2024 Vol. 6, No. 50
Domestic Sabin-strain inactivated poliovirus vaccine (sIPV) was approved for use in China in 2015 and introduced into the national immunization schedule in a sequential schedule with oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) in May 2016. However, a comprehensive analysis describing the characteristics, occurrences, and incidences of adverse events following immunization (AEFI) with sIPV in China is lacking.
Data on sIPV doses administered and AEFI reported from 2015 to 2022 were obtained from the Chinese National Immunization Information System (CNIIS). Descriptive epidemiological methods and statistics were used to analyze and describe the characteristics, occurrences, and incidences of AEFI following sIPV in China from 2015 to 2022.
From 2015 to 2022, over 110,000,000 sIPV doses were administered, and 46,748 sIPV AEFIs were reported, resulting in an AEFI reporting rate of 42.44/100,000. Most AEFIs (46,333, 99.11%) were non-serious. Causality assessment determined 46,061 (98.53%) AEFIs were vaccine product-related reactions, including 44,001 (94.12%) common and 2,060 (4.41%) rare vaccine reactions. Among common vaccine reactions, reporting rates for fever >38.5 °C, local redness and swelling ≥2.6 cm, and local induration ≥2.6 cm were 12.02/100,000, 5.13/100,000, and 1.67/100,000, respectively. Among rare vaccine reactions, reporting rates for anaphylactic rash, thrombocytopenic purpura, and febrile convulsion were 1.56/100,000, 0.09/100,000, and 0.03/100,000, respectively.
Most reported sIPV AEFIs were non-serious, and the reporting rate of rare vaccine reactions has been very low since sIPV was approved for use in China. As sIPV remains in use in China, surveillance of AEFIs associated with this vaccine needs to be maintained.
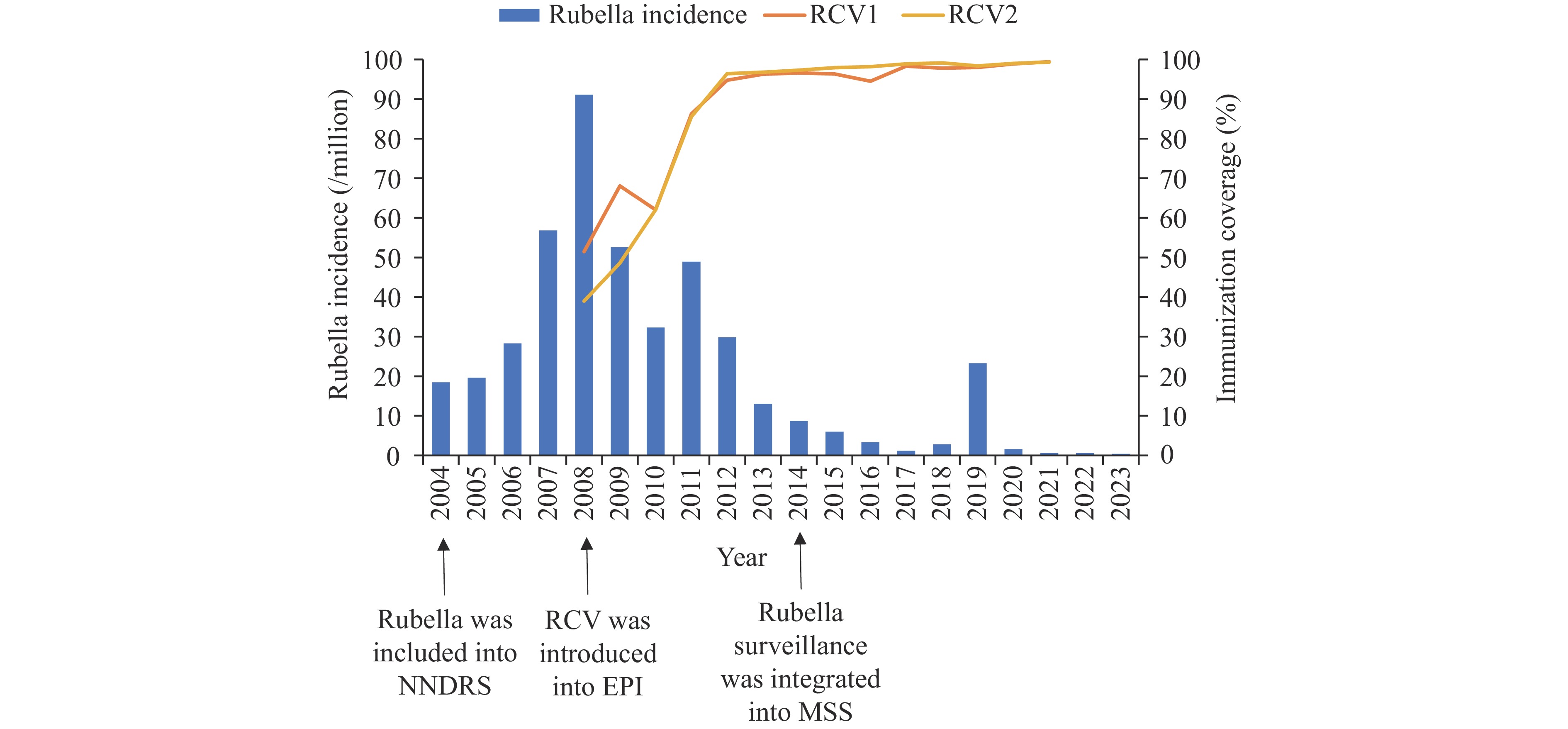
Since rubella was incorporated into the national disease surveillance system in 2004, rubella incidence has changed dramatically. This study analyzed the impact of immunization strategies on the age-specific and sex-specific incidence of rubella in China from 2004 to 2023 to inform efforts to accelerate rubella elimination.
Annual rubella-containing vaccine (RCV) coverage levels, reported rubella cases and incidence, and vaccination status of cases were obtained from the National Immunization Program Information Management System, the National Notifiable Diseases Reporting System, and the Measles Surveillance System, and used to describe temporal trends. Incidence trends and annual percent changes (APC) by age group and sex were estimated using joinpoint regression.
In 2008, RCV coverage was 51.5% for the first dose and 39.0% for the second dose, increasing to and stabilizing at 95% or above for both doses by 2012. There were 584,758 cases of rubella reported in China during 2004–2023. Joinpoint regression showed that rubella incidence initially increased, peaked in 2008, and then decreased (APC2004–2008=47.12%, APC2008–2023=–18.95%, P<0.05). Adolescents, aged 10–19 years, accounted for 67.8% of cases at a peak incidence in 2019 (APC2016–2019=103.70%, APC2016–2019=–89.76%, P<0.05); 77.8% of cases had no or unknown RCV history.
The decrease in rubella incidence is closely associated with vaccination. Nationwide inclusion of RCV significantly impacted on the prevention and control of rubella. Targeted measures to address immunization gaps and maintain high surveillance sensitivity are necessary to promote rubella elimination.
From 2010 to 2012, the incidence of adverse vaccine reactions from meningococcal vaccine (MenV) in China ranged from 8.46 to 56.30 per 100,000 doses.
From 2013 to 2021, the overall reported rate of adverse events following immunization (AEFI) of five types of market-authorized MenV-containing vaccines in China was 37.87 per 100,000 doses administered, with a reported incidence of adverse vaccine reactions of 37.39 per 100,000 doses. The reported incidence of adverse vaccine reactions was comparable to that from 2010 to 2012 and perceived to be within an acceptable range. Most rare vaccine reactions were allergic rashes, and most of these cases were transient and non-serious.
In China, the incidence of AEFI was very low, and serious abnormal reactions were extremely rare. We should continue to carry out technical training for vaccinators and on-site treatment capabilities to improve emergency treatment for anaphylactic shock and other serious events and ensure the continued safety of vaccination.
As one of the populations at high risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) require rapid and effective development of hepatitis B surface antibodies (anti-HBs).
The short-course, high-dose regimen of hepatitis B vaccination rapidly induced comparable immunological responses to the routine regimen, achieving a seroconversion rate of 88.5%, a high-response rate of 64.1%, and anti-HBs geometric mean concentrations of 824.1 mIU/mL.
The short-course, high-dose regimen represents an effective rapid immunization strategy for CKD patients, particularly when administered prior to immunosuppressive therapy. This study provides compelling evidence for optimizing immunization protocols in the CKD population.
The cost-effectiveness of vaccination strategies plays a crucial role in managing infectious diseases such as influenza within public health systems. This study evaluated the cost-effectiveness of vaccination compliance strategies by comparing an “adherence” strategy, which promoted continuous vaccination uptake, with a “volunteer” strategy through model-based simulations.
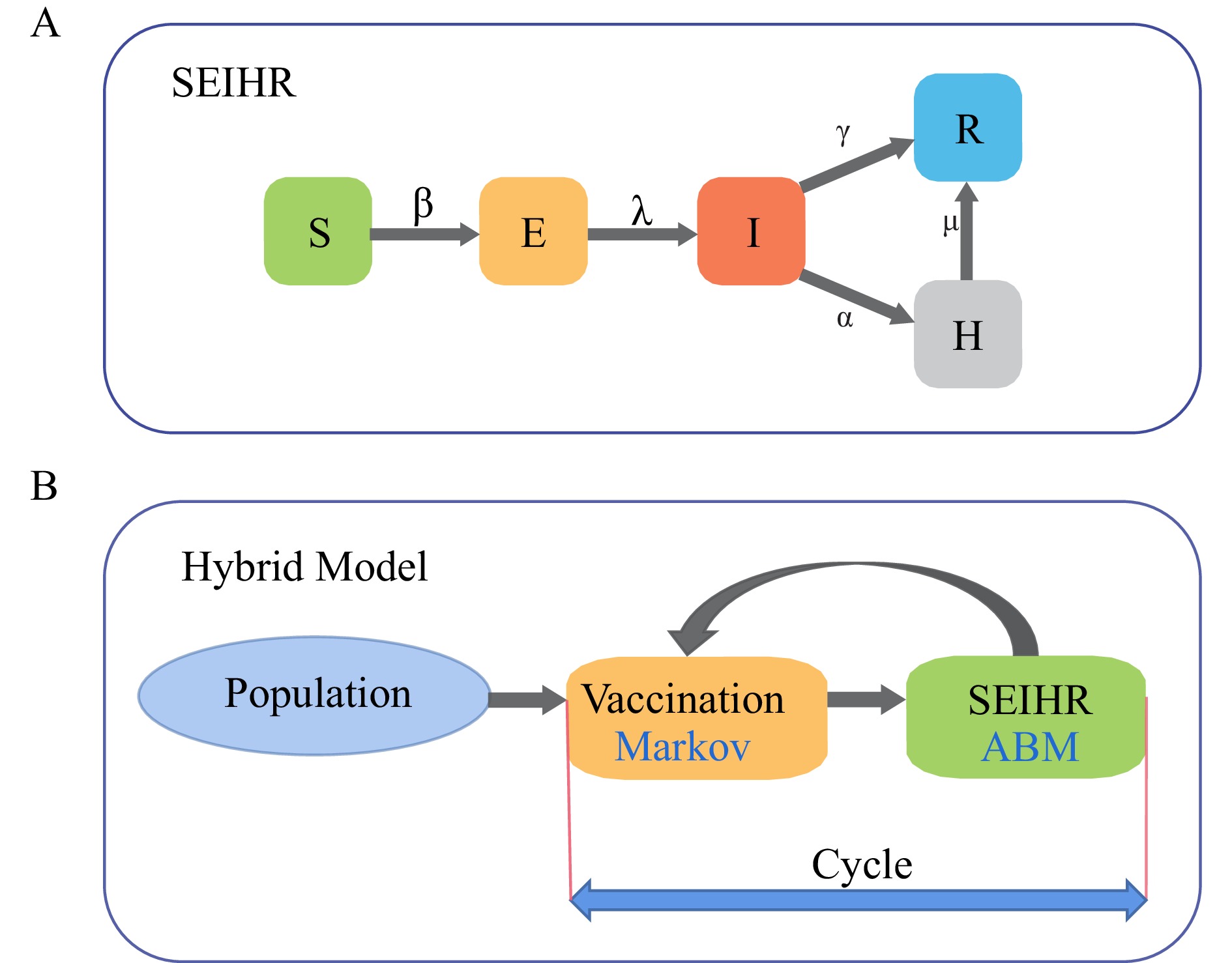
We developed a novel hybrid model that integrates continuous-time agent-based models (ABMs) with a Markov model to simulate vaccination behaviors and disease dynamics at the individual level. The model incorporated socioeconomic factors, vaccine efficacy, and population interactions to evaluate the long-term health outcomes and associated costs of different vaccination compliance strategies.
Simulation results demonstrated that the “adherence” strategy significantly enhanced vaccination coverage and reduced influenza cases, yielding an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of 33,847 CNY per quality-adjusted life year (QALY) gained, indicating superior cost-effectiveness compared to the “volunteer” strategy.
Our findings support implementing targeted influenza vaccination compliance strategies, presenting an innovative approach to strengthening public health interventions and enhancing vaccination program effectiveness. The hybrid model shows promise in informing public health policy and practice, warranting further investigation of its applications across diverse public health contexts.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed