2025 Vol. 7, No. 20
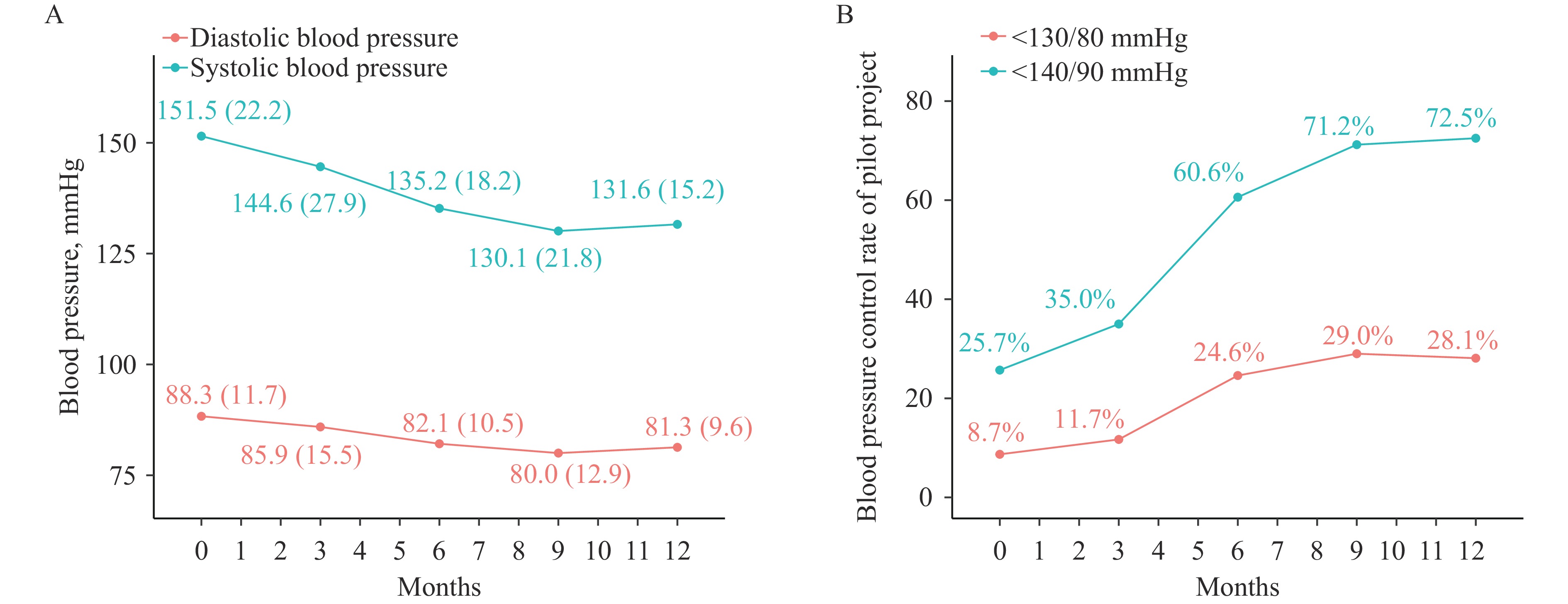
To evaluate the adaptability of the China Rural Hypertension Control Project (CRHCP) — a multifaceted village doctor-led intervention for blood pressure control in rural China — for widespread implementation in extension projects. This project comprises two phases: a pilot project and an extension project. It builds upon our CRHCP model, implementing a multi-level comprehensive hypertension management strategy targeting the general population across rural areas and township communities in China, aligning with national policies and local initiatives. In the pilot project, 5,088 hypertensive patients were enrolled. At baseline, 1,227 subjects (25.7%) met the 140/90 mmHg target for blood pressure control. After 13 months of intervention, the blood pressure control rate (<140/90 mmHg) reached 72.5%. In the extension project, 244,046 hypertensive patients were identified through screening of 1,002,845 residents in Changtu, Wujiang, and Tongguan. Average blood pressure decreased from 146.8/88.4 mmHg to 140.4/82.6 mmHg, and the proportion of patients with controlled blood pressure increased significantly from 20.8% to 44.0%. The translation of the CRHCP model into a public health program has demonstrated potential for enhancing hypertension control in selected regions of China. While these initial results are encouraging, further research and long-term evaluation are needed to confirm their effectiveness and adaptability. If proven successful, this model may offer a replicable framework for improving public health outcomes in other low- and middle-income countries and regions.
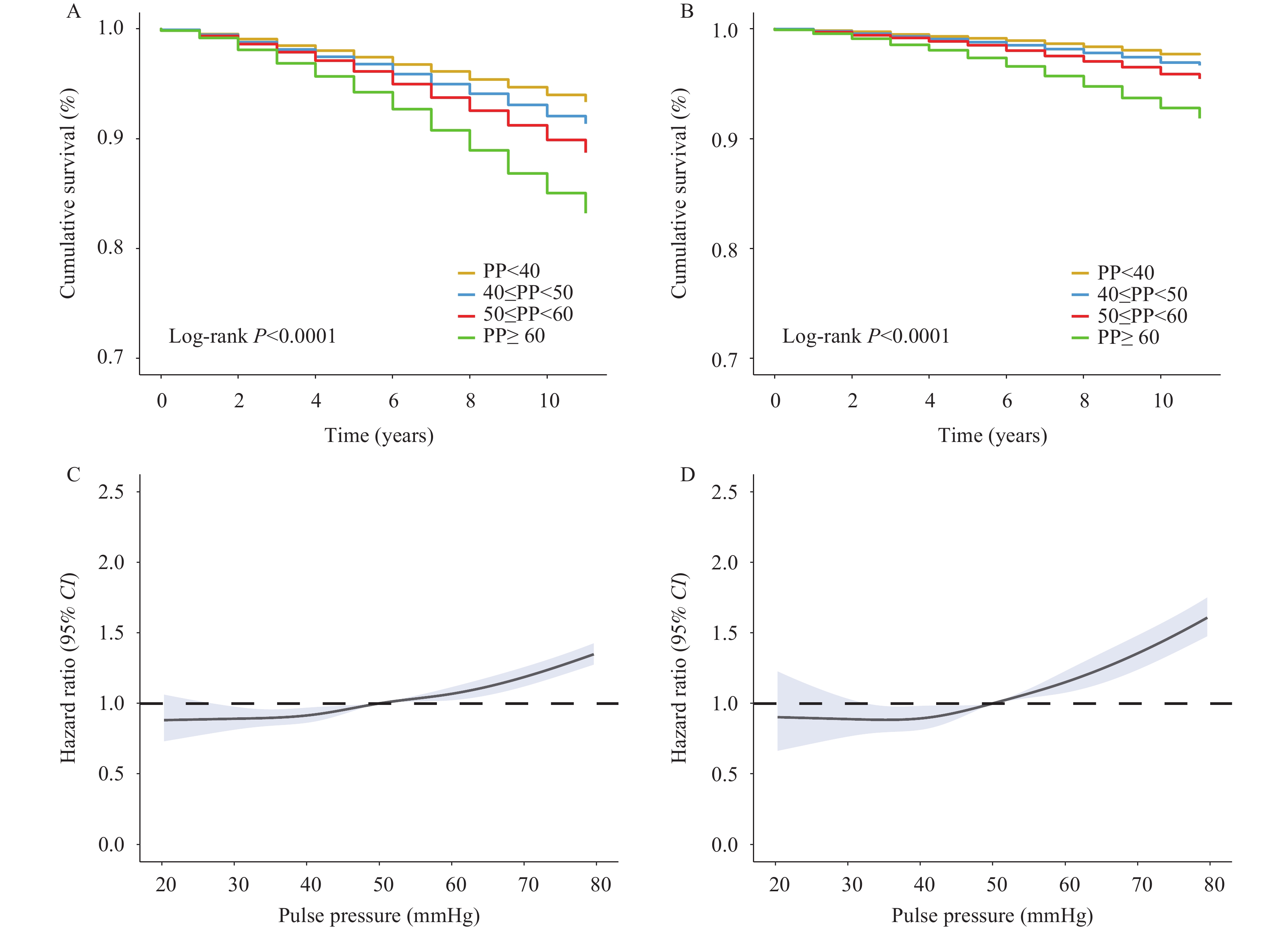
As an indicator of aortic stiffening, elevated pulse pressure (PP) has been established as a marker of poor clinical outcomes.
Compared with the lowest quartile of PP (<40 mmHg), mortality risk increased by 9.8%–23.9% among individuals with PP in the second to fourth quartiles. This association was particularly pronounced in females, adults aged 60–74 years, and overweight or obese individuals.
Our findings emphasize the need to develop comprehensive PP early screening and effective management strategies to reduce mortality, especially among identified high-risk groups.
Very limited research shows that the Mediterranean-dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) intervention for neurodegenerative delay (MIND) diet is not associated with incident hypertension in adults.
Based on three-year follow-up data, higher adherence to the MIND diet was significantly associated with decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure among older adults with and without hypertension, while confirming previous research showing it does not affect rates of incident hypertension.
The MIND diet can be beneficial for prevention, intervention, and management of hypertension among older adults.
Prediabetes increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Existing prediction models for incident diabetes from prediabetes have been primarily developed for the general adult population.
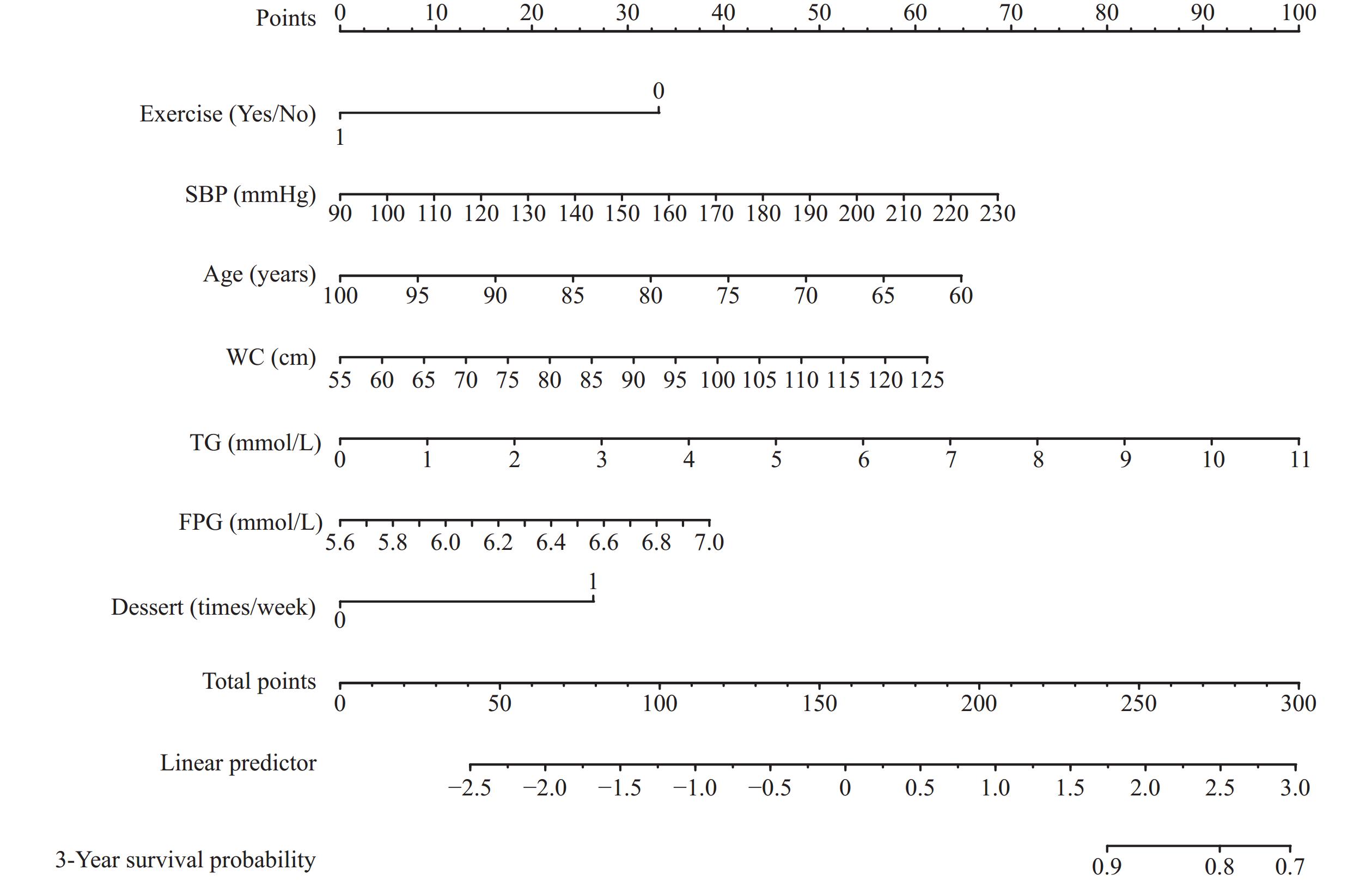
This report introduces a prediction model for progression to diabetes from prediabetes, specifically for older adults, which includes age, exercise, waist circumference, baseline fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and triglyceride concentrations, systolic blood pressure, and dessert intake.
The prediction model developed in this study can be used in older adults to identify high risk of progression from prediabetes, defined by FPG, to diabetes, thereby informing targeted interventions and avoiding unnecessary utilization of medical resources.
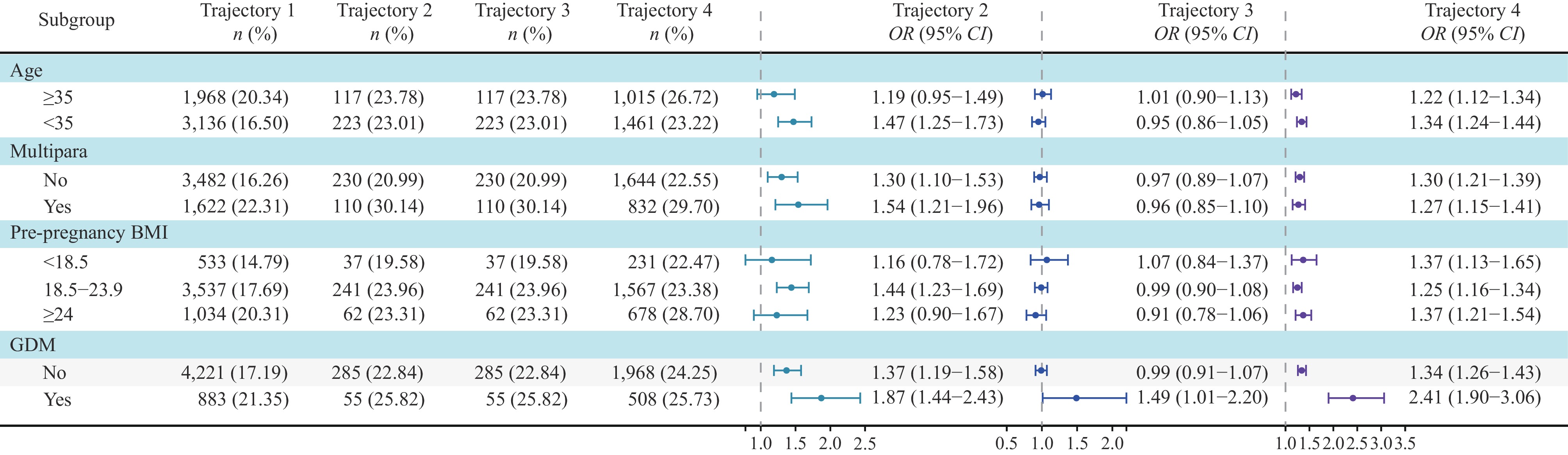
Large for gestational age (LGA) presents significant risks for both mothers and children. Studies have shown a positive association between the first trimester triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and LGA risk.
The TyG index in all three trimesters is positively associated with the risk of LGA. Managing the TyG index may help reduce this risk.
These results suggest that monitoring the TyG index from the first trimester throughout pregnancy could help clinicians identify women at higher risk for LGA, guiding early interventions to mitigate risks. Further research is needed to explore the relationship and mechanisms between the TyG index and LGA.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed