2024 Vol. 6, No. 39
Health-adjusted life expectancy (HALE) is a crucial indicator of global health, which is strongly correlated with the socio-demographic index (SDI) and population dynamics.
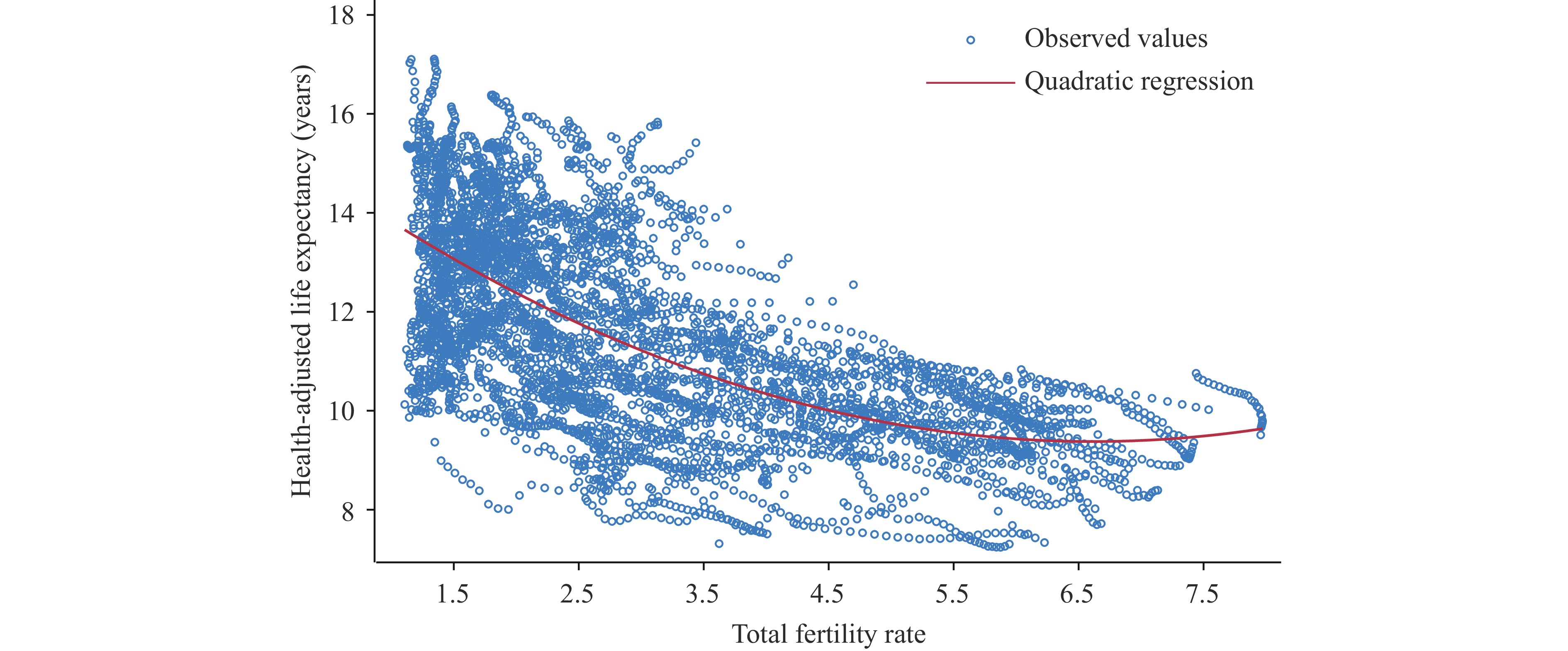
This study revealed that the correlation between total fertility rate (TFR) and HALE of older adults varies across countries with different SDI levels, offering valuable insights for the development of more targeted health promotion programs and interventions.
Different health interventions should be tailored to countries with different levels of SDI. In countries with both low fertility rates and low SDI, advanced measures are needed to address the challenge of an aging population that may live longer but face poorer health in the future.
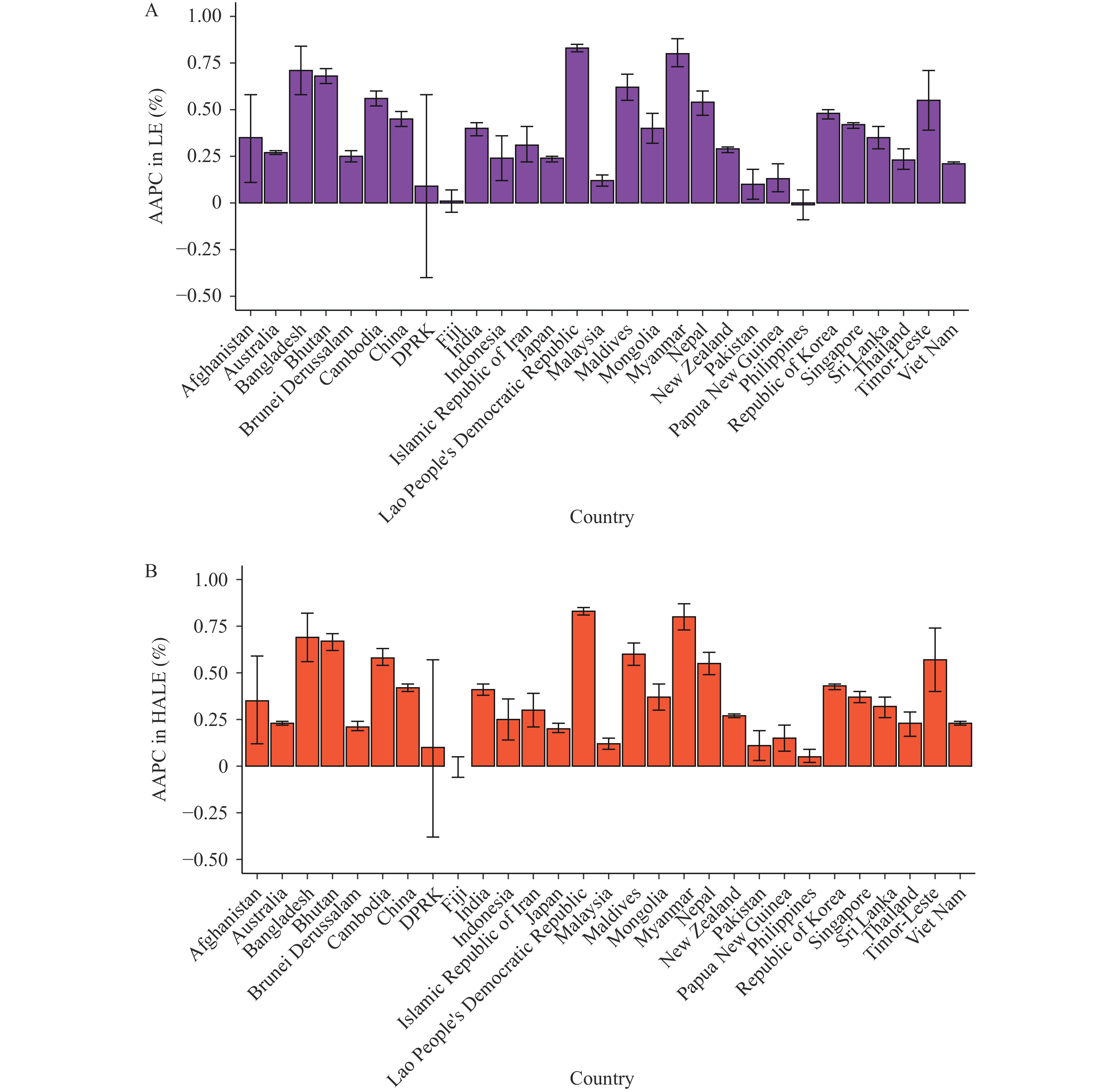
The Asia-Pacific region is the most populous and diverse globally, encompassing nations with both the longest and shortest life expectancies (LE). However, less is known about the health-adjusted life expectancy (HALE) situation in this region.
This study found diversity in the levels and trends of HALE among countries in the Asia-Pacific region, with HALE in 2021 ranging from 49.87 years in Afghanistan to 74.96 years in Singapore. The largest HALE increase from 1990 to 2021 was observed in the Lao People’s Democratic Republic and the smallest in Fiji. HALE continually increased as SDI increased, but different patterns of HALE across countries varied by SDI level.
The diversity among these countries provides a prerequisite and scientific basis for promoting the achievement of health goals in the Asia-Pacific region through multilateral and bilateral cooperation.
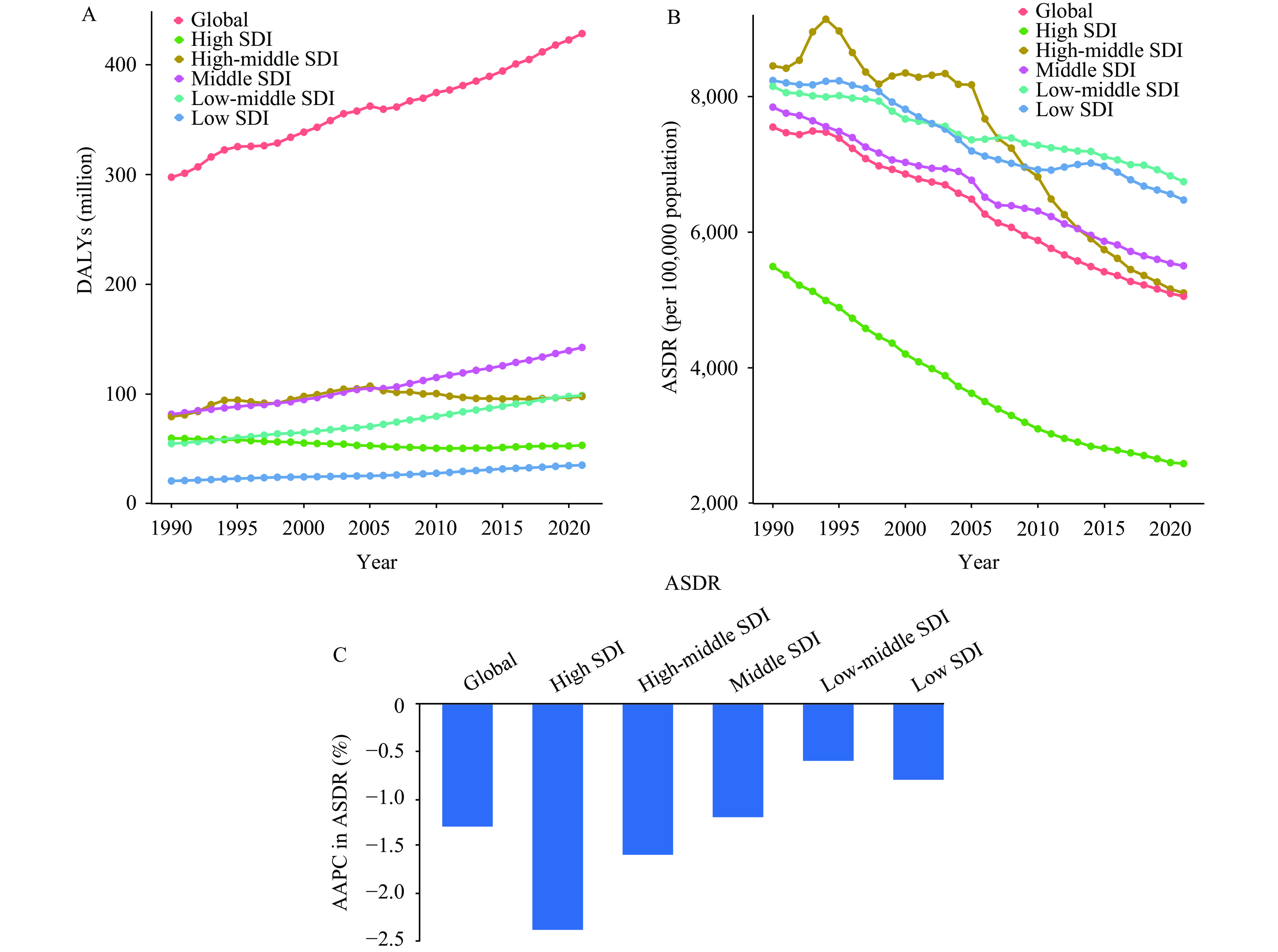
The influence of population aging on the disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD) is acknowledged, yet the magnitude of this impact remains unclear.
This research quantified the influence of population aging on CVD DALYs from 1990 to 2021 through decomposition analysis. The findings revealed that the proportion of DALYs attributable to aging varied widely, ranging from ‒77.0% to 148.9% across 204 countries. There was significant variation in the attributed DALY proportions among different countries or territories and types of CVD. Ischemic heart disease and stroke emerged as the leading contributors to DALYs influenced by aging.
Globally, the association of population aging with increased CVD DALYs underscores the critical need for enhancing health systems to cater to the needs of older adults. Mitigating the burden of CVD DALYs linked to demographic aging can be achieved by investing in resources and adjusting fertility policies.
The proportion of elderly living alone in China is approximately 10%. Living away from family poses enormous challenges for older adults.
Compared to those living with family, elderly individuals living alone exhibit a lower registration rate with general practitioners and have less social support.
While the current health service system for elderly people living alone is working relatively well, there is a need for additional programs to enhance social support and improve their social well-being.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed