2025 Vol. 7, No. 30
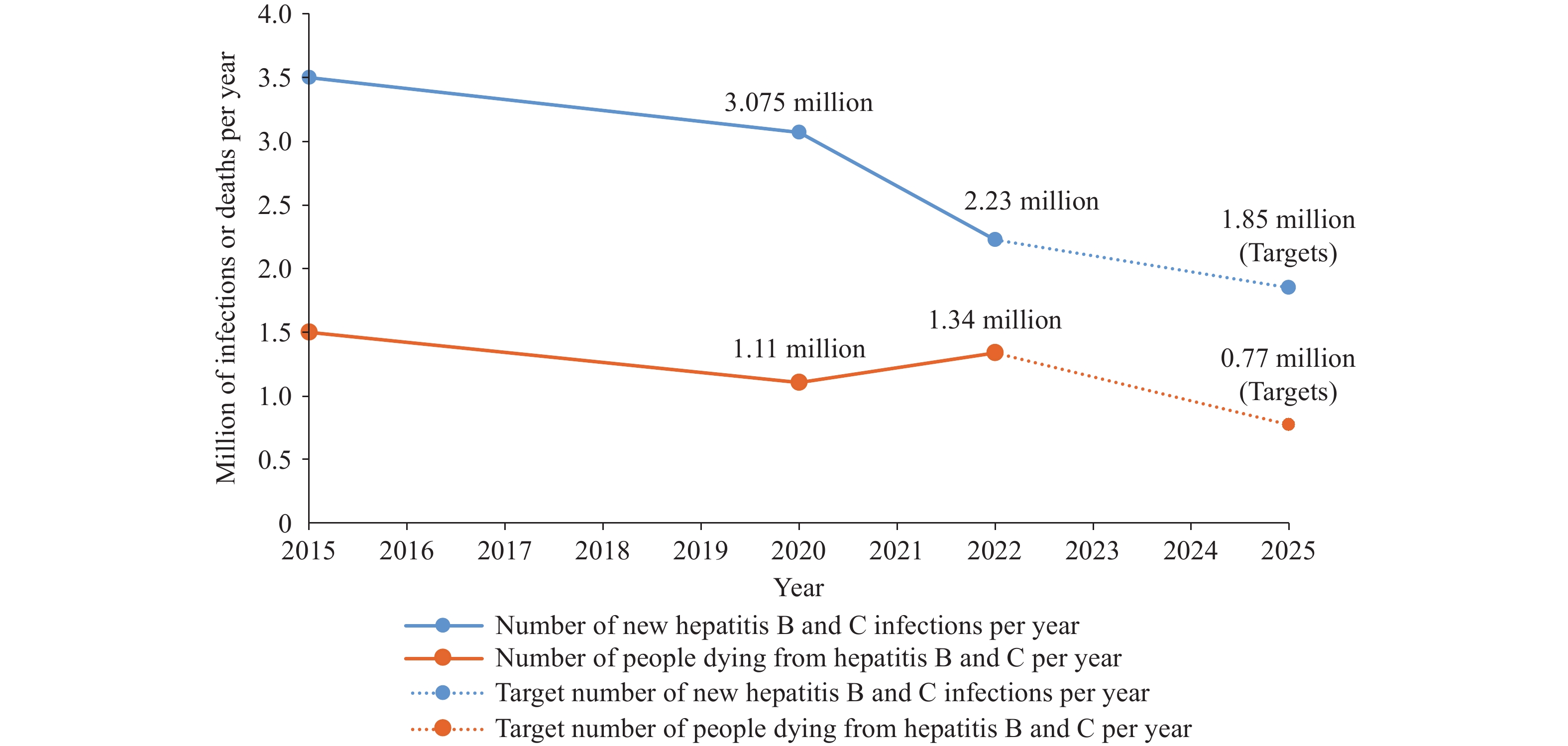
The year 2025 marks the 15th anniversary of World Hepatitis Day, a milestone that has witnessed remarkable progress in global viral hepatitis prevention and treatment. This article systematically examines the establishment and evolution of World Hepatitis Day, emphasizing the latest achievements in hepatitis control through 2025. Current data demonstrate that global hepatitis B vaccine coverage has surpassed the 90% target, while a cumulative 12,748,000 hepatitis C patients received direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) treatment from 2014 to 2023. Despite these advances, persistent challenges, including suboptimal diagnosis rates and pronounced regional disparities continue to impede progress toward the 2030 elimination objectives. Drawing from the most recent epidemiological data, this article presents targeted recommendations to accelerate global elimination efforts.
Current strategies for chronic viral hepatitis prevention and control include immunization, prevention of mother-to-child transmission, expanded testing, antiviral therapy, and national drug price negotiations. To advance high-quality, integrated prevention and treatment services, a decentralized service delivery approach may be beneficial.
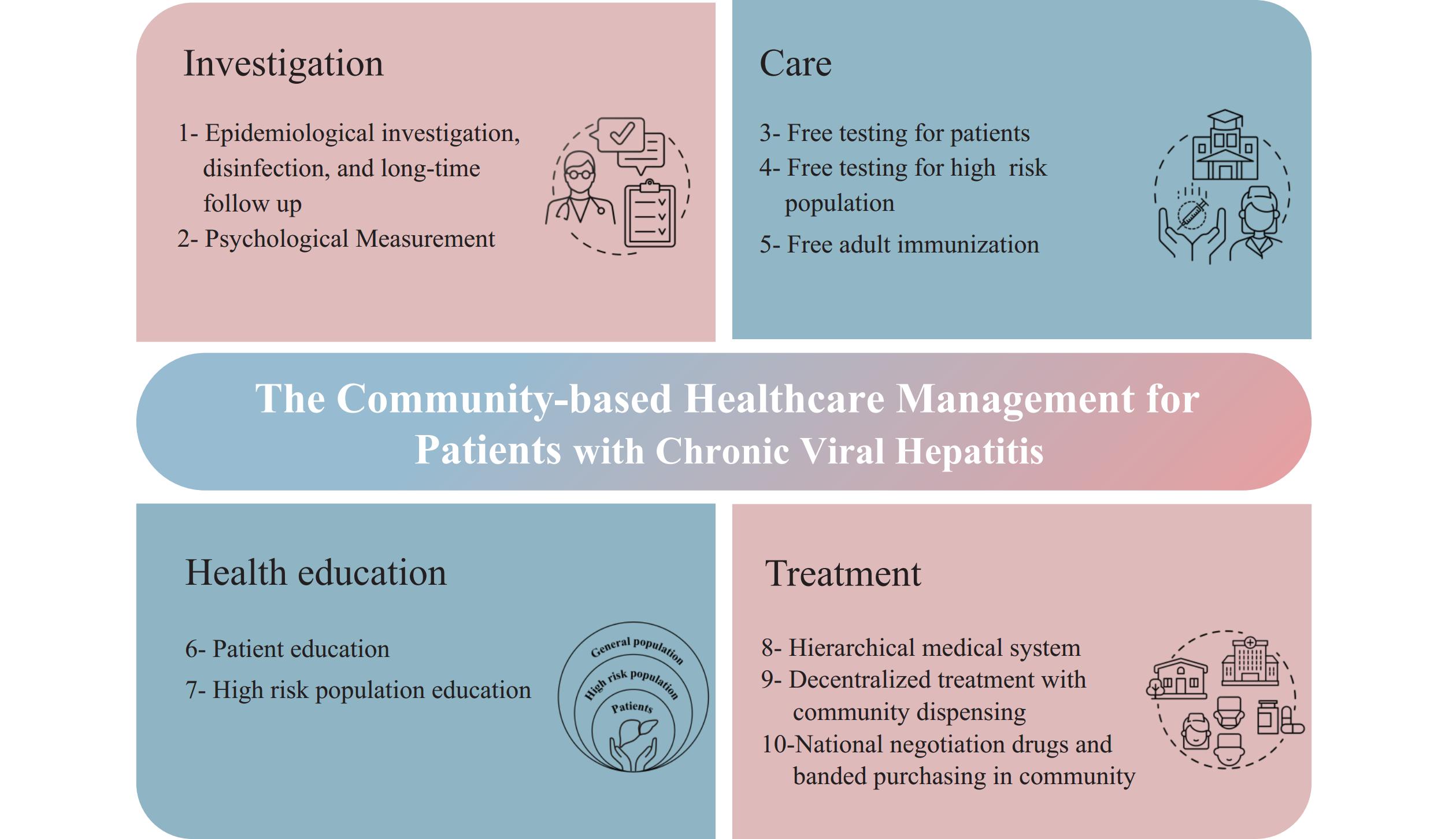
The chronic viral hepatitis community-based healthcare management program in Shanghai delivered comprehensive service packages across 4 categories encompassing 10 distinct interventions, including epidemiological investigation, health education, free testing, community dispensing services, and immunization to family caregivers. The enrolled patients increased substantially from baseline, and antiviral treatment utilization rates reached 64.5% and 58.2% in 2019 and 2023 from 24.5% in 2012. Concurrently, abnormality rates for hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid (HBV DNA), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), total bilirubin (TBIL), and hepatic fibrosis indices decreased significantly. The 2023 aMAP score demonstrated a significant reduction in hepatocellular carcinoma risk among patients under management. Additionally, community dispensing services were accessed by 14.1% (2019) and 18.2% (2023) of enrolled patients.
The community-based healthcare management program could effectively decentralize hepatitis-related testing and treatment services, and create a favorable environment for the viral hepatitis elimination efforts.
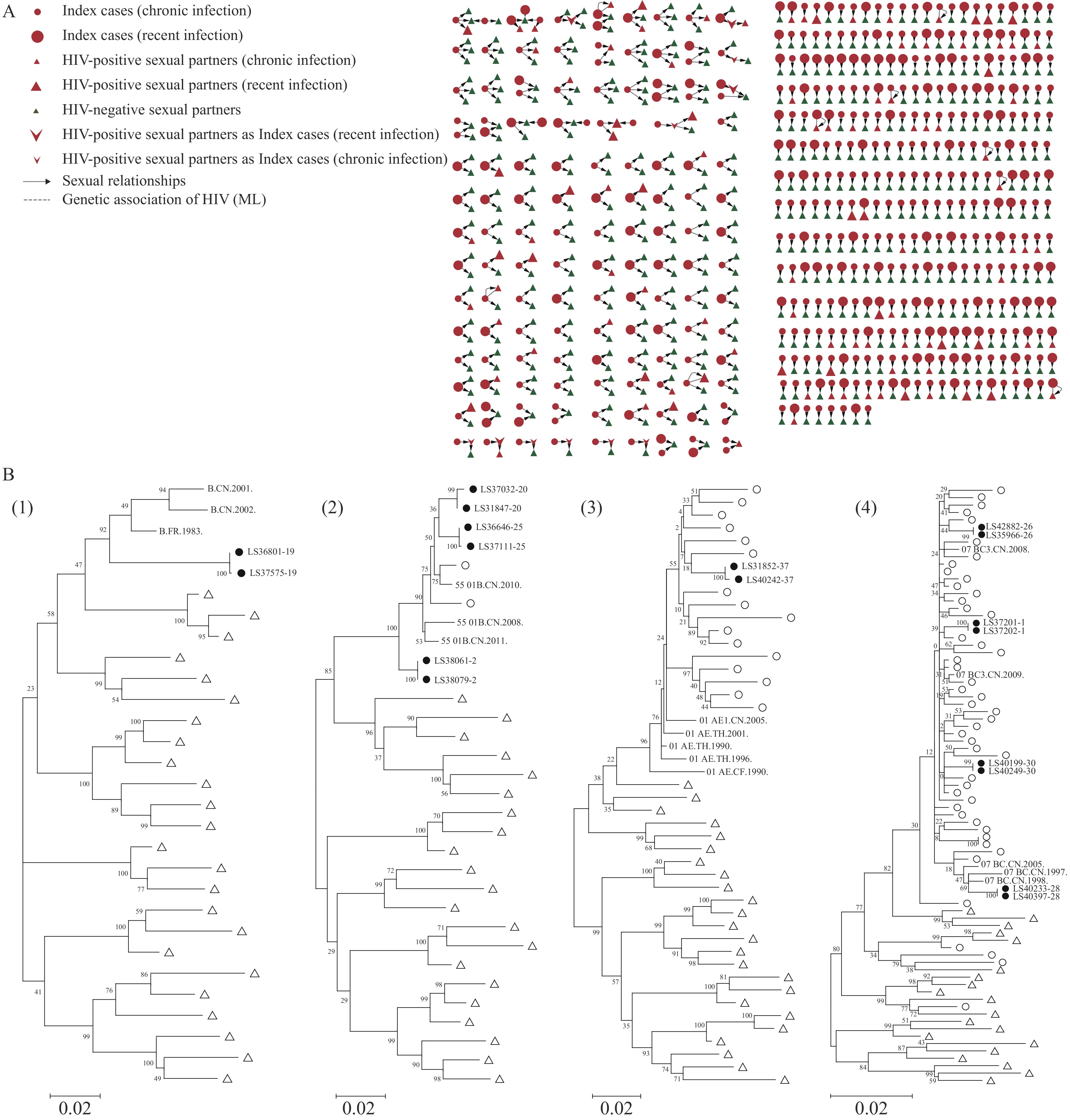
Partner tracing (PT) represents an established public health strategy for identifying undiagnosed individuals with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and contributes to controlling sustained HIV transmission.
Partner tracing among newly diagnosed HIV-infected men who have sex with men (MSM) demonstrates effectiveness in identifying undiagnosed infected individuals, with regular sexual partners showing higher likelihood of HIV-positive detection. However, phylogenetic analysis revealed that only a small proportion of epidemiologically linked pairs exhibited genetic linkage.
Sustained implementation and broader application of partner tracing may serve a critical role in HIV epidemic control by facilitating early identification of undiagnosed infections and interrupting potential transmission chains. Integrating partner tracing with phylogenetic analysis enhances the capacity to distinguish actual transmission chains from coincidental behavioral associations, thereby improving transmission linkage identification accuracy and informing more targeted intervention strategies.
Zika virus (ZIKV) is transmitted primarily through mosquito vectors, including Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti, both of which are distributed across multiple provinces in China. Approximately 80% of ZIKV infections remain asymptomatic, while symptomatic cases typically manifest as mild, self-limiting illnesses lacking pathognomonic features. Common clinical presentations include maculopapular rash, low-grade fever, conjunctivitis, arthralgia, and myalgia.
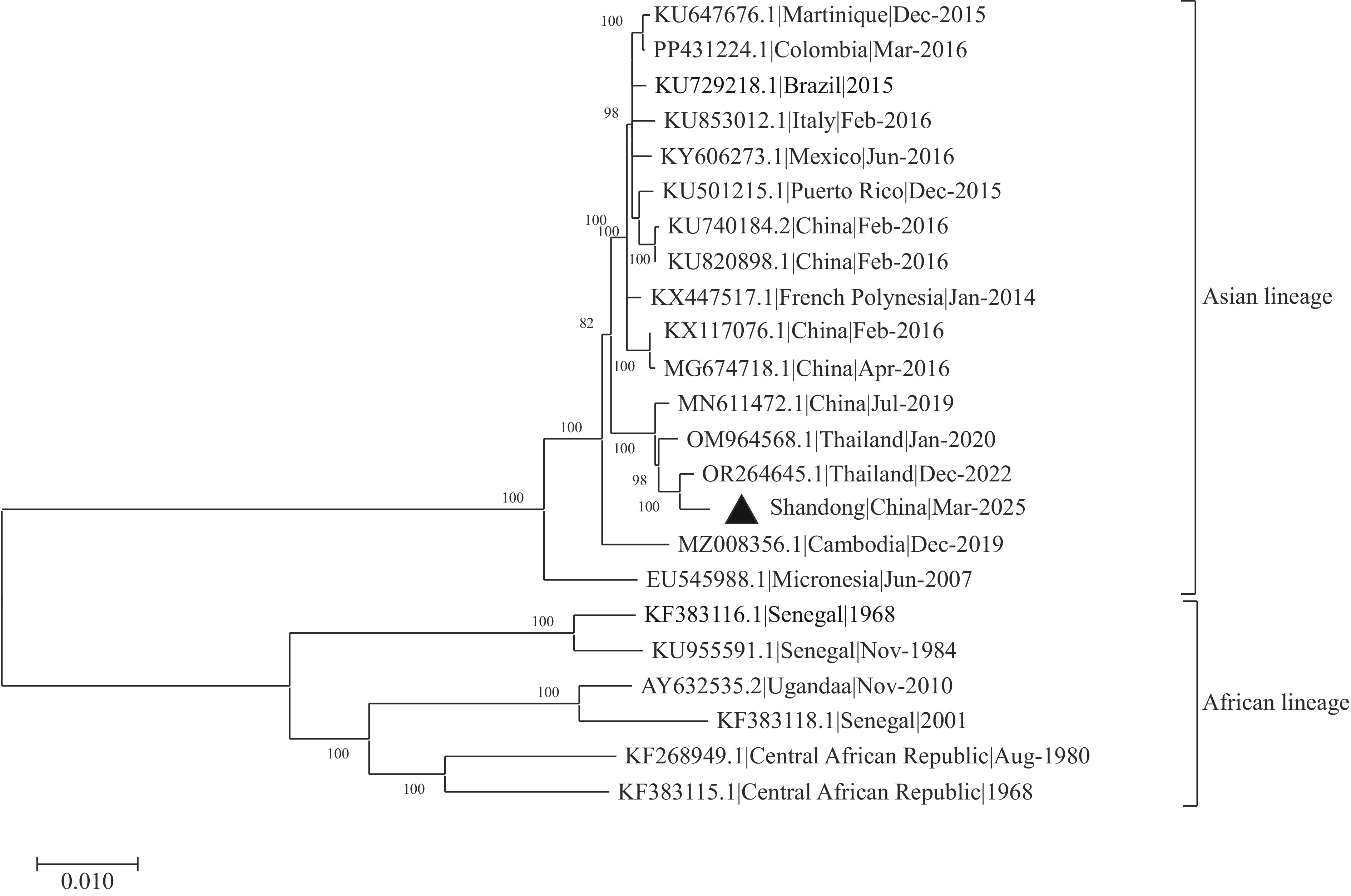
The clinical manifestations of ZIKV infection are nonspecific and may closely mimic other febrile illnesses, complicating differential diagnosis. This study documents the first laboratory-confirmed ZIKV infection case in Shandong Province. The patient exhibited fever accompanied by extensive subcutaneous petechiae, predominantly distributed across the chest and upper extremities.
This investigation provides a comprehensive epidemiological analysis and phylogenetic characterization of a ZIKV infection case imported from Thailand. In accordance with China’s Border Health and Quarantine Law, international port cities must strengthen surveillance and diagnostic testing for imported infectious diseases. For cases presenting with unclear diagnoses, healthcare providers should prioritize obtaining detailed 30-day travel histories to evaluate potential exposure risks of imported infectious diseases.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed