2025 Vol. 7, No. 14
The World Health Day 2025 calls for a global commitment to maternal health. Maternal health has long been a central focus in the global health agenda, prominently featured in both the Millennium Development Goals and Sustainable Development Goals. Substantial progress has been made in reducing maternal mortality through international collaboration. However, significant challenges persist, including reductions in global health financing and emerging threats such as climate change. Mindset changes are urgently needed for maternal health and broader global health governance. Sustainable investment and health system strengthening are imperative. Global health governance should be reformed through a paradigm shift toward an accountable, fair, efficient, and transparent ecosystem.
Human brucellosis persists as a critical public health challenge in China. Understanding disease clusters and trends is essential for implementing effective control strategies. This study evaluates the epidemiological characteristics and spatiotemporal distribution of brucellosis in China from 2011 to 2023.
Data were obtained from the National Notifiable Disease Reporting System (NNDRS). We conducted descriptive epidemiological analyses and employed SaTScan10.1 and ArcGIS10.7 software to identify disease clusters and generate county (district)-level incidence maps.
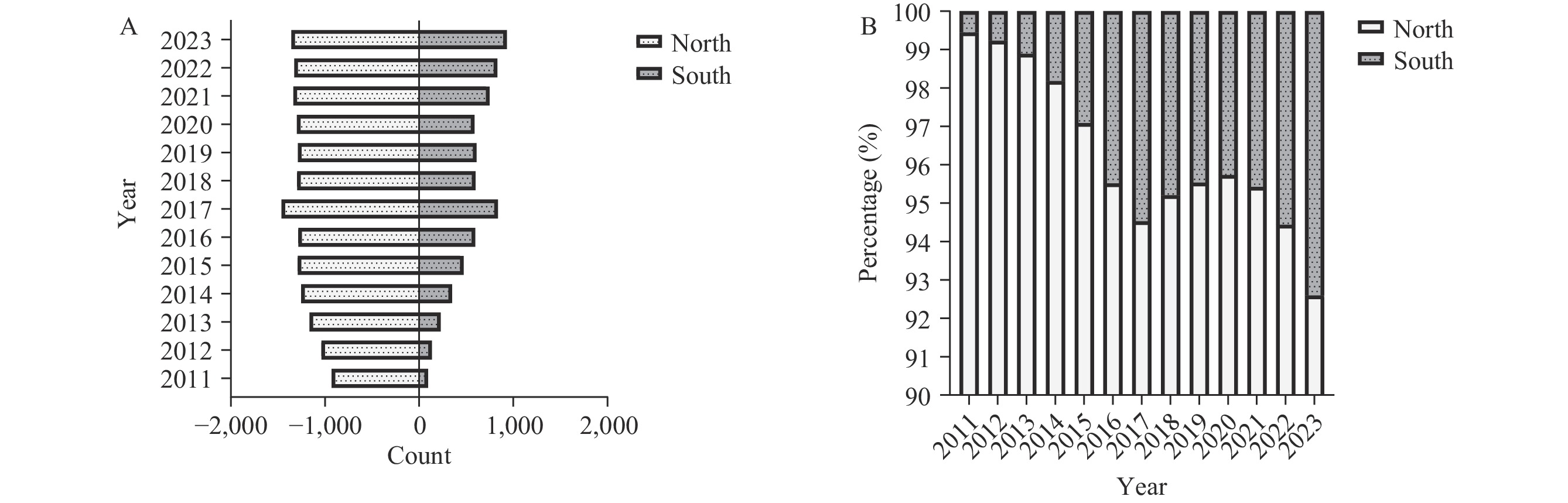
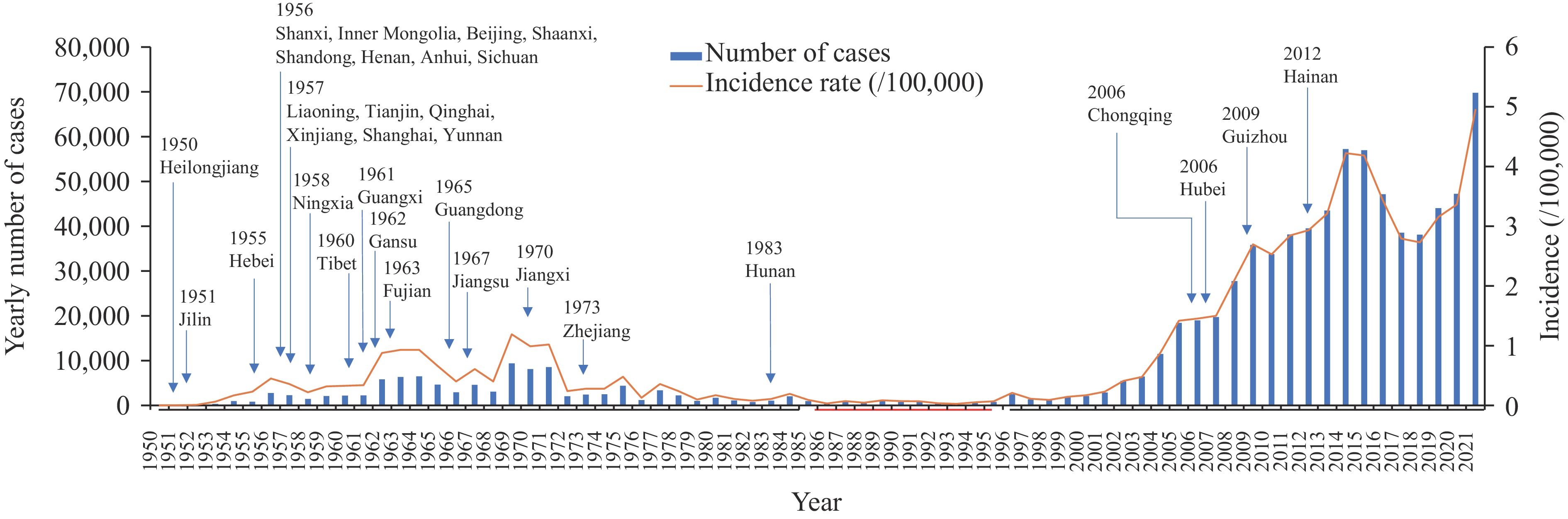
The incidence of human brucellosis in Chinese mainland increased substantially between 2011 and 2023, rising from 38,151 cases (2.8/100,000) across 834 counties (25.4%) to 70,439 cases (5.2/100,000) across 2,290 counties (76.9%). A significant upward trend in reported incidence emerged during 2018–2023 (average annual percentage change (AAPC)=14.9%, P=0.01). Most cases (89.3%) occurred in individuals aged 25–69 years, with an increasing proportion among those aged over 60 years. While 96.1% of cases were reported in northern provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs), southern regions demonstrated escalating incidence rates and expanding geographical spread. Southern PLADs exhibited a notable annual increase of 31.5% in reported incidence (P<0.01). Counties (districts) with incidence rates exceeding 10 per 100,000 expanded geographically from northwestern pastoral regions to southern areas and from rural to urban settings. Primary spatiotemporal clusters were concentrated in Inner Mongolia and adjacent provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs), with emerging clusters identified in Yunnan, Guangdong, and Xizang.
The human brucellosis epidemic in China continues to intensify, characterized by rebounding incidence rates and broader geographical distribution across counties (districts). While spatiotemporal clusters remain predominantly centered in Inner Mongolia and neighboring regions, targeted interventions and increased resource allocation for high-risk areas and populations are imperative.
Human brucellosis poses a serious public health concern in China, however, epidemiological evolution of disease in southern and northern China remains unclear.
The number of cases, incidence rate, geographic and temporal distribution, and social factors were analyzed to illustrate the epidemiological change.
About 97.6% of cases consistently located in the northern area are attributed to the tens of thousands of livestock farming. This underscores the need to prioritize strengthening surveillance and control measures in the northern. By contrast, only 2.4% of cases were in the southern area. These data indicate that controlling brucellosis in the northern will help reduce the incidence in the southern. There was an apparent shift from historical multiple-species prevalence to the present dominance of a single species, Brucella melitensis. Mutton price and production were closely correlated with the number of cases, implying that B. melitensis strains were accompanied by these factors, co-driving the persistent epidemic of brucellosis and expanding from the northern toward the southern.
The control and prevention of brucellosis in the northern have become extremely complex sociological issues. It is important to draw attention to the worsening epidemic situation and to mobilize the nation’s full strength to curb this trend.
Schistosomiasis is a water-borne parasitic disease that significantly threatens human health and socioeconomic development. In China, Schistosoma japonicum is the predominant pathogenic species, and transmission control criteria were successfully achieved nationwide in 2015.
This report comprehensively documents schistosomiasis epidemiology in China from 2016 to 2023, presenting provincial and county-level data on human infections, cattle reservoirs, and Oncomelania hupensis snail vector distribution. Serological findings at both provincial and county levels demonstrate persistently elevated seropositive rates in specific regions despite overall progress.
Development of highly sensitive diagnostic tools for low-intensity infections is essential, while intelligent early warning systems and multi-channel surveillance mechanisms must be strengthened to achieve the goal of schistosomiasis elimination in China.
Seasonal influenza poses a significant public health burden, causing substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide each year. In this context, timely and accurate vaccine strain selection is critical to mitigating the impact of influenza outbreaks. This article aims to develop an adaptive, universal, and convenient method for predicting antigenic variation in influenza A(H1N1), thereby providing a scientific basis to enhance the biannual influenza vaccine selection process.
The study integrates adaptive Fourier decomposition (AFD) theory with multiple techniques — including matching pursuit, the maximum selection principle, and bootstrapping — to investigate the complex nonlinear interactions between amino acid substitutions in hemagglutinin (HA) proteins (the primary antigenic protein of influenza virus) and their impact on antigenic changes.
Through comparative analysis with classical methods such as Lasso, Ridge, and random forest, we demonstrate that the AFD-type method offers superior accuracy and computational efficiency in identifying antigenic change-associated amino acid substitutions, thus eliminating the need for time-consuming and expensive experimental procedures.
In summary, AFD-based methods represent effective mathematical models for predicting antigenic variations based on HA sequences and serological data, functioning as ensemble algorithms with guaranteed convergence.Following the sequence of indicators specified in I, we perform a series of operations on A1, including feature extension, extraction, and rearrangement, to generate a new input dataset
Fluorescent probe-based recombinase aided amplification (RAA) offers the advantages of rapidity and simplicity but is limited by the requirement for complex and lengthy probe design, restricting its widespread application.
A novel EvaGreen dye-based RAA (EvaGreen-RAA) assay utilizing self-avoiding molecular recognition system (SAMRS) primers was developed for the detection of Pseudomonas fluorescens (PF) and Bacillus cereus (BC) in milk. Conventional RAA was used as a reference method. Sensitivity was evaluated using nucleic acids from recombinant plasmids and simulated milk specimens. Additionally, a dual EvaGreen-RAA assay was investigated for simultaneous detection of mixed BC and PF in simulated milk specimens.
The EvaGreen-RAA demonstrated superior sensitivity compared to conventional RAA, with detection limits of 1 copy/µL versus 10 copies/µL for both BC and PF plasmids, respectively. In simulated milk specimens, EvaGreen-RAA detected BC and PF at concentrations of 100 CFU/mL and 200 CFU/mL, respectively, compared to 400 CFU/mL and 600 CFU/mL for conventional RAA. The dual EvaGreen-RAA assay successfully detected mixed BC and PF in simulated milk specimens at concentrations of 200 CFU/mL for each pathogen.
The EvaGreen-RAA assay demonstrated significant advantages in terms of simplicity and enhanced sensitivity compared to fluorescent probe-based RAA, offering a novel approach for developing multiplex pathogen detection systems using melting curve analysis.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed