2023 Vol. 5, No. 16
Intimate partner violence (IPV) represents a significant global public health concern.
The burden of HIV/AIDS related to IPV demonstrated an upward trend from 1990 to 2019, exhibiting an annual growth of 4.66% in age-standardized death rates (ASDR) and 4.42% in age-standardized disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) rates. Notably, the age groups 30–34 and 50–54 experienced a higher IPV burden compared to other age groups.
There is a pressing need for public health policymakers to develop efficacious interventions aimed at bolstering the surveillance and prevention of IPV targeted at women in China.
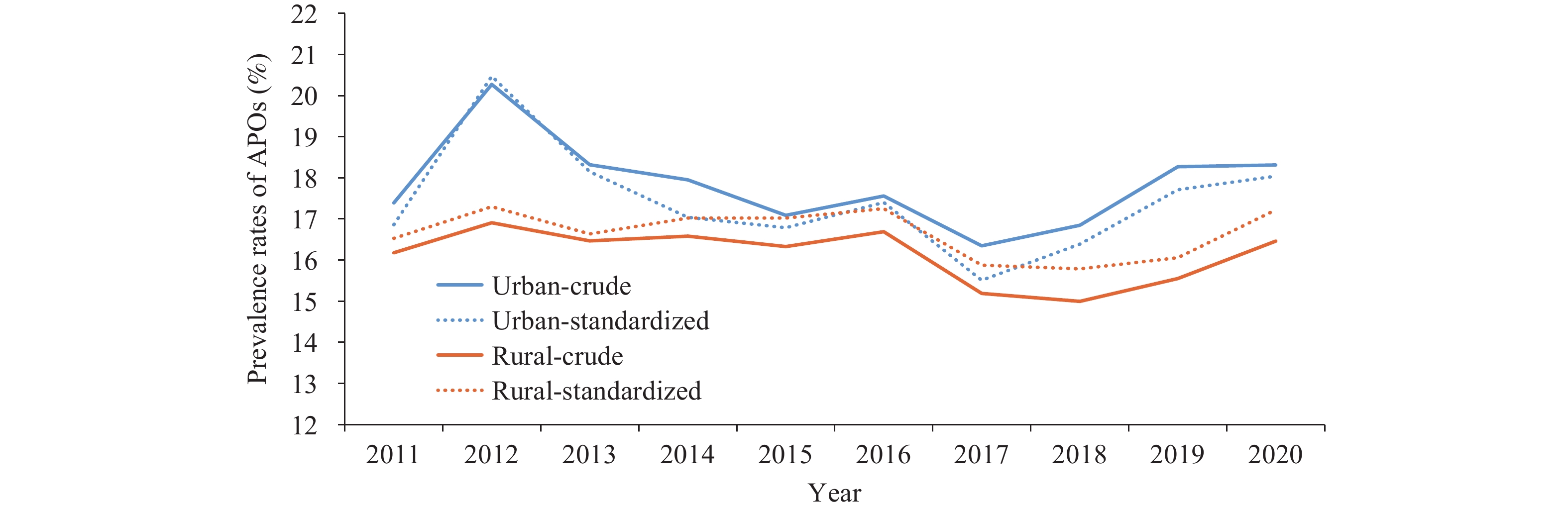
The prevalence of adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs) exhibits a disparity between urban and rural areas, which is commonly associated with various factors, such as demographic and socio-environmental factors. However, the specific contribution of each factor has not yet been elucidated.
This study demonstrates that the primary factors contributing to urban-rural differences in the prevalence of APOs are population structure, parental age, parity, and regional development.
Future prevention and control measures should be directed toward considering population structure and regional differences. Accurate interventions will enhance the efficiency of public health services.
Chronic pain has been identified as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Evidence shows that adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the cardiometabolic risks associated with chronic pain.
Results from this cohort study suggest a positive association between chronic pain and the development of new-onset metabolic-related multimorbidity, specifically metabolic multimorbidity and cardiometabolic comorbidity, within middle-aged and older Chinese adults. Furthermore, adopting healthy lifestyles can potentially mitigate or even reverse these associations.
The results of our study emphasize the importance of promoting healthy lifestyles among older Chinese adults as a preventative measure against the medical burdens and cardiometabolic risks associated with chronic pain.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed