2025 Vol. 7, No. 13
This paper addresses the World Tuberculosis (TB) Day 2025 theme, “Yes! We can end TB! Commit, Invest, Deliver”. Through comprehensive analysis of China’s TB epidemic landscape and associated challenges, we align with the “National TB Prevention and Control Plan (2024−2030)” which emphasizes that building Zero-TB communities through the integration of “active case finding” and “TB preventive treatment (TPT)” represents a viable pathway toward ending the TB epidemic. Active case finding serves as a critical intervention for early detection and transmission reduction, while TPT constitutes an essential strategy for decreasing latent TB infection incidence. By facilitating the rapid expansion of Zero-TB communities through governmental commitment, strategic resource allocation, and coordinated implementation, we anticipate achieving the ultimate goal of TB epidemic elimination.
Streptococcus agalactiae, or group B Streptococcus (GBS), can cause severe infections in humans, yet comprehensive genomic characterization from China remains limited. This study presents an extensive genomic analysis of GBS isolates collected in China from 1998 to 2024.
GBS genomes were obtained from public databases and through de novo sequencing. Serotype confirmation was conducted via pan-genomic analysis, phylogenetic relationships were established using maximum-likelihood methodology, and virulence and antibiotic resistance genes were identified through the Virulence Factor Database and Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 26.0, primarily employing Fisher’s exact tests.
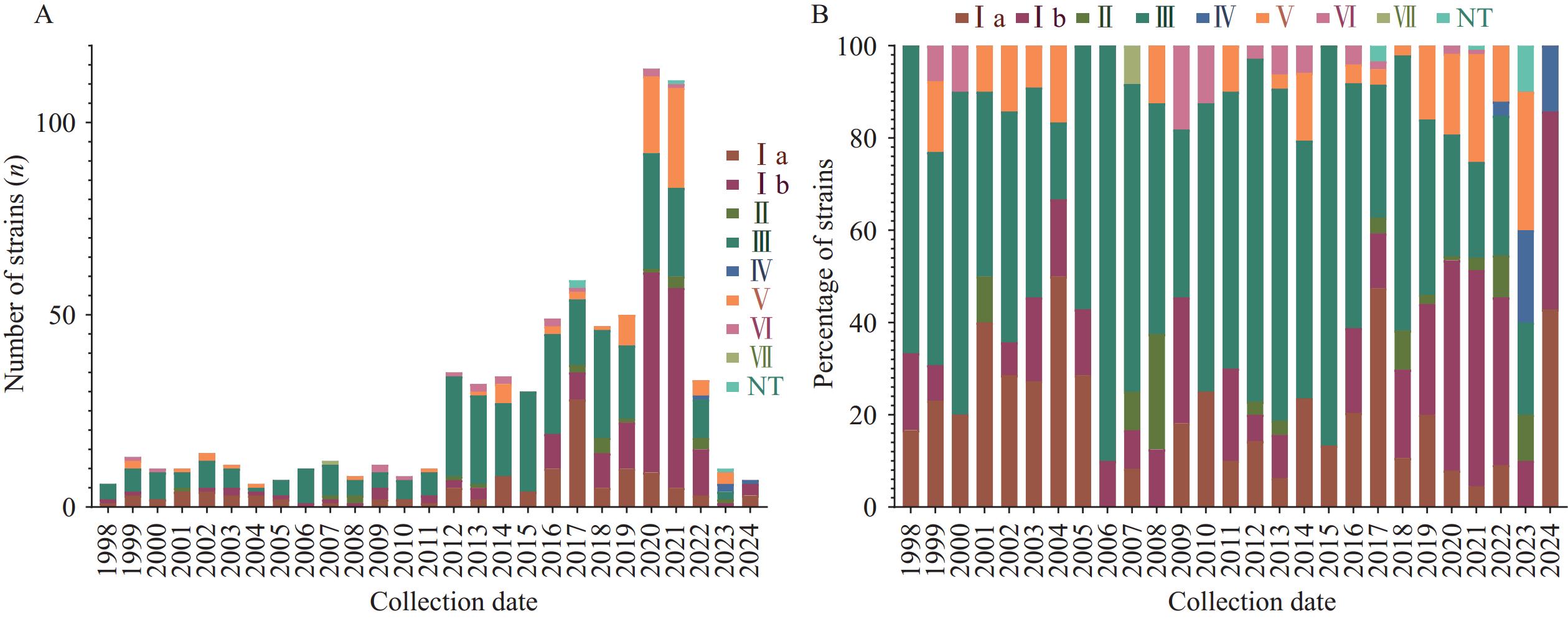
Analysis of 747 GBS genomes revealed eight serotypes (Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII) and nontypeable strains. Serotypes III, Ib, Ia, V, and II constituted 96.65% of all isolates. GBS prevalence remained low from 1998–2011 but increased substantially after 2012. Geographic distribution demonstrated significant regional heterogeneity. Phylogenetic analysis categorized the 747 genomes into five distinct lineages, with lineage 5 being predominant. Six virulence factor categories encompassing 56 virulence-associated genes were identified, with 33 genes present in nearly all genomes. Twenty-seven antibiotic resistance genes spanning nine drug classes were detected, particularly those conferring resistance to peptides and macrolide antibiotics, indicating widespread antimicrobial resistance mechanisms in GBS.
GBS infections in China exhibit serotype distributions similar to global patterns but with notable regional variations. This comprehensive genomic characterization provides critical insights for developing targeted prevention strategies and treatment approaches for GBS infections in China.
Leptospirosis has historically been a severe public health concern across multiple Chinese provinces. Despite an overall decline in incidence in recent years, the disease continues to exhibit fluctuations and occasionally triggers localized outbreaks. This study aimed to characterize the demographic and spatiotemporal patterns of leptospirosis in Anhui Province — a historically significant epidemic region — from 2004 to 2023, to investigate potential climatic and environmental risk factors, and to identify critical targets for disease prevention and control.
Spatiotemporal cluster analysis was conducted using SaTScan software. Spearman correlation analysis was performed using SPSS to examine the short-term lagged effects of rainfall, temperature, and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) on leptospirosis incidence in the high-risk counties of Huaiyuan and Jingde.
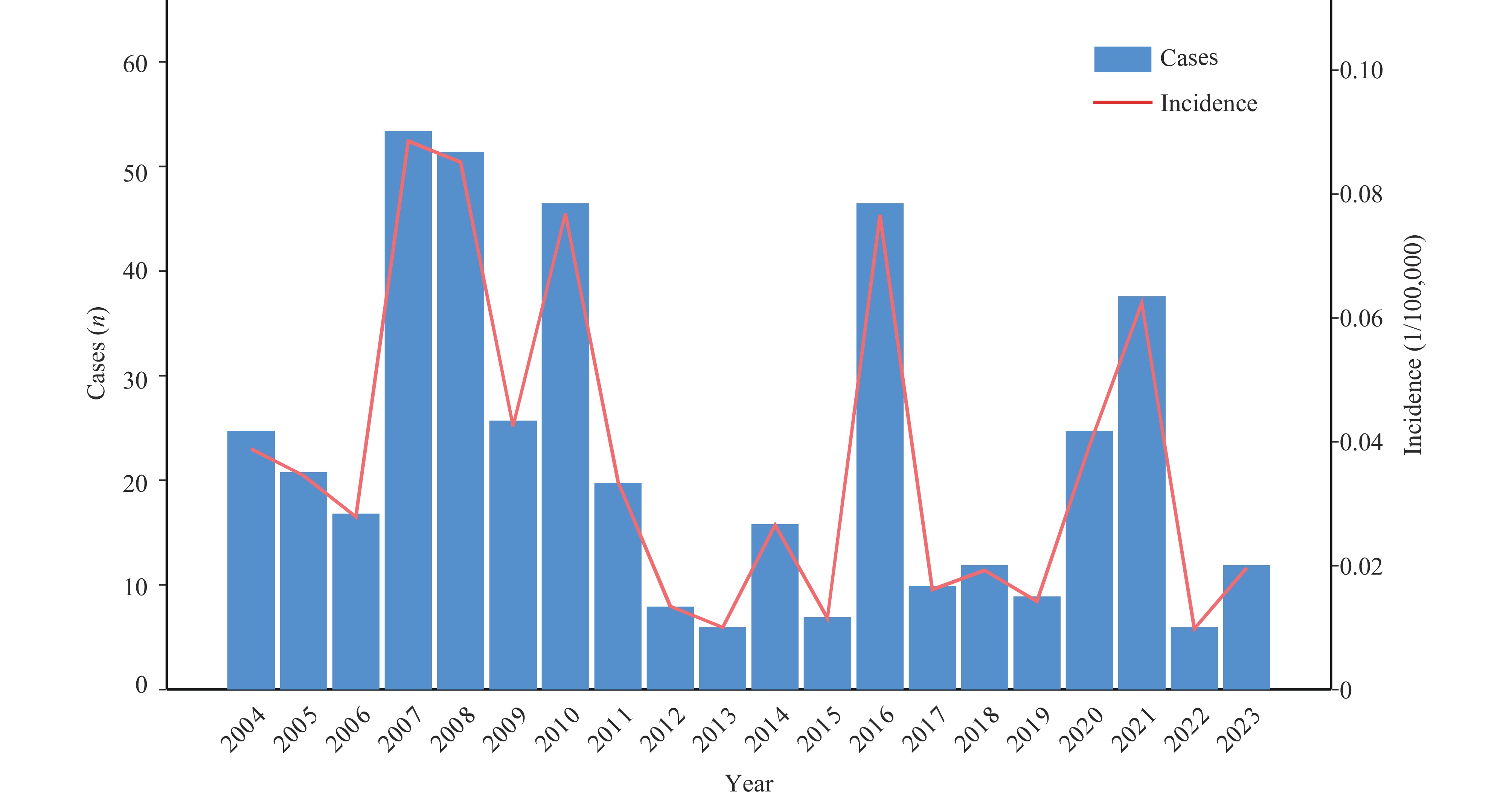
A total of 458 leptospirosis cases were reported across Anhui Province during the 20-year study period. Middle-aged individuals (40–59 years), males, and agricultural workers constituted the primary high-risk populations. Spatiotemporal scanning identified nine adjacent hotspots in southern Anhui during 2004–2012, with a subsequent shift to Huaiyuan County in the northern Huaihe River Basin during 2016–2021. Significant associations were observed between leptospirosis cases and temperature, rainfall, and NDVI in both Huaiyuan and Jingde counties.
This study revealed significant spatial heterogeneity, distinct spatiotemporal clustering patterns, and potential climatic and environmental risk factors for leptospirosis in Anhui Province during 2004–2023. These findings provide critical information regarding target regions, high-risk populations, and climatic and environmental factors to inform early warning systems and enhance prevention and control strategies for leptospirosis.
Tuberculosis (TB) disproportionately affects socially vulnerable populations, particularly the migrant population. Shanghai has implemented a policy providing additional reimbursement for TB diagnosis and treatment beyond standard health insurance coverage for residents. However, comprehensive evidence on TB care utilization patterns and treatment costs remains limited, especially on the disparities between local and migrant populations
From 2020 to 2021, local and migrant TB patients in Shanghai demonstrated comparable outpatient visit frequencies with an overall hospitalization rate of 85.7%. Migrant TB patients without resident permits are ineligible for government reimbursement, resulting in over half of the patients encountering out-of-pocket costs that exceed 20% of their annual household income for TB treatments.
The government’s reimbursement policy should be expanded to include the most vulnerable populations, specifically migrant patients without residency permits, to strengthen the financial risk protection for TB patients.
Phylogenetic analysis has revolutionized the detection and understanding of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) transmission patterns.
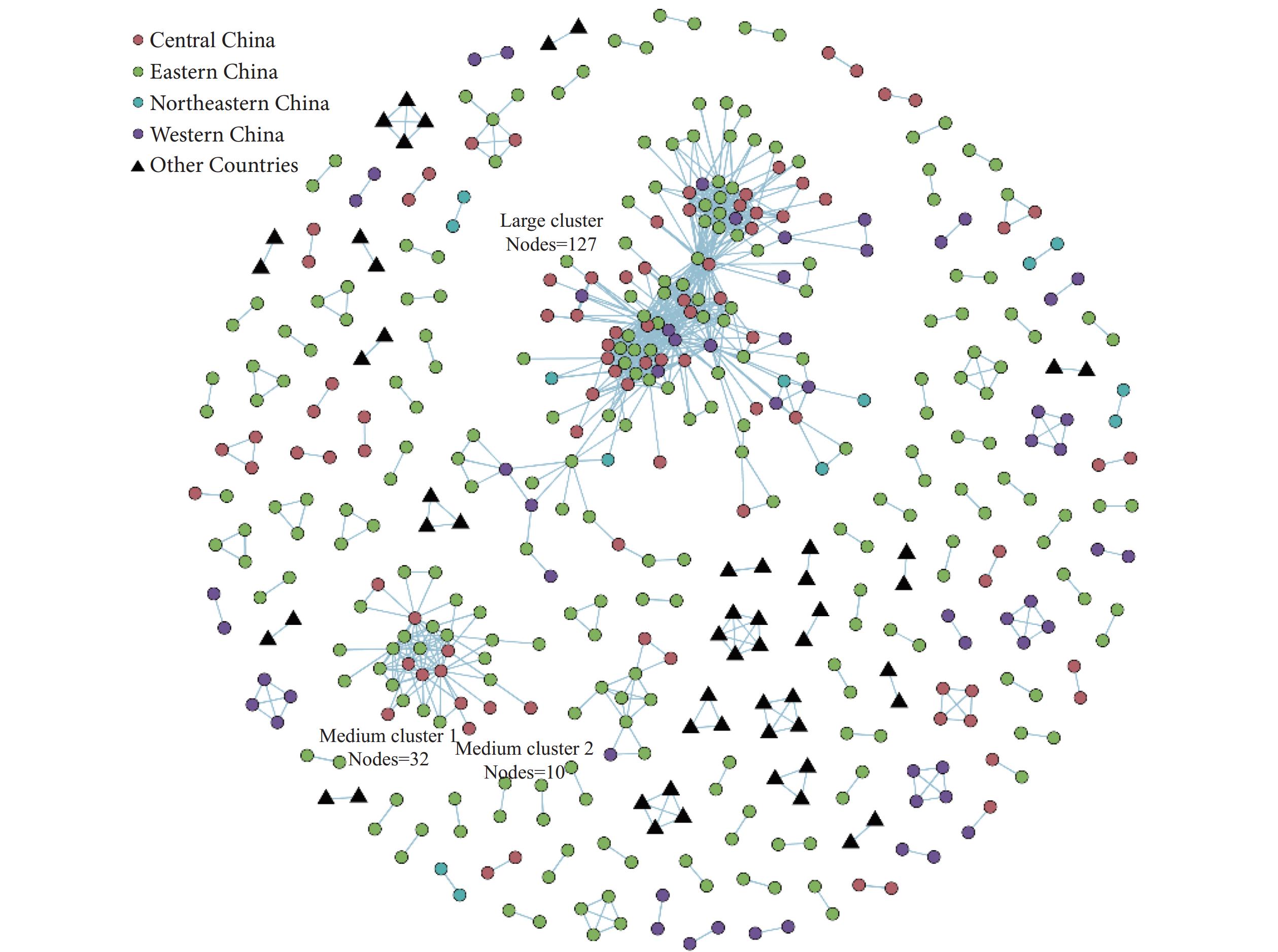
Three distinct transmission cluster patterns were identified across China: a large cluster with nationwide distribution, two medium clusters predominantly in the Central and Eastern China, and 103 small clusters scattered across 19 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs). Each cluster type exhibited unique characteristics of expansion risk and inter-provincial transmission patterns. No genetic linkages were found between Chinese sequences and those from other countries.
These findings underscore the critical need for a comprehensive national molecular epidemiological surveillance network.
The incidence of tetanus in China remains significantly higher than in economically developed regions. Tetanus vaccination represents the most scientifically validated and efficient approach to tetanus prevention. However, vaccine hesitancy presents substantial barriers to the widespread implementation of non-neonatal tetanus vaccination programs across China.
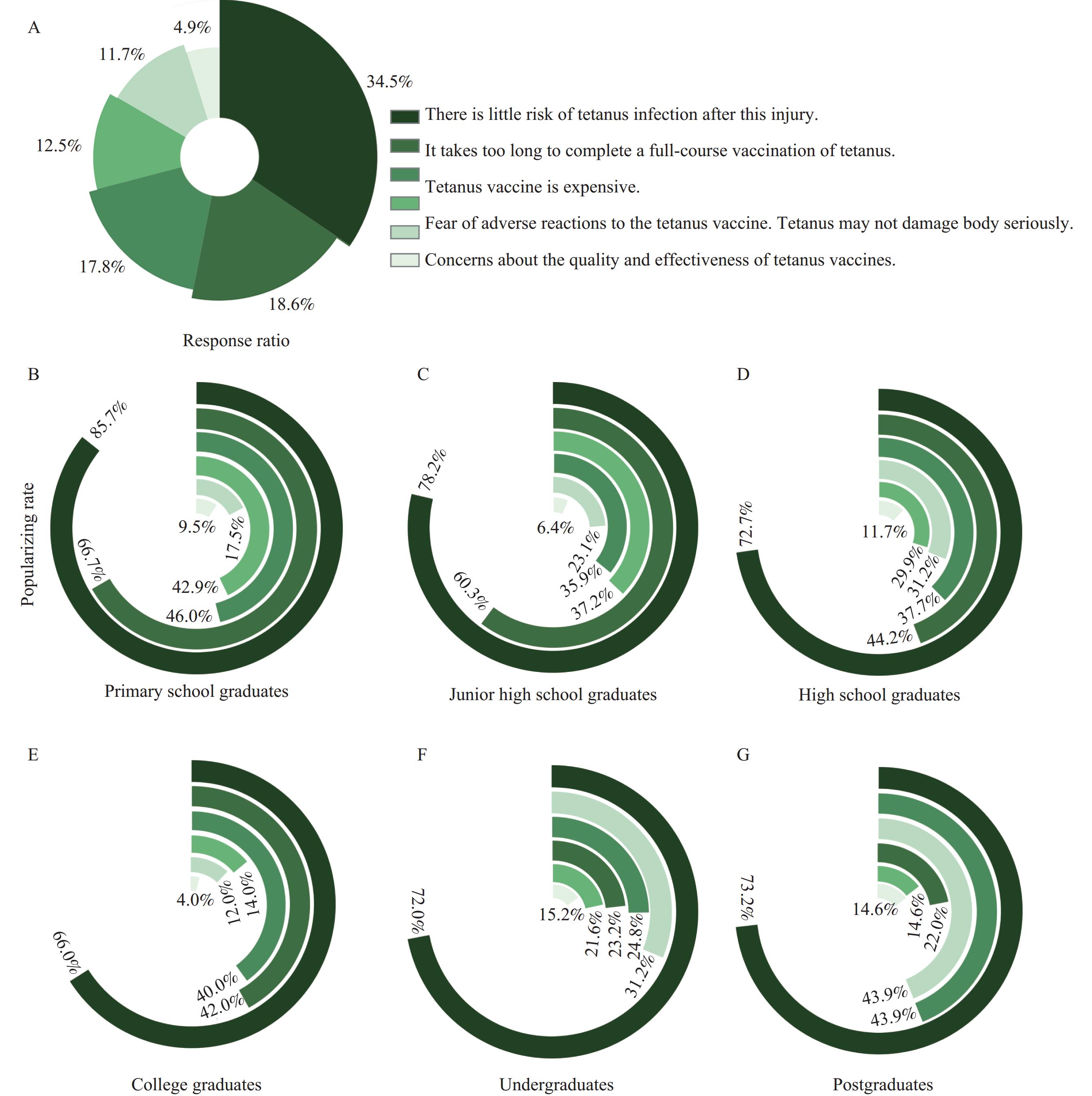
This study constitutes the first comprehensive investigation of tetanus vaccine hesitancy in China, documenting its current prevalence and underlying determinants. Findings reveal that limited knowledge about tetanus vaccines, complacency regarding tetanus risk, advanced age, and other factors significantly contribute to vaccination hesitancy. The research demonstrates that medical institutions and healthcare providers offering evidence-based information about tetanus prevention may substantially enhance vaccination uptake.
By elucidating the specific reasons for tetanus vaccine refusal among trauma patients, this study provides critical insights for government agencies and health policymakers to develop contextually appropriate interventions aligned with China’s national circumstances, ultimately facilitating improved tetanus vaccination coverage.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed