2024 Vol. 6, No. 48
This study aimed to provide a comprehensive analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) epidemiological landscape in China through a historical review and current assessment.
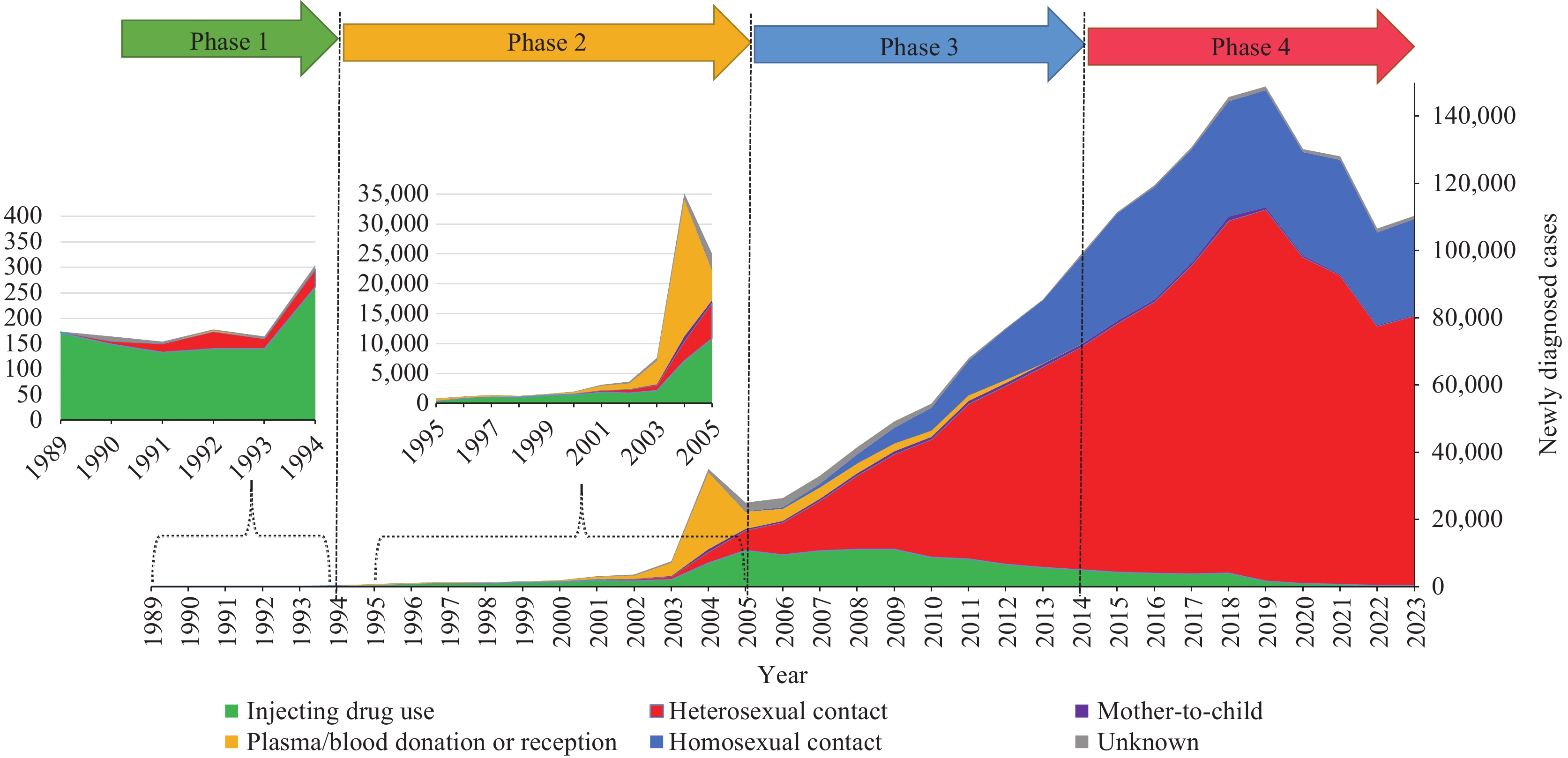
Data were extracted from China’s HIV/AIDS Comprehensive Response Information Management System (CRIMS). Transmission patterns across different phases were visualized using stacked area charts. Geographical correlations between transmission routes were analyzed using scatter plots and Pearson correlation coefficients. The extent and trends of HIV spread among the general population were evaluated using Venn diagrams and Cochran-Armitage tests.
The HIV epidemic in China evolved through four distinct phases: injecting drug user (IDU) dominated (1989–1994), former plasma donor (FPD) outbreak (1995–2005), sexual transmission dominance (2006–2014), and general population spread (2015–present). A strong correlation was observed between provinces reporting high numbers of IDU cases and those with elevated heterosexual transmission (r=0.88, P<0.001). Between 2015 and 2023, 393,926 cases were identified among the general population through non-marital and non-commercial heterosexual contact (NMNCHC). The proportion of general population cases among heterosexual transmissions increased significantly from 46.2% to 55.7% (Z=42.7, P<0.001).
The significant spread of HIV into the general population necessitates the development of targeted prevention strategies for both high-risk and general populations to address emerging epidemiological challenges.
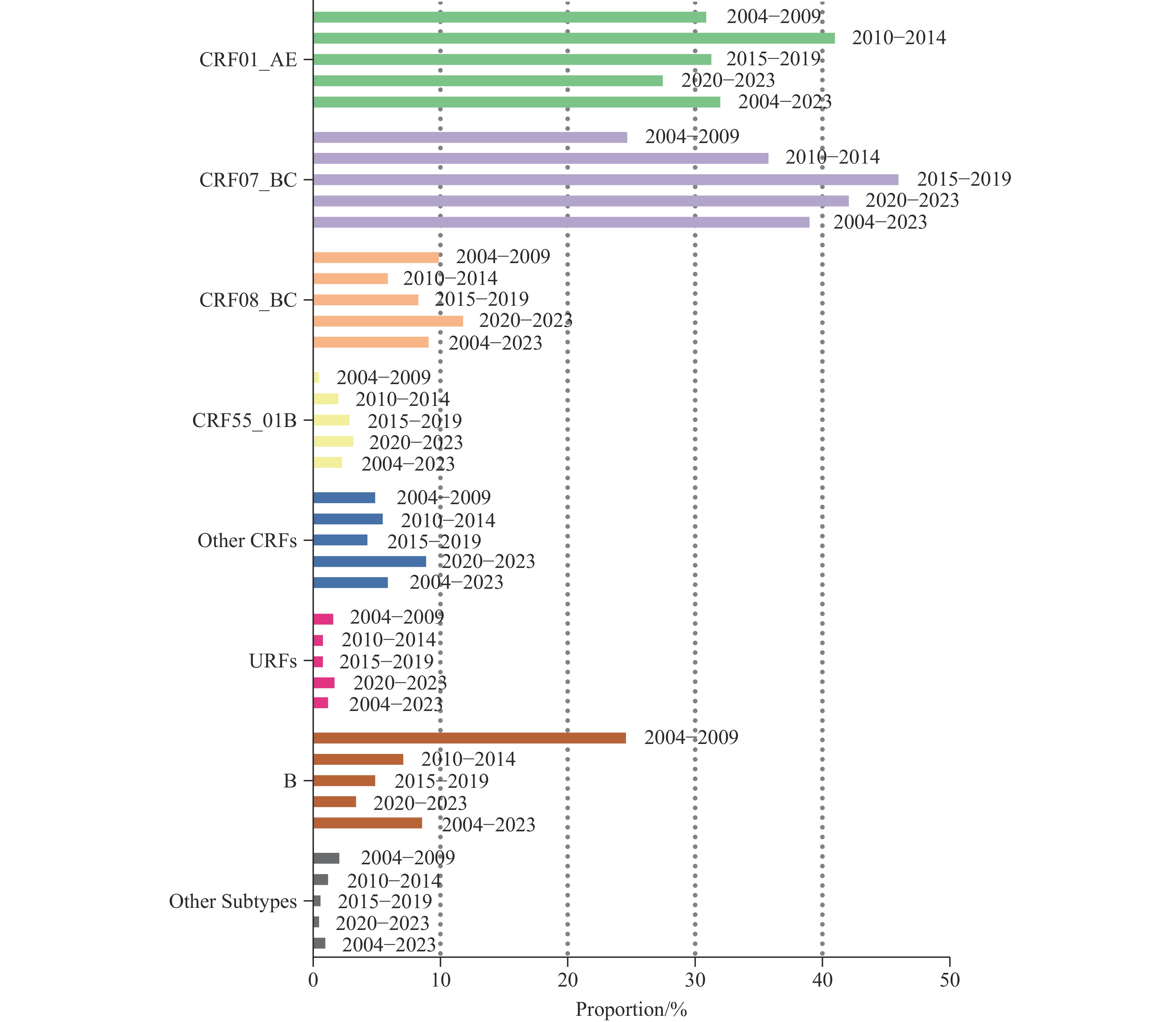
The genetic diversity of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 subtypes significantly influences the effectiveness of diagnostic tools, antiretroviral therapy (ART), and vaccine development. This study aimed to assess the regional and national prevalence of HIV-1 subtypes and recombinants in China between 2004 and 2023 using pol gene segment analysis.
We analyzed annual HIV/AIDS reports and pol gene segment sequences from all Chinese provinces between 2004 and 2023. The distribution of HIV-1 subtypes and recombinants across China and within its regions was estimated by multiplying the proportion of each subtype, circulating recombinant form (CRF), and unique recombinant form (URF) in each province by the corresponding number of reported HIV infections.
Analysis of 94,476 pol gene segments from 31 provinces revealed that CRF01_AE strain accounted for 32.1% of HIV-1 infections during 2004–2023, while CRF07_BC lineage represented 39.1%. CRF08_BC strain contributed 9.2%, followed by subtype B (8.7%) and CRF55_01B (2.4%). Other CRFs collectively comprised 6.0% of infections, while URFs and other subtypes accounted for 1.3% and 1.1%, respectively.
The study revealed significant regional variations and temporal changes in the proportions of HIV-1 CRFs, subtypes, and URFs across China, emphasizing the importance of continued surveillance of strain distribution patterns.
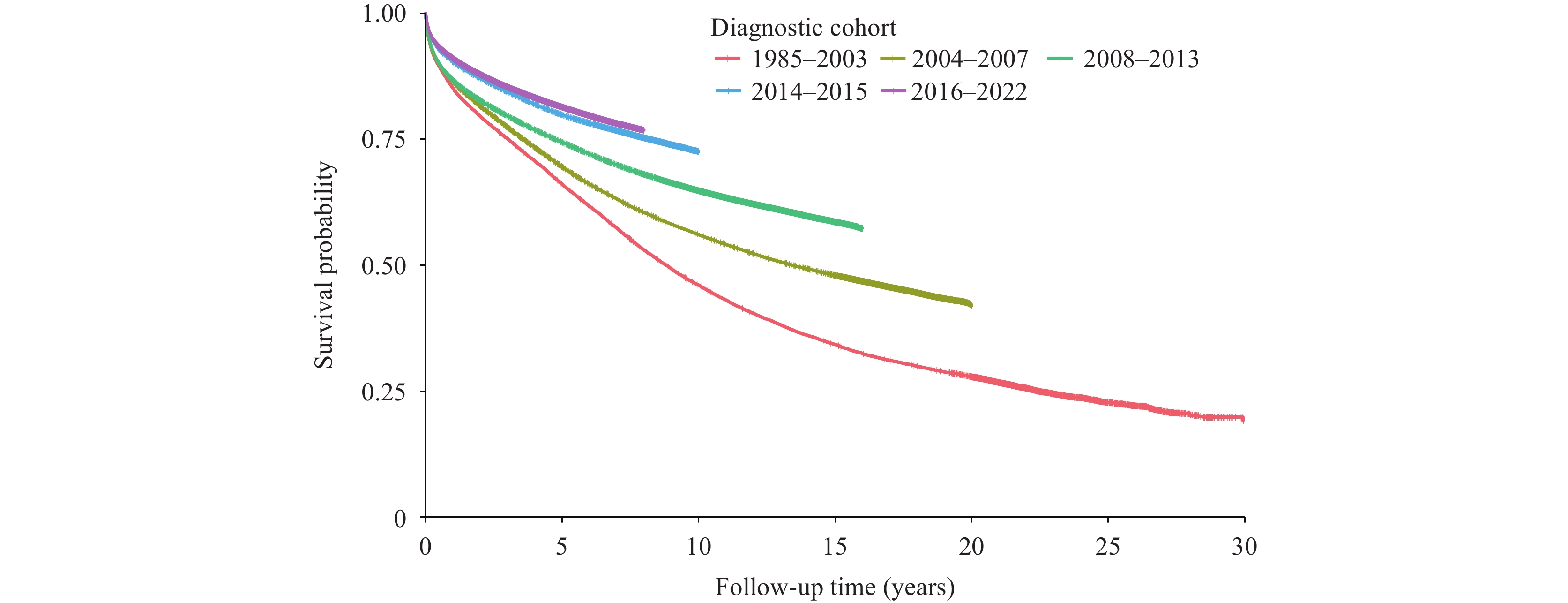
A comprehensive analysis of nationwide survival trends for people living with human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS, PLWHA) from the initial reported case to present has not been conducted. This study evaluated the survival outcomes of PLWHA reported in China from 1985 to 2022.
We analyzed data from PLWHA recorded in the National HIV/AIDS Comprehensive Response Information Management System from 1985 to 2022. Survival rates were calculated using Kaplan-Meier curves, and factors associated with survival time were analyzed using Cox proportional hazard models.
Progressive relaxation of antiretroviral therapy initiation criteria led to significant improvements in survival rates across different diagnostic periods in China. The 1-year and 5-year cumulative survival rates increased from 85.2% and 66.1% in the 1985–2003 cohort to 91.1% and 81.4% in the 2016–2022 cohort. Cox proportional hazard analysis revealed elevated mortality risks among males, individuals aged ≥65 years, those with injection drug use or other transmission routes, hospital-tested patients, and those with lower CD4 counts at diagnosis or without treatment.
Antiretroviral therapy has effectively reduced mortality risk among PLWHA in China. Future efforts should focus on expanding HIV testing to reduce the proportion of late diagnoses with lower CD4 counts and providing targeted, differentiated services for older populations to further decrease mortality risk among PLWHA.
A substantial proportion of people living with human immunodeficiency virus (PLWH) remain unaware of their infection status. Contact tracing serves as an effective public health tool for identifying human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections and supports progress toward achieving the 95-95-95-95 goals.
An egocentric contact tracing study conducted in Yunnan, China, between January 2022 and June 2024 enrolled 1,981 index cases, of whom 314 (15.9%) had at least 1 HIV-positive sexual contact. These index cases reported 2,171 sexual contacts, with 1,509 (69.5%) receiving HIV testing and 317 (21.0%) testing positive. Higher education levels and employment status among sexual contacts were positively associated with HIV testing uptake. HIV infection was more likely among contacts when the index case was female and identified through active HIV testing. Long-term sexual partnerships and inconsistent condom use demonstrated elevated infection risk.
The effectiveness of contact tracing outcomes is influenced by characteristics of both index cases and their sexual contacts. These factors should be incorporated into the design and implementation of sexual contact tracing programs.
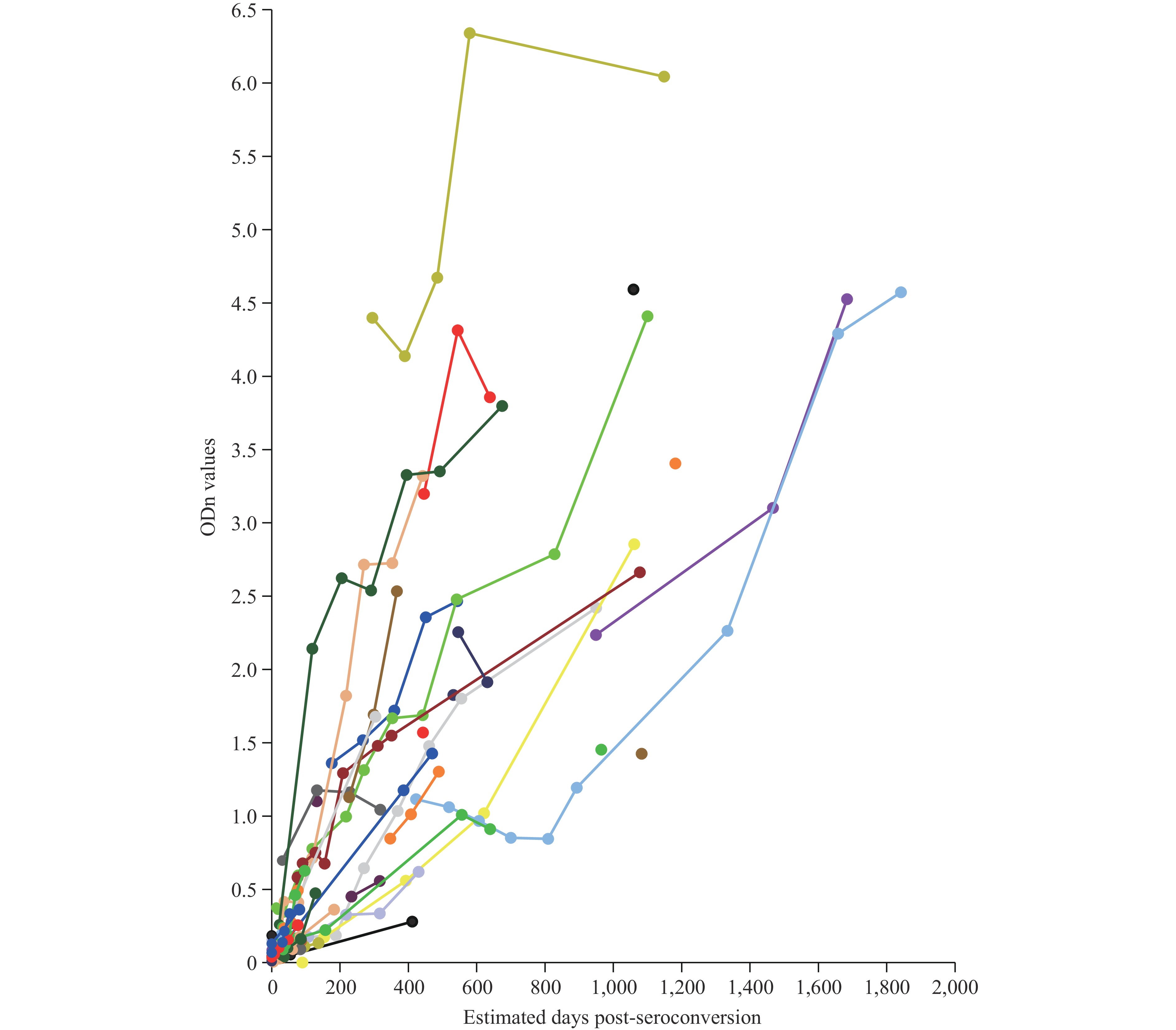
A novel recombinant antigen-based capture enzyme immunoassay (RAg-CEIA) was optimized and used to determine technical parameters for estimating human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) incidence in China.
We employed orthogonal experimental design to optimize RAg-CEIA by adjusting raw material dilution ratios. The assay was used to measure normalized optical density (ODn) values in 171 longitudinal plasma specimens from 51 HIV-1 seroconverting individuals, plotted against estimated days post-seroconversion. We determined the optimal ODn threshold value for differentiating recent from long-term infections and calculated the mean duration of recent infection (MDRI) for incidence estimation. The false recent rate (FRR) was determined using 481 HIV-1 antibody-positive specimens with infection durations exceeding twice the MDRI.
Optimal RAg-CEIA parameters were established with a raw material dilution ratio of 1/12 for calibrator preparation and an enzyme conjugate titer of 1:1200. ODn values demonstrated consistent temporal increases across HIV-1 seroconverting individuals, though with notable kinetic heterogeneity in individual responses. The optimal ODn threshold value of 0.8 for distinguishing recent from long-term infections corresponded to an MDRI of 205 days and an FRR of 4.78%.
The optimized RAg-CEIA effectively differentiates recent from long-term HIV-1 infections at the population level, enabling reliable HIV-1 incidence estimation in China.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed