2025 Vol. 7, No. 27
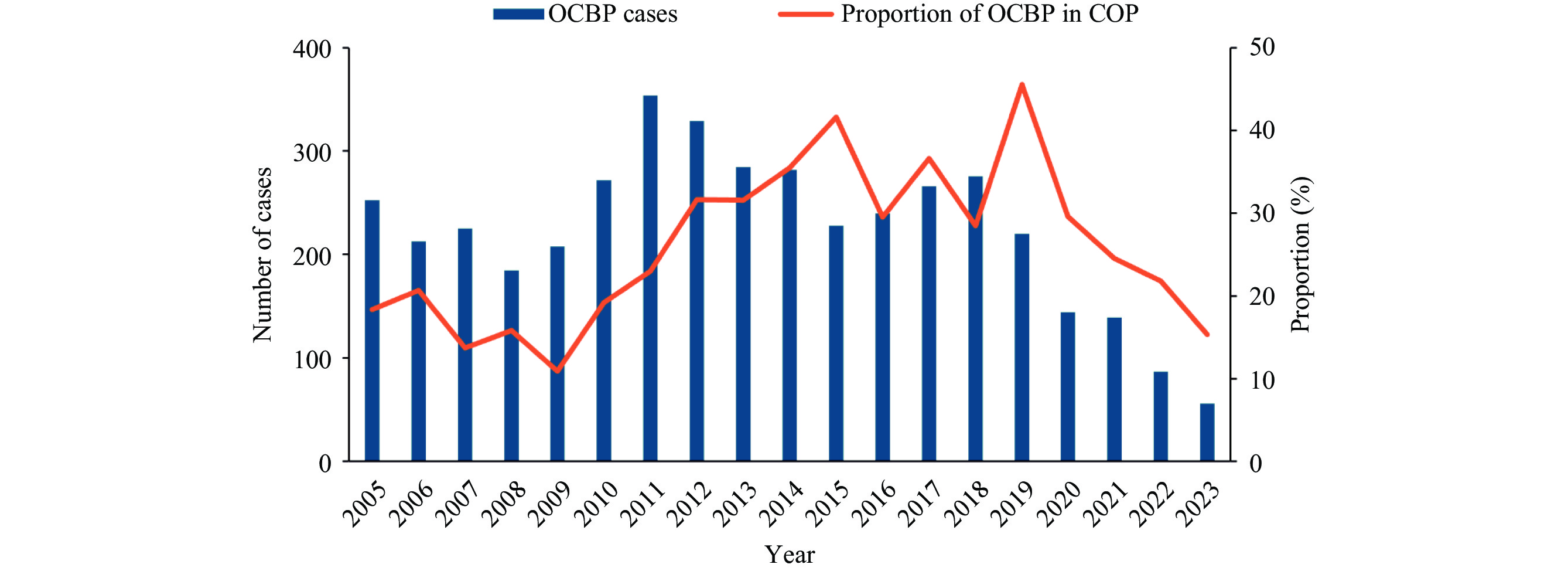
As a major producer and consumer of benzene, China has long confronted the challenge of occupational chronic benzene poisoning (OCBP). Between 2005 and 2019, OCBP in China primarily occurred in private enterprises, small- and medium-sized enterprises, and the general/special-purpose equipment manufacturing industry. However, with the continuous strengthening of national supervision and restrictions on the use of benzene-containing materials, the industrial distribution of OCBP may have changed from 2020 to 2023.
A total of 6 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) with concentrated benzene-related industries — Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shandong, Sichuan, Fujian, and Tianjin — were selected for analysis. We collected data on 162 newly reported OCBP cases from 2020 to 2023. Based on the National Economic Industry Classification standards, we analyzed these cases according to enterprise size, economic type, and industry classification.
The number of OCBP cases in China decreased significantly, reaching a historical low of 56 cases in 2023 [accounting for 15.3% of chronic occupational poisoning (COP)], compared to an average of 256 cases annually from 2005 to 2019 (26.7% of COP). From 2020 to 2023, OCBP continued to occur predominantly in manufacturing, private, and small- and medium-sized enterprises. However, the primary industry associated with OCBP shifted to chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing, followed by petroleum, coal, and other fuel processing industries.
OCBP remains a major component of COP in China. While continuing to regulate the manufacturing industry, especially small- and medium-sized enterprises, supervision should be strengthened in the evolving industries where benzene poisoning now predominantly occurs.
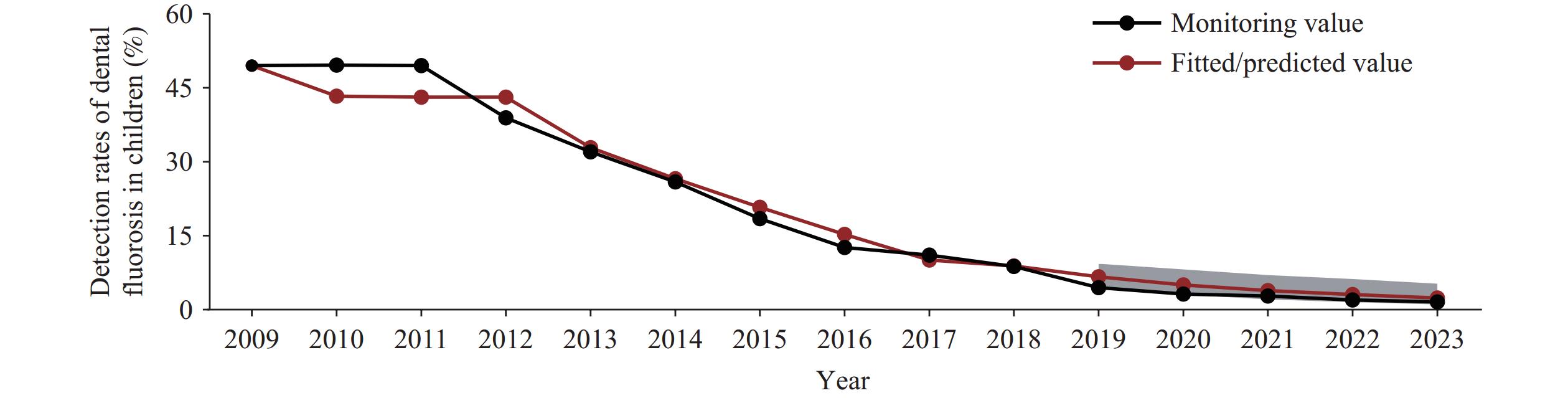
Coal-burning pollution type of endemic fluorosis poses a serious health threat to rural inhabitants in certain regions of China.
The detection rate of dental fluorosis among children aged 8–12 years in China’s coal-burning endemic fluorosis areas showed a significant decreasing trend from 2009 to 2023. Nine provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) were classified as low-prevalence clusters, while only Yunnan was identified as a high-prevalence cluster during 2022–2023.
Prevention and control of coal-burning endemic fluorosis should be managed with precision based on the epidemiological characteristics of each PLAD. Efforts should enhance surveillance and early warning systems while strengthening preventive measures in high-risk regions.
The prevalence of hypertension in children and adolescents is increasing, which is closely associated with cardiovascular disease risk in adulthood. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) has demonstrated effectiveness in reducing blood pressure in adults. However, limited evidence exists regarding its effects among children in China.
This cross-sectional study found that 15.4% of Chinese children and adolescents aged 7 to 17 years had elevated blood pressure. The median DASH score was 24 [interquartile range (IQR) 21–28]. Students with higher DASH scores demonstrated a lower prevalence of elevated blood pressure compared to those with lower scores.
DASH adherence was inversely associated with elevated blood pressure prevalence among students aged 7–17 years in China. Increasing adherence to the DASH dietary pattern could play an effective role in the prevention and management of hypertension among children and adolescents.
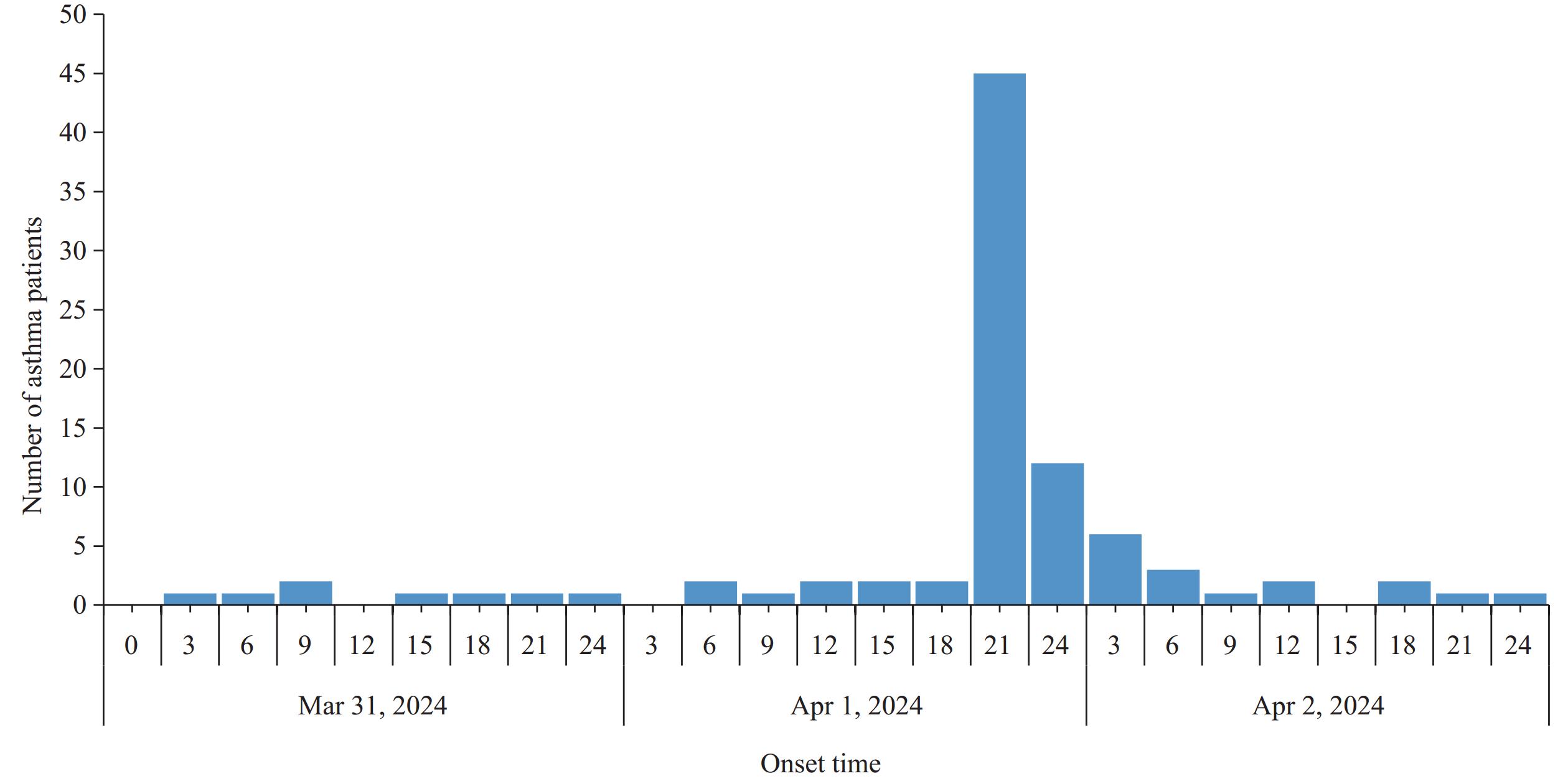
Thunderstorm asthma (TA) is triggered by specific severe convective weather conditions and elevated airborne allergen concentrations, leading to a rapid increase in asthma cases within a short period. Three TA incidents have been previously reported in China, occurring in Shaanxi, Ningxia, and Inner Mongolia.
We report the first documented thunderstorm asthma event (TAE) in Chongqing, China, and conducted a case-control study revealing that allergic rhinitis is an independent risk factor among susceptible individuals.
Health organizations should conduct targeted health education for at-risk populations to improve public emergency response capabilities. Further studies are needed to investigate the meteorological conditions leading to TAE.
Trichloromethane (chloroform), a volatile halogenated solvent, is widely used in printing and industrial operations. Occupational exposure occurs predominantly through inhalation. Chronic exposure can induce hepatotoxicity, but early symptoms are non-specific, frequently resulting in underdiagnosis and severe adverse health outcomes.
This study identified 43 cases of occupational trichloromethane-induced liver injury. The trichloromethane content in both solvents analyzed (57.65% and 66.59%) exceeded the regulatory limit of 20%. Furthermore, the peak airborne trichloromethane concentration in the printing workshop reached 110.3 mg/m3 — 5.5-fold the occupational exposure limit. Solvent exposure was established as the primary risk factor.
This incident highlights effective occupational health response strategies through coordinated occupational health examinations, solvent composition verification, environmental monitoring, and corporate guidance. It also underscores the need for environmental agencies to incorporate trichloromethane-specific exposure limits into VOC regulations. Enterprises should strengthen management of their Environmental, Health and Safety (EHS) departments.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed