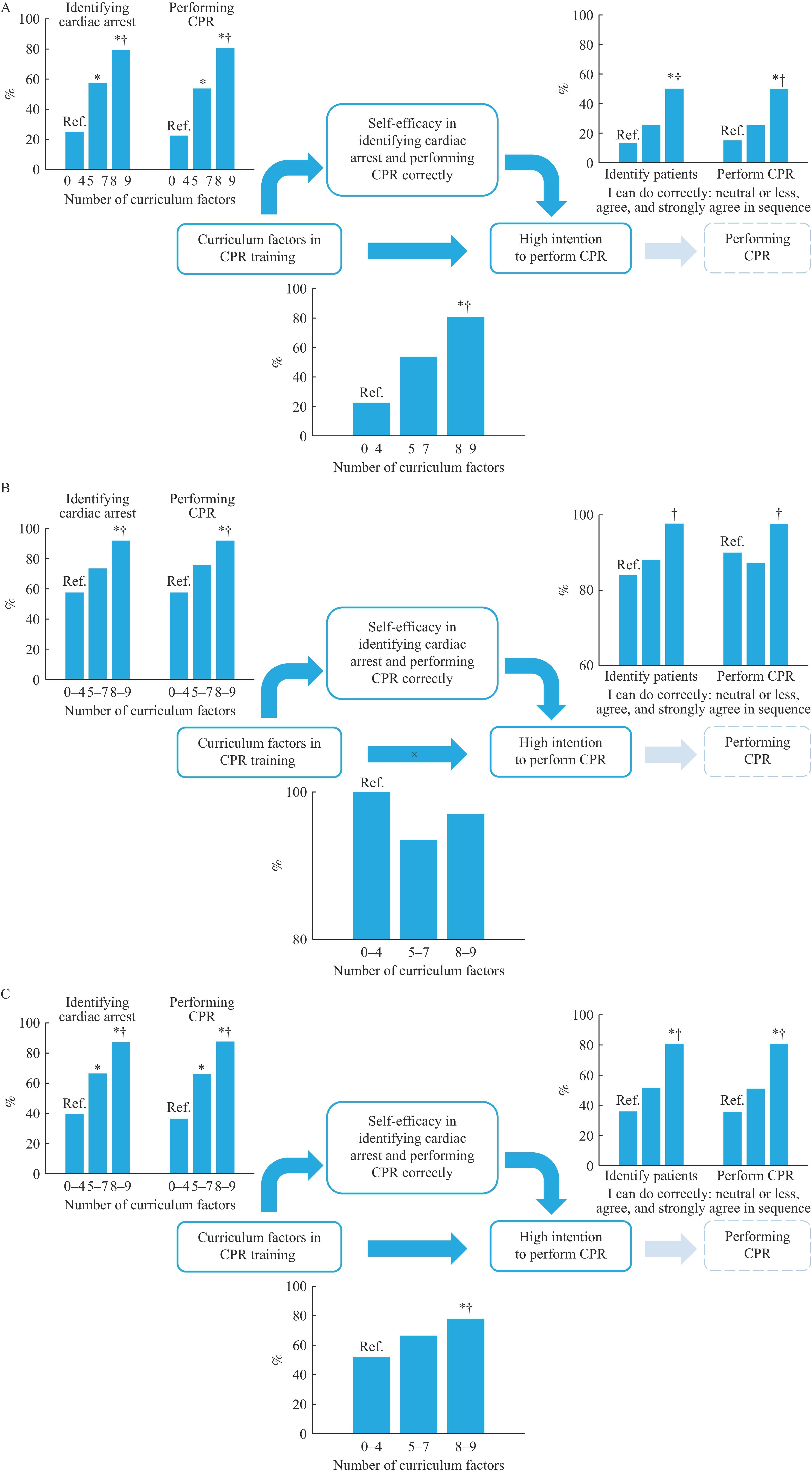
Key curriculum factors in CPR training can effectively improve laypersons’ intention to perform CPR following training, and 74.7% of the laypersons enrolled in the training programs reported high CPR intention following training. In the low-intention laypersons, relative to the presence of zero to four factors, the coexistence of five to seven factors and eight or nine factors were associated with 174.7% [rate ratio (RR)=2.747; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.964–7.826] and 283.6% (RR=3.836; 95% CI: 1.493–9.857) increase in high-intention incidence, respectively. A dose–response relationship was found in an indirect pathway in high-intention laypersons before training. However, the overall proportion of participants exposed to all nine curriculum factors was only 57.7%.
The translation of training into high post-course intention remains suboptimal in China. Identifying and improving curriculum factors linked to CPR intention would increase the prevalence of layperson interventions in China, especially factors that can increase trainees’ self-efficacy in recognizing cardiac arrest and performing CPR correctly.
Dengue fever represents one of the most prevalent viral infections annually affecting the general population in endemic regions. It is widely recognized as an acute self-limiting disease, with the virus typically being completely cleared within 2–3 weeks post-infection, without establishing long-term latency. The current consensus is that primary infection with a specific serotype confers lifelong type-specific immunity, thereby preventing reinfection with an identical dengue virus serotype.
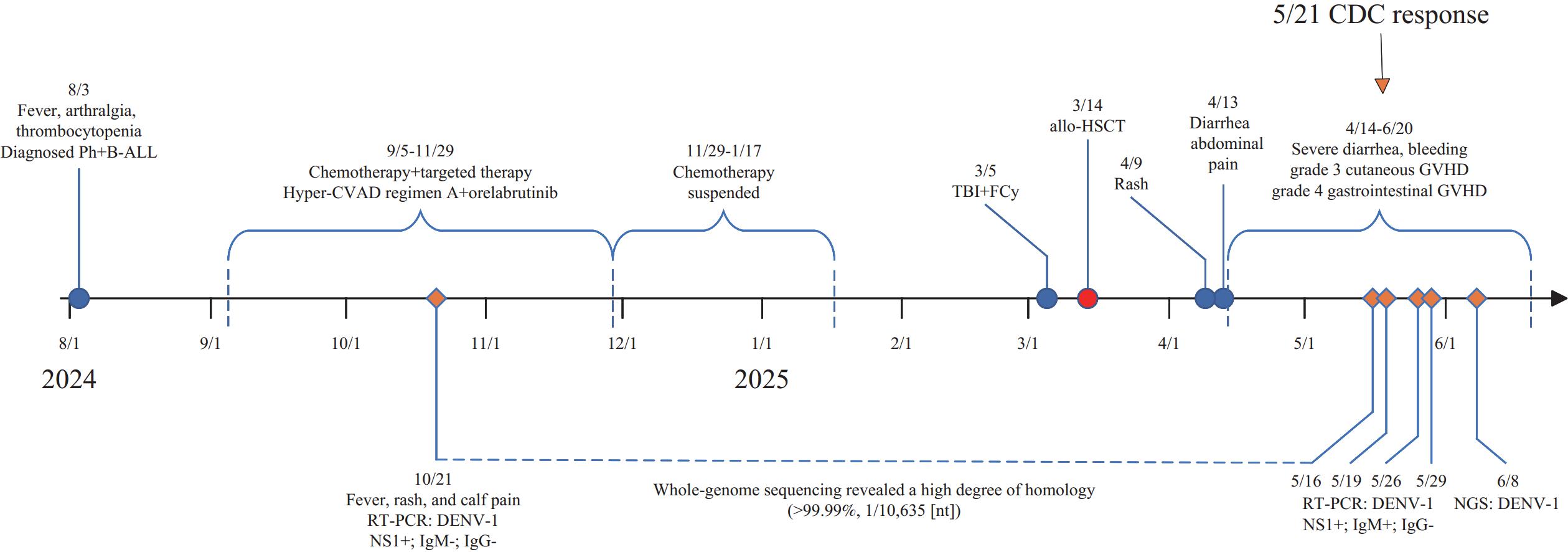
We report the case of a patient with leukemia who developed a confirmed dengue virus serotype 1 (DENV-1) infection during chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Notably, 6 months after the resolution of the initial infection, the same patient tested positive again for DENV-1 nucleic acid while undergoing intensive immunosuppression following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
For patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and receiving immunosuppressive therapy, clinicians should be vigilant about the potential for persistent dengue infection, particularly in dengue-endemic regions. Furthermore, implementing prolonged serological monitoring post-infection is also crucial for the clinical management of this patient population.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed