2025 Vol. 7, No. 31
The first week of August marks World Breastfeeding Week. It provides a valuable opportunity to review progress in breastfeeding initiatives, analyze the enabling environment for breastfeeding support, and propose targeted actions to protect, promote, and support breastfeeding practices.
Smartphones have consistently served as the primary device for internet access among younger populations. Recent research demonstrates that more than 25% of Chinese adolescents experience smartphone addiction. This study aims to examine the association between family upbringing environment and Mobile Phone Dependence Syndrome (MPDS) among middle school students in Guangzhou.
This study demonstrates that middle school students whose fathers had educational attainment levels of junior high school [odds ratio (OR)=0.39, 95% confidence interval (95% CI): 0.17–0.90], senior high school, junior college, technical secondary school, or vocational university (OR=0.28, 95% CI: 0.12–0.67), or a bachelor’s degree and above (OR=0.34, 95% CI: 0.12–0.92) may function as a protective factor against MPDS among adolescents. Additionally, students whose fathers employed an authoritarian parenting style (OR=1.98, 95% CI: 1.22–3.21) are also associated with middle school students’ MPDS.
These findings indicate that democratic parenting approaches and higher educational attainment among fathers play essential roles in mitigating adolescent MPDS, providing valuable guidance for developing evidence-based strategies and interventions aimed at promoting adolescent physical and mental health.
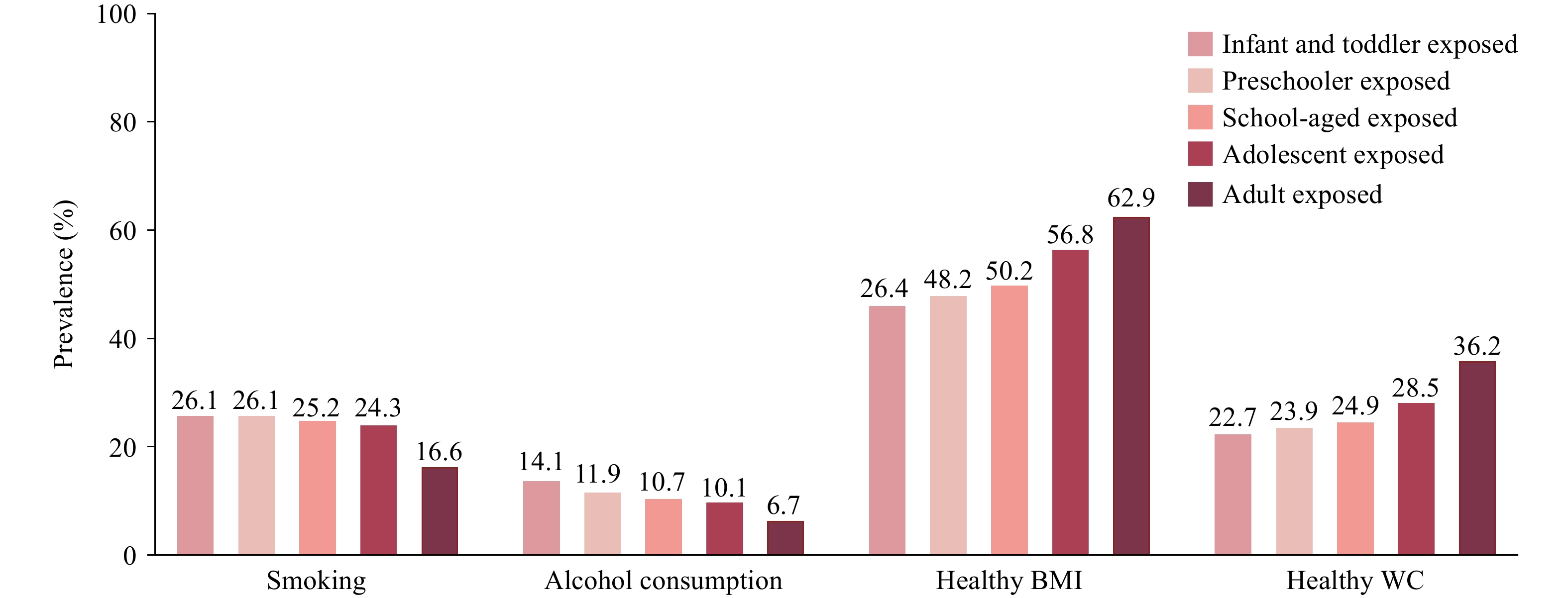
Early-life malnutrition influences lifestyle behaviors and health outcomes, particularly in vulnerable populations, such as elderly hypertensive populations.
This study revealed that malnutrition among infant and toddler exposed, preschool exposed, school-aged child exposed, and adolescent exposed groups was associated with increased smoking and drinking behaviors and a lower likelihood of maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding central obesity.
Public health interventions should target elderly individuals exposed to early-life malnutrition to address long-term risks and mitigate the health impacts of food scarcity and natural disasters.
Chronic diseases and multimorbidity impose substantial burdens on healthcare systems globally, particularly in aging populations, resulting in elevated healthcare utilization rates and increased expenditures.
This study validates previous research findings using an extensive administrative database from a major city in South China. Additionally, it provides comprehensive estimates of annual hospitalization expenditures per patient associated with chronic diseases and multimorbidity patterns among older adults, elucidating the economic burden and cost variations across specific diseases and multimorbidity combinations. Cancer, cerebrovascular disease (CVD), and heart disease — whether occurring individually or in conjunction with other chronic conditions, particularly within complex multimorbidity patterns — were associated with substantial annual hospitalization expenditures and significant healthcare resource utilization.
Disease burden studies provide critical evidence for prioritizing public health policies and targeted interventions. Policymakers should implement comprehensive prevention strategies, evidence-based interventions, appropriate reimbursement policies, and integrated management approaches to control disease progression and reduce healthcare expenditures.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed