2025 Vol. 7, No. 45
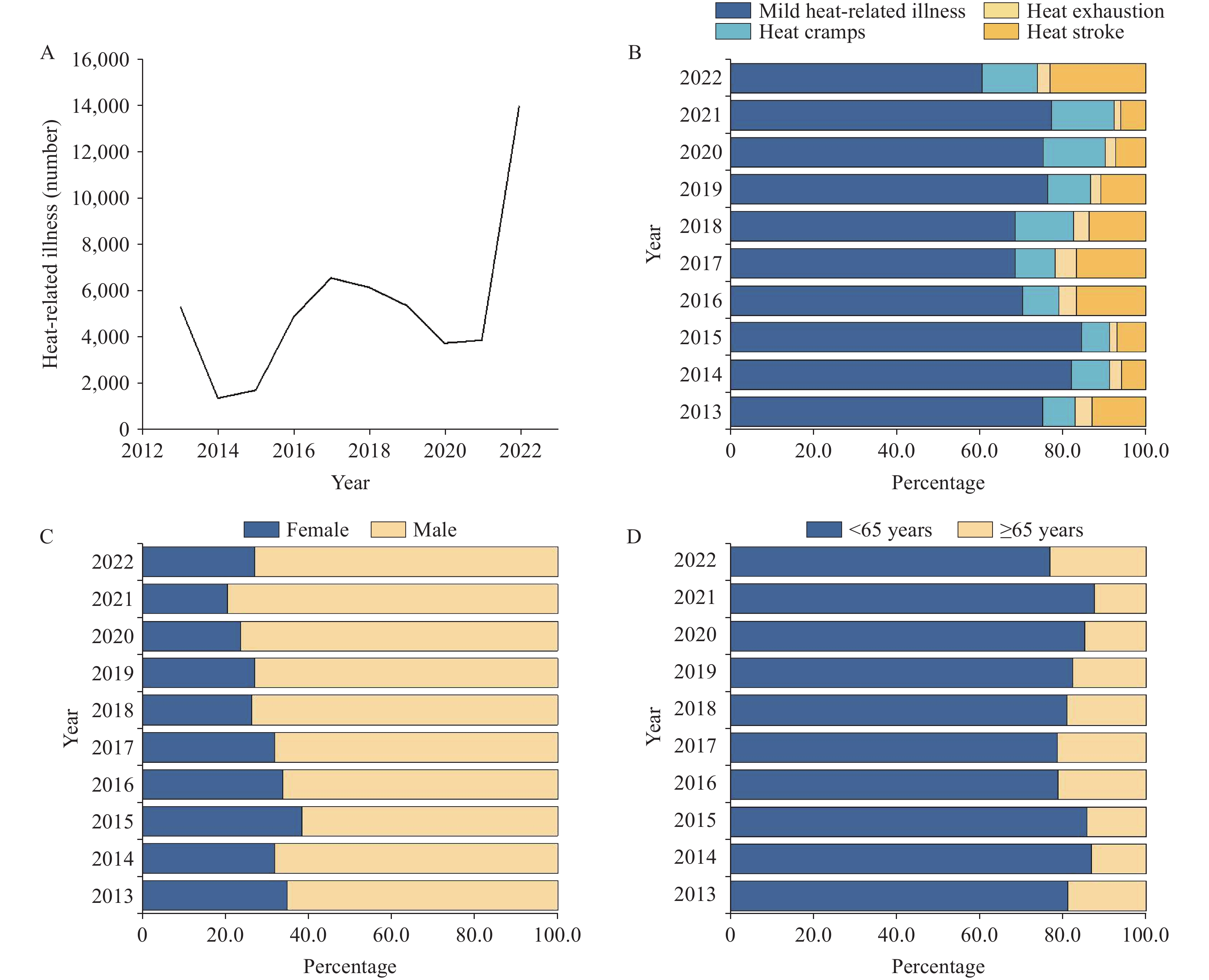
The frequent occurrence of extreme heat events in the context of global warming poses a serious threat to public health. Increasing evidence has highlighted the limitations of China’s traditional early heat warning system, including an overemphasis on meteorological factors, the absence of health risk assessments, limited regional adaptability, and a disconnect between observations and public perception. These shortcomings hinder the ability of the system to meet the growing demand for precise health protection warnings and initiatives. Consequently, the development of an early warning system that focuses on the health risks of high temperatures has emerged as a critical strategy for addressing climate change-related health impacts. This study systematically reviews the existing standards and service limitations of heat warning systems in China and analyzes the necessity of advancing research on and applications of health-oriented heat risk warnings. In the future, the broader social scope of such meteorological warning systems is expected to transform them into health risk assessment systems that benefit the entire population.
We analyzed the spatial distribution of years lived with disability (YLDs) among patients with Kashin–Beck disease (KBD) at the county level across the country, identified hotspot regions and the primary areas of disease burden. This provides a foundation for the prevention and control of KBD and the rational allocation of healthcare resources to regions with high disease burden.
The data were obtained from the National KBD Surveillance System. Spatial autocorrelation analysis was conducted to assess spatial clustering and to identify hotspots of YLDs in patients with KBD. Geographically weighted regression (GWR) models were used to identify counties with limited economic and healthcare resources and a high burden of health losses.
Spatial aggregation of YLDs among patients with KBD was observed nationwide, with hotspots concentrated in diseased counties in western China, including Shaanxi, Gansu, and Sichuan, and in the northern regions of Heilongjiang and Inner Mongolia. Among the variables, the number of health technicians was negatively correlated with the YLD rate of patients with KBD across 2 years (P<0.05). Significant geographical differences were found in the spatial distribution of YLDs, with key disease burden areas in 85 northern counties, including Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Inner Mongolia, and 145 western counties, including Shaanxi, Shanxi, and other provincial-level administrative divisions.
YLDs among patients with KBD at the county level in China demonstrated spatial clustering, with hotspots primarily in the western regions. Strengthening the recruitment and training of health professionals in high-burden, underserved areas may help improve the quality of life of patients.
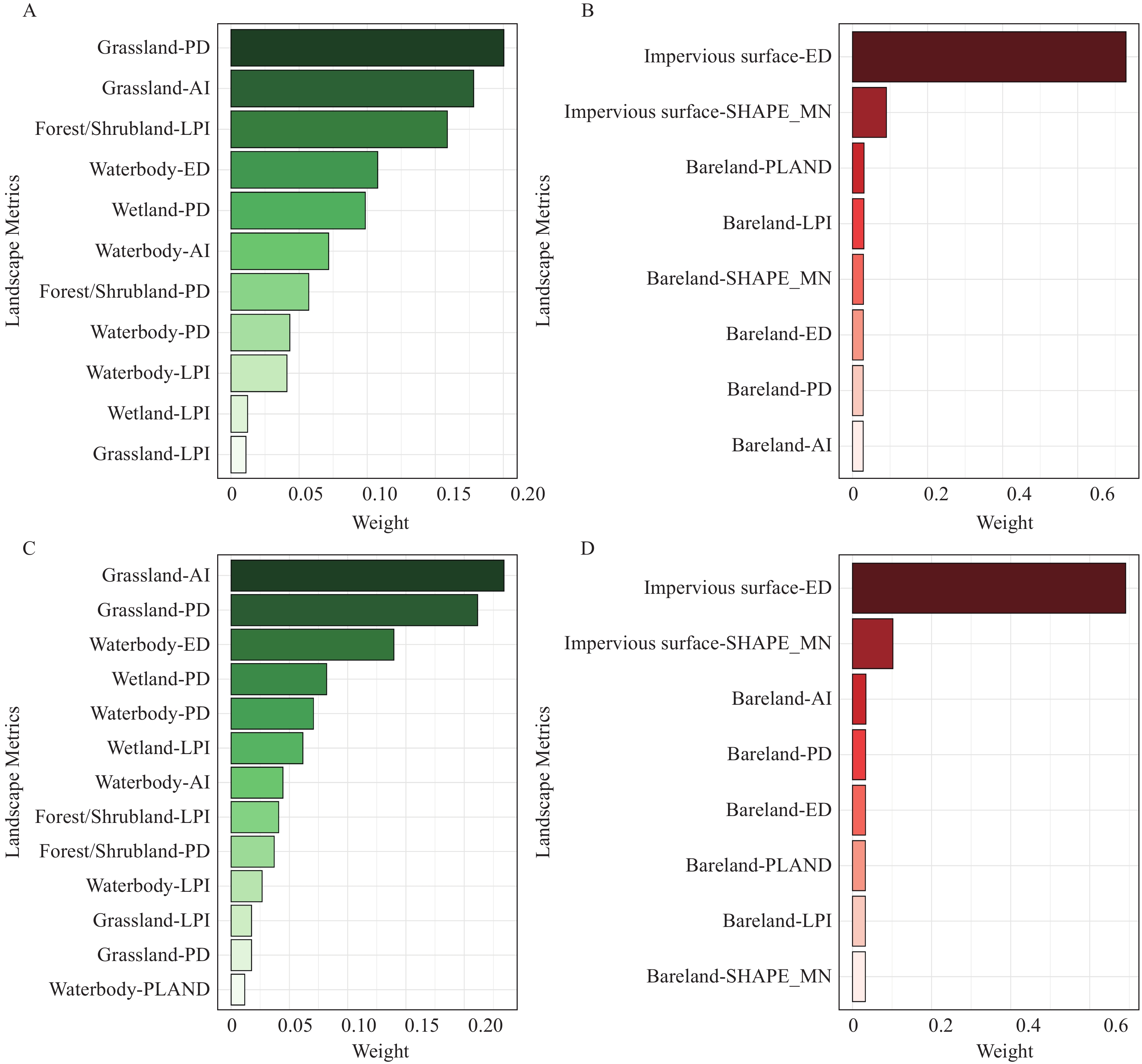
Urban landscape patterns influence population health and are traditionally measured using landscape indices. However, current indices suffer from a single-dimensional focus, multicollinearity, and limited health relevance.
Using a two-stage Generalized Weighted Quantile Sum (GWQS) regression, we developed a Landscape Pattern Health Index (LPHI), integrating composition/configuration metrics. This index revealed seasonal protective/hazard effects and represents a holistic tool for assessing urban landscape health impacts.
The LPHI identifies high-risk areas and seasonal priorities, thereby guiding targeted interventions to mitigate health risks through landscape optimization.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed