2024 Vol. 6, No. 40
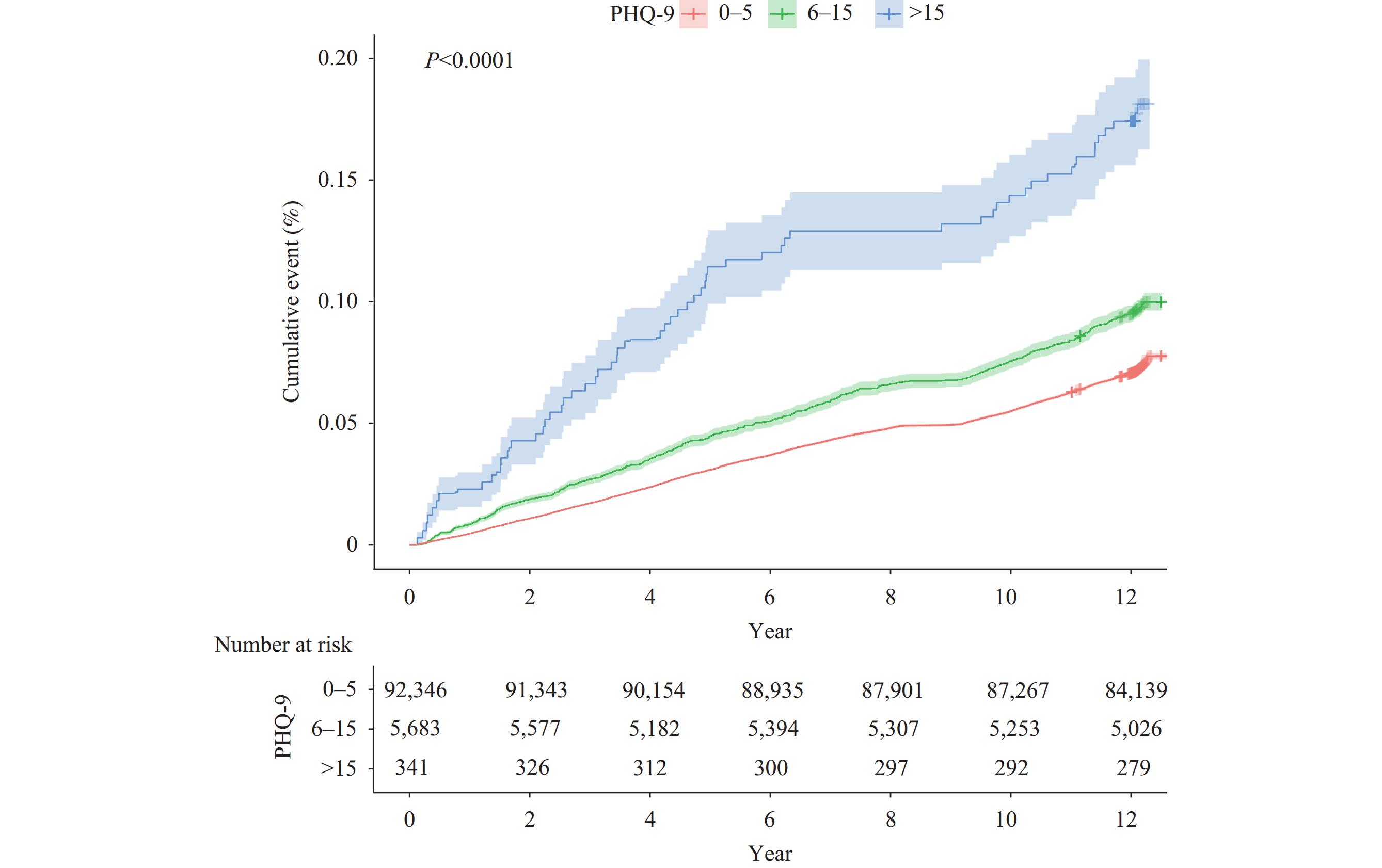
Depression is linked to higher all-cause and cardiovascular mortality rates, but its effects on specific subgroups and non-cardiovascular mortality in the Chinese population remain unclear.
Both severe and mild to moderate depression were found to elevate mortality rates among the Chinese population. The impact was particularly notable among males, urban residents, younger individuals, and those with higher education levels. Depression exhibited a stronger connection with fatalities related to suicide and non-suicidal injuries.
Individuals experiencing mild depression require healthcare attention to avoid negative consequences. Enhanced physical and psychological support is particularly crucial for high-risk subgroups.
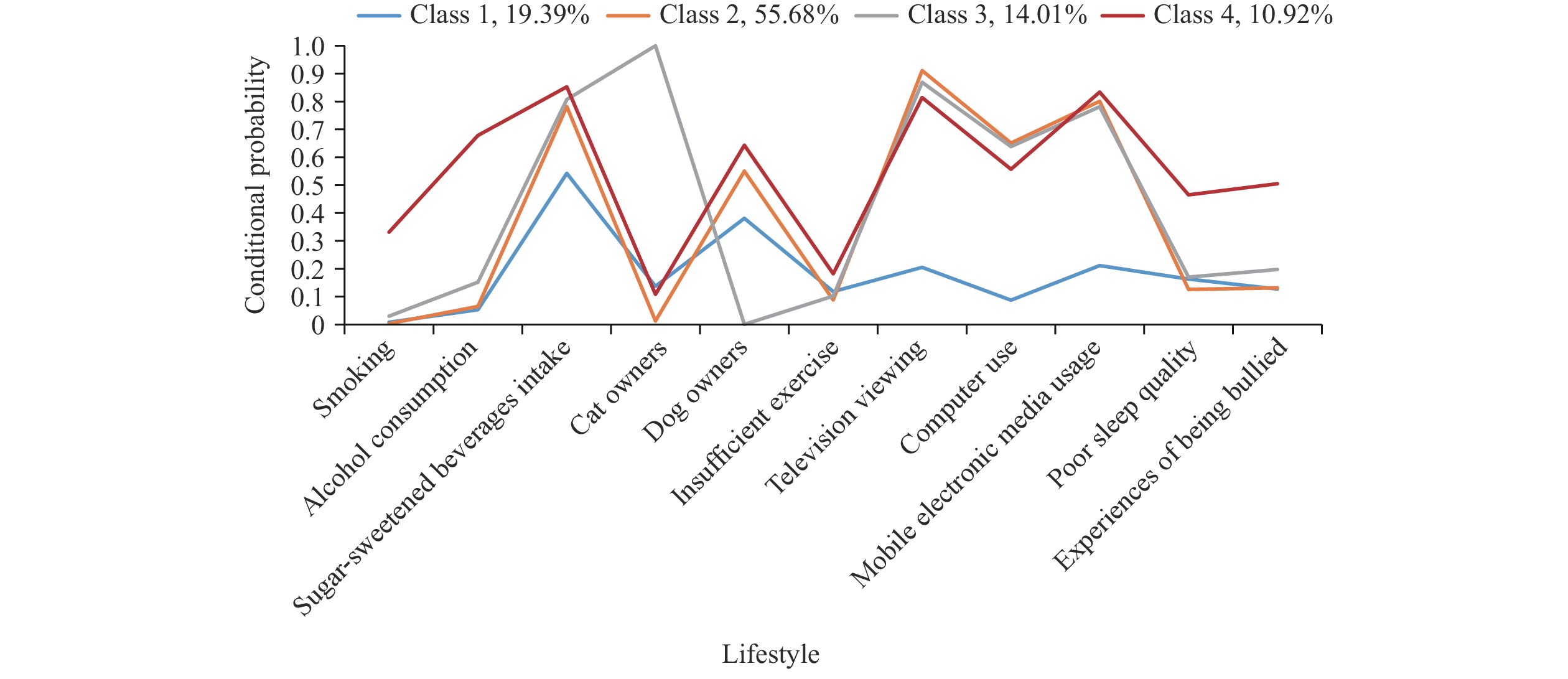
Interventions aimed at modifying lifestyle behaviors can effectively reduce the risk of depression among adolescents. These lifestyle behaviors tend to be interconnected; thus, changes to one behavior can often lead to changes in others, usually occurring simultaneously.
Adolescents from Jiangsu Province displayed distinct lifestyle patterns, with those engaging in multiple specific behaviors, such as excessive consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages and prolonged screen time, showing increased odds of depression.
Early implementation of anti-depression interventions in adolescents should be advocated and prioritized, particularly targeting multiple high-risk lifestyles.
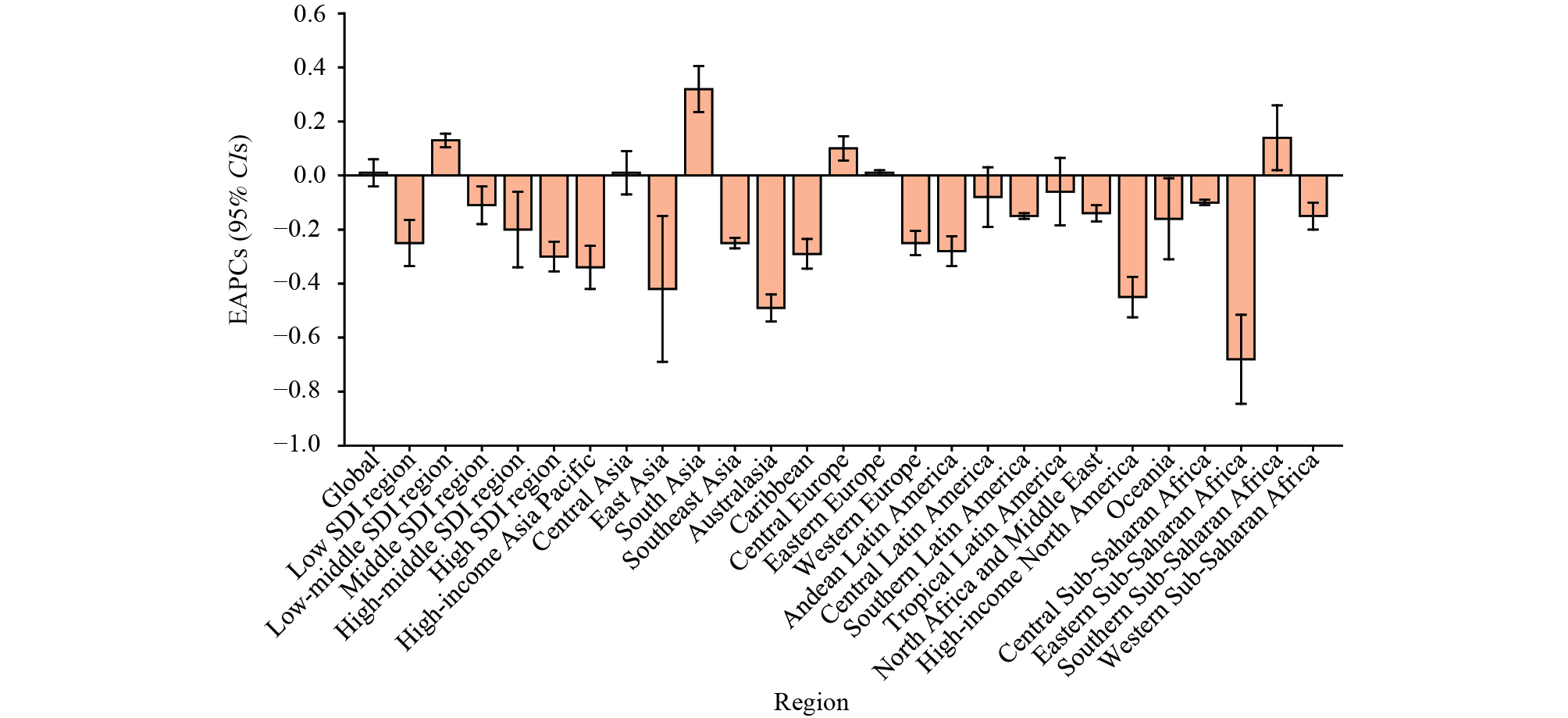
Genital herpes infection is a chronic condition that can cause recurrent symptoms, significantly affecting both quality of life and sexual relationships. However, there is currently no available data on the global trends and regional variations in the incidence of genital herpes among individuals of reproductive age.
From 1990 to 2021, there was a 51.97% increase in global incident cases of genital herpes among individuals aged 15–49 years. The incidence rates also rose in low-middle socio-demographic index region, South Asia, Southern Sub-Saharan Africa, and Central Europe. Among these regions, countries in Southern Sub-Saharan Africa experienced the highest burden of genital herpes among individuals aged 15–49 years.
Given the rise in global incident cases and incidence rates in some regions among individuals of reproductive age from 1990 to 2021, it is imperative to prioritize the implementation of preventive strategies and interventions for genital herpes infection. This includes a significant focus on the development of vaccines.
Previous studies indicate that an increase in physical activity can diminish the risk of mortality. However, the relationship between longitudinal changes in physical activity and health improvement among Chinese adults with or without hypertension has not been explored.
This study found that increasing or maintaining moderate to high physical activity levels reduced the risk of all-cause mortality, irrespective of the baseline physical activity level. In addition, the beneficial effects were particularly pronounced in people with hypertension.
It may be beneficial to encourage adults in China, especially those with hypertension, to actively increase physical activity and deter the issue of physical inactivity that accompanies aging.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed