-
Epidemic meningococcal meningitis is a severe acute infectious disease caused by Neisseria meningitis (Nm) infection, which spreads through respiratory secretions. Based on Nm-specific surface polysaccharide antigens, there are 13 serogroups (A, B, C, D, E, X, Y, Z, W135, H, I, K, and L) (1). The incidence of invasive meningococcal disease in China has declined since 1985, when large-scale vaccination with group A meningococcal vaccine (MenV) began (2). MenV vaccination programs align with broad healthcare principles, including generally accepted benefit-risk approaches to vaccination and the World Health Organization’s goal of defeating meningitis by 2030 (3). The current MenV-containing vaccines marketed in China are group A meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine (MPV-A), group A and C meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine (MPV-AC), group A and C meningococcal polysaccharide conjugated vaccine (MPCV-AC), group A, C, Y, and W135 meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine (MPV-ACYW135), and group A and group C meningococcal polysaccharide conjugated vaccine in combination with Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine (MPCV-AC/Hib). With the increasing number and diversity of MenV-containing vaccines in use, adverse events following immunization (AEFI) with these vaccines have also increased (2). AEFI is reported through the Chinese National Immunization Information System (CNIIS). Our analysis of AEFI reports found that from 2013 to 2021, the total incidence of reported AEFI for five MenV-containing vaccines was 37.87/100,000 doses administered, which falls within an acceptable range (4). Rare vaccine reactions were reported, mainly allergic rash, with incidences between 0.81 and 3.19 per 100,000 doses; most cases were transient and non-serious. Post-marketing surveillance of MenV AEFI in China should be strengthened, especially for serious allergic reactions.
We obtained the number of MenV-containing vaccine doses administered and AEFI cases reported from 2013 to 2021 from the CNIIS. The system includes basic case information (e.g., gender, age), vaccination status (e.g., vaccine type, vaccination time), and other important information (e.g., reaction onset time, event diagnosis). According to national AEFI surveillance guidelines, standard practice in China is that following verification and causality assessment by relevant professionals, AEFIs are classified as vaccine product-related reactions, coincidental events, immunization anxiety-related reactions, suspected immunization error-related reactions, or suspected vaccine quality defect-related reactions. Vaccine product-related reactions are further classified as common (usually minor) or rare (possibly serious) vaccine reactions. According to national AEFI surveillance guidelines, AEFIs that are required to be reported include fever (≥38.6 °C), local redness (>2.5 cm), induration (>2.5 cm), anaphylactic shock, allergic rash, allergic purpura, thrombocytopenic purpura, angioedema, laryngeal edema, local allergic necrosis reaction (Arthus reaction), febrile convulsions, epilepsy and ADEM, GBS, encephalitis and meningitis, polyneuritis, encephalopathy, and any other serious disease. A serious AEFI is an AEFI that is life-threatening, results in permanent or significant disability, results in organ function impairment, or leads to death.
We used descriptive epidemiological methods to analyze the characteristics of reported AEFI associated with meningococcal vaccines. Data were exported from the CNIIS into Microsoft Excel 2020 for descriptive and statistical analyses. The incidence of reported AEFI per 100,000 doses of meningococcal vaccines was calculated as the number of AEFI cases reported in a given period divided by the number of meningococcal vaccine doses administered in the corresponding period ×100,000.
From 2013 to 2021, over 65,000,000 doses of MenV-containing vaccines were administered in China. There were 248,675 MenV-containing vaccine AEFI cases reported, with an overall reporting rate of 37.87 per 100,000 doses. Of the reported AEFIs, 98.74% were classified as vaccine product-related reactions (94.85% common vaccine reactions and 5.15% rare vaccine reactions); 1.14% were coincidental events; 0.06% were immunization anxiety-related reactions; and 0.05% were other reactions, including unclassified reactions, with respective incidences of 37.39, 35.47, 1.93, 0.43, 0.02, and 0.02 per 100,000 doses (Table 1). Incidences for MPV-A, MPV-AC, MPCV-AC, MPSV-ACWY135, and MPCV-AC/Hib were 45.82/100,000 doses, 22.98/100,000 doses, 77.43/100,000 doses, 31.09/100,000 doses, and 42.95/100,000 doses, respectively. The incidences of reported common vaccine reactions and rare vaccine reactions per 100,000 doses were 45.61 and 0.20 for MPV-A; 21.59 and 1.39 for MPV-AC; 72.97 and 4.46 for MPCV-AC; 27.67 and 3.42 for MPSV-ACWY135; and 40.45 and 2.50 for MPCV-AC/Hib.
Year Serious AEFI Classification by cause Adverse vaccine reaction Coincidental events Immunization anxiety-related reactions Others Total Common vaccine reaction Rare vaccine reaction No. of cases Reporting rate No. of cases Reporting rate No. of cases Reporting rate No. of cases Reporting rate No. of cases Reporting rate No.of Cases Reporting Rate No. of cases Reporting rate 2013 127 0.18 15,975 22.33 945 1.32 235 0.33 10 0.01 8 0.01 17,174 24.01 2014 148 0.21 20,650 29.18 1,139 1.61 296 0.42 6 0.01 12 0.02 22,104 31.23 2015 149 0.20 22,806 30.06 1,279 1.69 290 0.39 13 0.02 11 0.01 24,400 32.16 2016 245 0.36 29,551 43.93 1,544 2.30 375 0.56 13 0.02 18 0.03 31,504 46.83 2017 197 0.25 34,239 42.87 1,675 2.10 363 0.45 18 0.02 15 0.02 36,315 45.47 2018 206 0.26 34,539 44.09 1,786 2.28 392 0.50 25 0.03 38 0.05 36,784 46.96 2019 211 0.28 33,602 44.76 1,991 2.66 405 0.54 21 0.03 10 0.01 36,032 47.99 2020 152 0.21 24,900 34.39 1,450 2.01 301 0.42 28 0.04 9 0.01 26,692 36.86 2021 110 0.17 16,631 25.39 832 1.27 182 0.28 12 0.02 10 0.02 17,670 26.97 Total 1,545 0.24 232,893 35.47 12,641 1.93 2,839 0.43 146 0.02 131 0.02 248,675 37.87 Abbreviation: MenV=meningococcal vaccine; AEFI=adverse events following immunization. Table 1. Number of MenV-containing vaccine AEFI and incidence per 100,000 doses administered reported in China from 2013 to 2021 by classification category.
The male-to-female ratio among reports of vaccine product-related reactions was 1.22:1. Of these reports, 68.01% involved infants, and 64.19% were for the first MenV-containing vaccine dose. Non-serious AEFIs accounted for 99.64% of reports, and 99.57% of reports documented resolution or improvement. Regarding the timing of reactions, 69.86% of common reactions and 76.05% of rare reactions occurred on the day of vaccination. Furthermore, 28.85% of common reactions and 20.75% of rare reactions occurred from days 1–3, while 1.08% and 2.49% occurred from days 4–14. Finally, 0.21% of common reactions and 0.71% of rare reactions occurred more than 15 days after vaccination (Table 2).
Characteristics MPV-A MPV-AC MPCV-AC MPV-ACWY135 MPCV-AC/Hib Total No. of
casesPercentage (%) No. of
casesPercentage (%) No. of
casesPercentage (%) No. of
casesPercentage (%) No. of
casesPercentage (%) No. of
casesPercentage (%) Gender Male 75,675 54.22 37,263 55.90 13,611 54.90 4,979 57.34 3,216 55.10 134,744 54.88 Female 63,886 45.78 29,399 44.10 11,180 45.10 3,704 42.66 2,621 44.90 110,790 45.12 Age (years) ≤1 138,174 99.01 456 0.68 22,863 92.22 73 0.84 5,422 92.89 166,988 68.01 2–6 1,344 0.96 64,172 96.26 1,747 7.05 8,079 93.04 412 7.06 75,754 30.85 ≥7 43 0.03 2,034 3.06 181 0.73 531 6.12 3 0.05 2,792 1.14 Region* Eastern 67,242 48.18 26,884 40.33 12,964 52.29 5,187 59.74 2,189 37.51 114,466 46.62 Central 42,305 30.31 25,028 37.54 9,680 39.05 2,638 30.38 2,966 50.81 82,617 33.65 Western 30,014 21.51 14,750 22.13 2,147 8.66 858 9.88 682 11.68 48,451 19.73 Year 2013 8,560 6.13 4,843 7.27 2,993 12.07 524 6.03 0 0 16,920 6.89 2014 12,874 9.22 5,380 8.07 2,822 11.38 713 8.21 0 0 21,789 8.87 2015 13,662 9.79 6,273 9.41 3,231 13.03 763 8.79 156 2.67 24,085 9.81 2016 19,884 14.25 7,962 11.94 2,146 8.66 672 7.74 431 7.38 31,095 12.66 2017 23,583 16.90 8,053 12.08 2,390 9.64 852 9.82 1,036 17.75 35,914 14.63 2018 21,891 15.69 9,235 13.85 2,606 10.51 1,028 11.84 1,565 26.81 36,325 14.79 2019 18,689 13.39 11,320 16.98 2,653 10.70 1,299 14.96 1,632 27.96 35,593 14.51 2020 12,635 9.05 7,782 11.67 3,549 14.32 1,374 15.82 1,010 17.31 26,350 10.73 2021 7,783 5.58 5,814 8.73 2,401 9.69 1,458 16.79 7 0.12 17,463 7.11 Quarter 1 26,599 19.06 13,225 19.84 4,773 19.25 1,838 21.16 1,094 18.74 47,529 19.36 2 44,085 31.59 18,568 27.86 7,849 31.66 2,556 29.44 2,062 35.33 75,120 30.59 3 41,032 29.40 17,475 26.21 7,508 30.29 2,365 27.24 1,737 29.76 70,117 28.56 4 27,845 19.95 17,394 26.09 4,661 18.80 1,924 22.16 944 16.17 52,768 21.49 Doses 1 86,815 62.21 45,609 68.42 14,588 58.84 7,136 82.18 3,448 59.07 157,596 64.19 2 52,700 37.75 20,661 30.99 9,563 38.58 1,242 14.31 1,552 26.59 85,718 34.91 3 36 0.03 207 0.31 593 2.39 181 2.08 826 14.15 1,843 0.75 4 10 0.01 185 0.28 47 0.19 124 1.43 11 0.19 377 0.15 Reaction interval time (day)† <1 102,948 73.77 42,634 63.96 16,642 67.13 6,270 72.21 3,814 65.34 172,308 70.18 1–3 34,906 25.01 23,007 34.51 7,784 31.40 2,336 26.90 1,777 30.45 69,810 28.43 4–14 1,441 1.03 845 1.27 283 1.14 57 0.66 202 3.46 2,828 1.15 ≥15 266 0.19 176 0.26 82 0.33 20 0.23 44 0.75 588 0.24 Serious AEFI Yes 363 0.26 341 0.51 85 0.34 68 0.78 29 0.50 886 0.36 No 139,198 99.74 66,321 99.49 24,706 99.66 8,615 99.22 5,808 99.50 244,648 99.64 Total 139,561 100 66,662 100 24,791 100 8,683 100 5,837 100 245,534 100 Abbreviation: MPV-A=group A meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine; MPV-AC=group A and C meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine; MPCV-AC=group A and C meningococcal polysaccharide conjugated vaccine; MPV-ACWY135=group A, C, Y, and W135 meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine; MPCV-AC/Hib=group A and group C meningococcal polysaccharide conjugated vaccine in combination with Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine; PLAD=provincial-level administrative division; XPCC=Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps.
* The eastern region includes Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Liaoning, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Shandong, Guangdong and Hainan PLADs; the central region includes Shanxi, Jilin, Heilongjiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, Henan, Hubei and Hunan PLADs; the western region includes Inner Mongolia, Guangxi, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Xizang, Shanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang PLADs; and XPCC.
† Reaction interval time: Reaction time-inoculation time.Table 2. Characteristics of MenV-containing vaccine adverse vaccine reactions reported in China from 2013 to 2021 by vaccine type.
The reported incidence of severe fever (≥38.6 °C) after MenV vaccination was 14.52/100,000 doses. The highest incidence was after the MPCV-AC vaccination (27.85/100,000 doses), followed by MPV-A (19.89/100,000 doses), MPCV-AC/Hib (17.12/100,000 doses), MPSV-ACYW135 (11.53/100,000 doses), and MPV-AC (7.78/100,000 doses). The reported incidence of serious redness and swelling (>5.0 cm) after MenV vaccination was 0.60/100,000 doses. The highest incidence was after MPCV-AC vaccination (1.84/100,000 doses), followed by MPV-ACYW135 (0.73/100,000 doses), MPCV-AC/Hib (0.62/100,000 doses), MPV-AC (0.61/100,000 doses), and MPV-A (0.45/100,000 doses). The reported incidence of serious induration (>5.0 cm) after MenV vaccination was 0.21/100,000 doses. The highest incidence was after MPCV-AC vaccination (0.64/100,000 doses), followed by MPV-ACYW135 (0.27/100,000 doses), MPCV-AC/Hib (0.26/100,000 doses), MPV-AC (0.24/100,000 doses), and MPV-A (0.13/100,000 doses).
Allergic reactions and nervous system reactions were the most frequent rare vaccine reactions reported. The most frequently reported allergic reaction was allergic rash (1.23/100,000 doses), followed by angioedema (0.05/100,000 doses), allergic purpura (0.03/100,000 doses), thrombocytopenic purpura (0.02/100,000 doses), and anaphylactic shock (0.01/100,000 doses). Laryngeal edema and Arthus reactions were reported at rates less than 0.005/100,000 doses. The incidence of reported allergic rash was highest for MPCV-AC (3.19/100,000 doses), followed by MPV-ACYW135 (1.87/100,000 doses), MPV-A (1.37/100,000 doses), MPCV-AC/Hib (1.32/100,000 doses), and MPV-AC (0.81/100,000 doses). Febrile convulsion was the most frequent nervous system reaction reported (0.05/100,000 doses). The incidence of reported febrile convulsions was highest for MPCV-AC (0.12/100,000 doses), followed by MPV-A and MPV-ACYW135 (0.06/100,000 doses), and MPV-AC and MPCV-AC/Hib (0.03/100,000 doses). Other nervous system reactions — GBS, ADEM, epilepsy, syncope, polyneuritis, encephalitis, and meningitis — were reported at rates less than 0.005/100,000 doses (Figure 1).
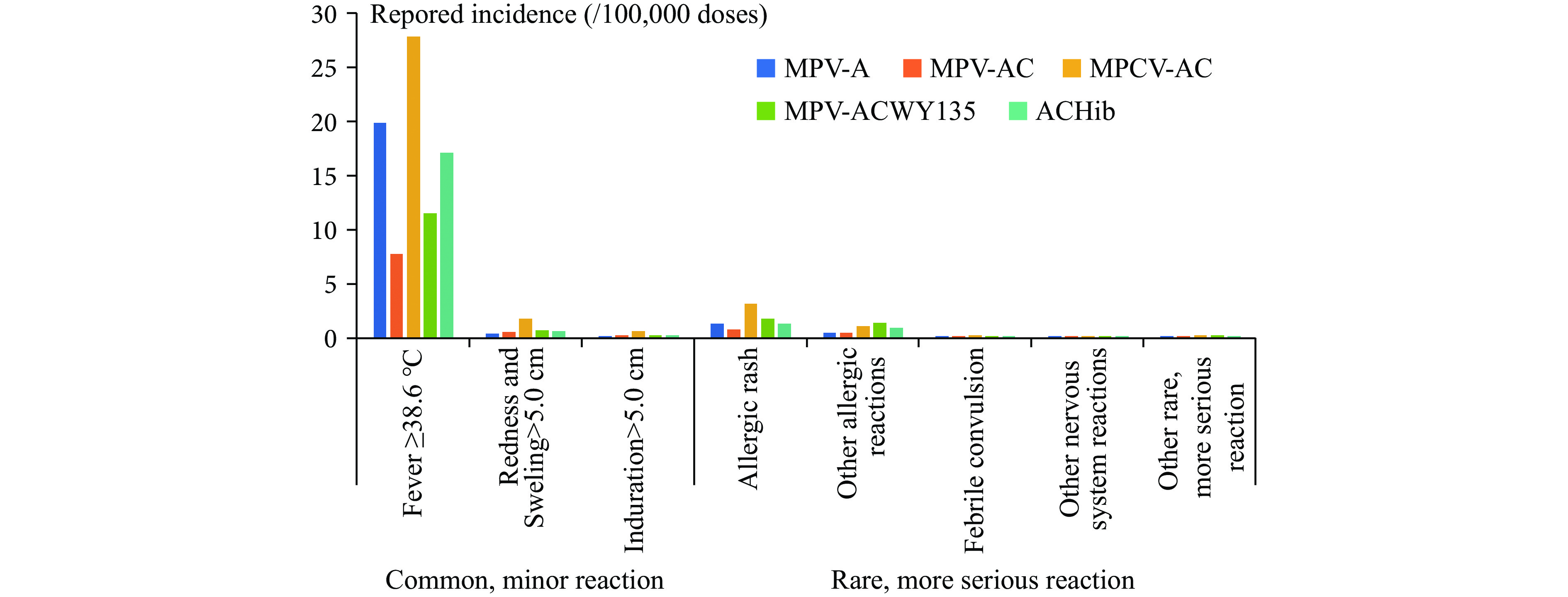 Figure 1.
Figure 1.Incidence (/100,000 doses) of reported common vaccine reactions and rare vaccine reactions after administration of any of five MenV-containing vaccines.
Abbreviation: MPV-A=group A meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine; MPV-AC=group A and C meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine;MPCV-AC=group A and C meningococcal polysaccharide conjugated vaccine; MPV-CWY135=group A, C, Y, and W135 meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine; MPCV-AC/Hib=group A and group C meningococcal polysaccharide conjugated vaccine in combination with Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine. -
Our analysis of MenV-containing vaccine AEFI reported to the CNIIS from 2013 to 2021 found that the incidence of common vaccine reactions ranged from 21.59 to 72.97 per 100,000 doses, while the incidence of rare vaccine reactions ranged from 0.20 to 4.46 per 100,000 doses, depending on the specific MenV-containing vaccine administered. The reported incidence of adverse vaccine reactions was comparable to that observed from 2010 to 2012 and was perceived to be within an acceptable range.
In 2008, China established an online AEFI surveillance system to report suspected vaccine-related reactions or events following immunization, laying the foundation for vaccine post-marketing pharmacovigilance. As the system continuously improved and strengthened, national AEFI reporting levels increased annually (3-4), consistent with global AEFI monitoring improvements (5). Our study found that the reported incidence of MenV-containing vaccine AEFI reports also increased annually from 2013 to 2019. However, the annual incidence of AEFI with MenV-containing vaccines, as well as the number of vaccination doses and AEFI reports, decreased annually in 2020–2021; this decrease was likely related to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. In early 2020, vaccination work — other than birth doses of hepatitis B and BCG vaccines and rabies postexposure prophylaxis — was suspended in most of China, and the number of reported AEFIs decreased significantly. The COVID-19 epidemic situation was under strict prevention and control, and the subsequent mass emergency use of COVID-19 vaccines impacted AEFI surveillance. Monitoring in other countries has shown that the sensitivity of AEFI reporting is usually high during the early stages of vaccine introduction or when new recommendations are implemented and will decrease and stabilize as vaccination becomes routine (3-4). In the context of mass vaccination with the new COVID-19 vaccines, patients and healthcare providers may be more concerned about COVID-19 vaccines than other vaccines, increasing reporting sensitivity for COVID-19 vaccination and biasing relative incidences.
This study found that the percentage of MenV-containing vaccine AEFI was highest in the eastern region and lowest in the western region. The highest incidence was for MPCV-AC, followed by MPV-A, MPCV-AC/Hib, MPV-ACYW135, and MPV-AC. These incidence variations may be related to parental sensitivity to AEFI, with parents expressing more concern about non-NIP vaccines. Additionally, differences may be related to the various ages at vaccination. The starting age for MPCV-AC vaccination is 3 months, earlier than other MenV-containing vaccines. Younger age is associated with a greater probability of reaction. The estimated incidence of total and common vaccine reactions reported for MPV-A was higher than for MPV-AC, while the estimated incidence of rare vaccine reactions was lower for MPV-A than MPV-AC. This incidence difference may be related to the different ages of vaccination. The starting age for MPV-A vaccination is 6 months, while MPV-AC vaccination begins at 3 years. Compared with the WHO’s expected incidence of allergic reactions of less than 0.1/100,000 doses (1,6), the incidence findings for both MPV-A and MPV-AC were lower than those expected by the WHO and reported in relevant domestic and international studies. In China, MPCV-AC, MPV-ACYW135, and MPCV-AC/Hib are non-NIP vaccines, meaning families can select these vaccines as substitutes for the program MenV-containing vaccines but must pay for them out-of-pocket. The reported incidence of all AEFI, common vaccine reactions, and rare vaccine reactions for MPCV-AC and the overall incidence found in this study was higher than respective incidences for MPV-ACYW135 and MPCV-AC/Hib but lower than incidences reported in relevant domestic and international studies (7-8).
Of common vaccine reactions, the incidence of fever was the greatest, followed by local redness and local induration. The most common of the rare vaccine reactions was allergic rash, and most cases were transient and non-serious. Febrile convulsion was the most common neurological reaction. Anaphylactic shock, laryngeal edema, GBS, ADEM, and other serious cases were all very rare, with estimated reported incidences of lower than 0.01/100,000 doses. Most reactions followed the first dose of a MenV series, consistent with previous experience (9). Most rare events recovered spontaneously or resolved after treatment. Evidence from our analyses augments clinical trials showing that these five types of MenV-containing vaccine have good immunogenicity and acceptable incidences of AEFI (7-8).
Vaccine antigens, residual animal proteins, antibacterial agents, and preservatives can cause allergic reactions. Allergic rashes are frequent in early childhood and this will make vaccination prone to coincidence with vaccination, necessitating investigation to determine whether the relation between rash and vaccination is causal or coincidental. Febrile convulsion is a relatively frequent event in infants and very young children who have high or rapidly increasing fever, usually from acute viral infections. The reported incidence of high fevers was relatively high, and therefore causal relationships between vaccination and febrile convulsion needs further study (3). Other neurological reactions, including ADEM, GBS, encephalitis, and meningitis, have insufficient evidence of causal association with vaccines (4,10).
In China, the incidence of MenV-containing vaccine AEFI was very low and serious abnormal reactions were extremely rare. We should continue to carry out the technical training of vaccinators and on-site emergency treatment capabilities, focusing on treatment for anaphylactic shock and other serious events to ensure the safety of vaccination.
-
We thank the staff of the provincial, prefectural and county CDCs and all vaccination clinics for conducting the adverse event surveillance. We thank Lance Rodewald, senior consultant of China CDC, for his comments and recommendations for editing the manuscript.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:




