-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2) are large double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Both types can lead to the development of genital herpes, characterized by recurring and often painful genital sores, also known as genital ulcer disease (1–2). HSV-1 is primarily transmitted through oral-to-oral contact, causing oral herpes, and can also be transmitted through oral-genital contact during oral sex, resulting in genital herpes, although this occurs less frequently (3). HSV-2 is predominantly sexually transmitted and causes genital herpes (3). In 2016, approximately 66.6% of the global population under the age of 50 was estimated to have HSV-1 infection, while 13.2% of individuals aged 15–49 years had HSV-2 infection (4). Genital herpes is a significant global health concern, not only due to the physical pain and discomfort experienced by those affected but also because of the social consequences that can profoundly impact sexual and reproductive health. Currently, there is a lack of comprehensive global and regional data on the incidence of genital herpes, particularly among key populations such as reproductive-age individuals.
Data on annual incident cases and incidence rates of genital herpes among the population aged 15–49 years from 1990 to 2021, disaggregated by sex and location, were obtained from the Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD). The GBD utilized the DisMod-MR 2.1 tool, a Bayesian meta-regression model, to generate final estimates of genital herpes incidence and prevalence by imposing coherence between different data parameters (5). The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes used for genital herpes were A60 (ICD-10 code) and 054.1 (ICD9) (5). To assess temporal trends, we computed the percentage changes in incident cases and calculated the estimated annual percentage changes (EAPCs) in incidence rates of genital herpes among individuals aged 15–49 years between 1990 and 2021 at the global, regional, and national levels. The percentage changes were determined using the formula: percentage change =
$ \dfrac{\mathrm{I}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{d}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{t}\; \mathrm{c}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{s}\; \mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\; 2021-\mathrm{ }\mathrm{I}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{d}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{ }\mathrm{c}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{s}\; \mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\; 1990}{\mathrm{I}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{d}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{t}\; \mathrm{c}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{s}\; \mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\; 1990}\times $ 100%. The EAPC, widely used as a measure of rate trends over a defined time period, was derived through fitting a regression line to the natural logarithm of the incidence rate, represented by y=α + βx + ε, where y=ln (incidence rate) and x=calendar year. The EAPC was calculated as$ 100\times {(e}^{\beta }-1) $ , and its 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated to reflect the temporal trend. Statistical analyses were conducted using SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA). A two-tailed P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.Globally, the number of new cases of genital herpes among individuals aged 15–49 years increased by 51.97% from 1990 to 2021. However, the incidence rate remained stable during this period, with rates of 0.87% in 1990 and 0.91% in 2021 (Table 1 and Figure 1). In 2021, there were a total of 35.81 million new cases of genital herpes worldwide, with 61.46% (22.01 million) occurring in females and the remaining 38.54% (13.80 million) in males (Table 1). The incidence rate of genital herpes in females aged 15–49 years was nearly twice as high as that in males of the same age group in 2021, with rates of 1.13% and 0.69%, respectively (Table 1). The incidence rates increased in males aged 15–49 years (EAPC=0.07; 95% CI: 0.00, 0.13) and remained stable in females aged 15–49 years from 1990 to 2021 (Table 1).
Characteristics 1990 2021 1990–2021 Incident cases in million (95% UI) Incidence rate, % (95% UI) Incident cases in million (95% UI) Incidence rate, % (95% UI) Percentage change in incident cases (%) EAPC in incidence rates (95% CI) Overall 23.56 (19.76, 27.59) 0.87 (0.73, 1.02) 35.81 (29.88, 41.97) 0.91 (0.76, 1.06) 51.97 0.01 (−0.04, 0.06) Sex Male 8.93 (7.34, 10.59) 0.65 (0.53, 0.77) 13.80 (11.29, 16.37) 0.69 (0.56, 0.82) 54.50 0.07 (0.00, 0.13) Female 14.63 (12.42, 17.02) 1.09 (0.93, 1.27) 22.01 (18.43, 25.63) 1.13 (0.95, 1.31) 50.43 −0.02 (−0.07, 0.02) SDI region Low 3.00 (2.55, 3.44) 1.36 (1.15, 1.56) 7.33 (6.15, 8.46) 1.35 (1.13, 1.56) 144.13 −0.25 (−0.33, −0.16) Low-middle 4.46 (3.71, 5.22) 0.81 (0.67, 0.95) 8.75 (7.29, 10.24) 0.86 (0.72, 1.01) 96.03 0.13 (0.07, 0.20) Middle 8.27 (6.94, 9.69) 0.91 (0.76, 1.06) 11.56 (9.61, 13.59) 0.92 (0.77, 1.08) 39.70 −0.11 (−0.18, −0.04) High-middle 4.07 (3.35, 4.83) 0.72 (0.59, 0.86) 4.51 (3.66, 5.42) 0.72 (0.58, 0.86) 11.03 −0.20 (−0.34, −0.06) High 3.74 (3.13, 4.41) 0.81 (0.68, 0.96) 3.63 (2.94, 4.33) 0.72 (0.59, 0.86) −2.87 −0.30 (−0.36, −0.25) GBD region High-income Asia Pacific 0.63 (0.55, 0.71) 0.68 (0.59, 0.77) 0.44 (0.36, 0.53) 0.57 (0.46, 0.68) −29.23 −0.34 (−0.42, −0.26) Central Asia 0.21 (0.17, 0.25) 0.63 (0.51, 0.75) 0.31 (0.25, 0.37) 0.63 (0.51, 0.76) 46.81 0.01 (−0.07, 0.09) East Asia 4.70 (3.84, 5.64) 0.68 (0.56, 0.82) 4.78 (3.88, 5.76) 0.69 (0.56, 0.84) 1.77 −0.42 (−0.69, −0.15) South Asia 2.61 (2.11, 3.12) 0.49 (0.40, 0.59) 5.44 (4.41, 6.53) 0.54 (0.44, 0.65) 108.06 0.32 (0.24, 0.41) Southeast Asia 2.42 (2.02, 2.83) 1.02 (0.85, 1.20) 3.58 (2.97, 4.25) 0.97 (0.80, 1.15) 48.01 −0.25 (−0.27, −0.23) Australasia 0.09 (0.07, 0.11) 0.83 (0.69, 1.02) 0.09 (0.08, 0.11) 0.66 (0.54, 0.78) 5.79 −0.49 (−0.90, −0.08) Caribbean 0.28 (0.24, 0.33) 1.55 (1.29, 1.81) 0.35 (0.29, 0.40) 1.45 (1.21, 1.69) 22.86 −0.29 (−0.34, −0.23) Central Europe 0.27 (0.22, 0.32) 0.43 (0.35, 0.51) 0.23 (0.18, 0.27) 0.43 (0.34, 0.52) −14.87 0.10 (0.05, 0.14) Eastern Europe 0.95 (0.78, 1.13) 0.86 (0.71, 1.03) 0.78 (0.63, 0.93) 0.81 (0.66, 0.97) −18.03 0.01 (−0.08, 0.10) Western Europe 1.21 (1.00, 1.44) 0.62 (0.52, 0.75) 1.09 (0.88, 1.29) 0.58 (0.47, 0.68) −10.15 −0.25 (−0.30, −0.21) Andean Latin America 0.32 (0.27, 0.36) 1.69 (1.46, 1.92) 0.56 (0.47, 0.65) 1.60 (1.36, 1.86) 77.86 −0.28 (−0.34, −0.23) Central Latin America 1.18 (1.00, 1.34) 1.44 (1.22, 1.65) 1.79 (1.49, 2.07) 1.34 (1.12, 1.56) 51.95 −0.08 (−0.19, 0.03) Southern Latin America 0.27 (0.25, 0.30) 1.12 (1.01, 1.22) 0.37 (0.31, 0.44) 1.08 (0.90, 1.26) 36.20 −0.15 (−0.16, −0.14) Tropical Latin America 1.45 (1.22, 1.69) 1.85 (1.55, 2.15) 2.09 (1.76, 2.43) 1.75 (1.47, 2.03) 44.58 −0.06 (−0.18, 0.07) North Africa and Middle East 1.18 (0.97, 1.38) 0.73 (0.61, 0.86) 2.32 (1.90, 2.76) 0.69 (0.57, 0.83) 97.44 −0.14 (−0.17, −0.11) High-income North America 1.64 (1.35, 1.95) 1.10 (0.91, 1.31) 1.58 (1.30, 1.88) 0.94 (0.77, 1.12) −3.51 −0.45 (−0.53, −0.38) Oceania 0.04 (0.03, 0.05) 1.32 (1.09, 1.57) 0.09 (0.08, 0.11) 1.32 (1.09, 1.55) 120.11 −0.16 (−0.31, −0.01) Central Sub-Saharan Africa 0.55 (0.48, 0.62) 2.26 (1.95, 2.56) 1.44 (1.24, 1.63) 2.20 (1.91, 2.49) 160.48 −0.10 (−0.11, −0.09) Eastern Sub-Saharan Africa 1.69 (1.45, 1.92) 2.02 (1.73, 2.30) 3.99 (3.35, 4.61) 1.91 (1.60, 2.20) 136.82 −0.68 (−0.84, −0.51) Southern Sub-Saharan Africa 0.55 (0.46, 0.64) 2.14 (1.80, 2.47) 0.92 (0.79, 1.05) 2.14 (1.82, 2.44) 67.15 0.14 (0.02, 0.26) Western Sub-Saharan Africa 1.34 (1.12, 1.55) 1.56 (1.30, 1.82) 3.56 (2.98, 4.15) 1.55 (1.30, 1.81) 166.11 −0.15 (−0.20, −0.10) Abbreviation: CI=confidence interval; EAPC=estimated annual percentage change; GBD=Global Burden of Disease Study; SDI=socio-demographic index; UI=uncertainty interval. Table 1. Incident cases and incidence rates of genital herpes among individuals aged 15–49 years in 1990 and 2021, and trends from 1990 to 2021.
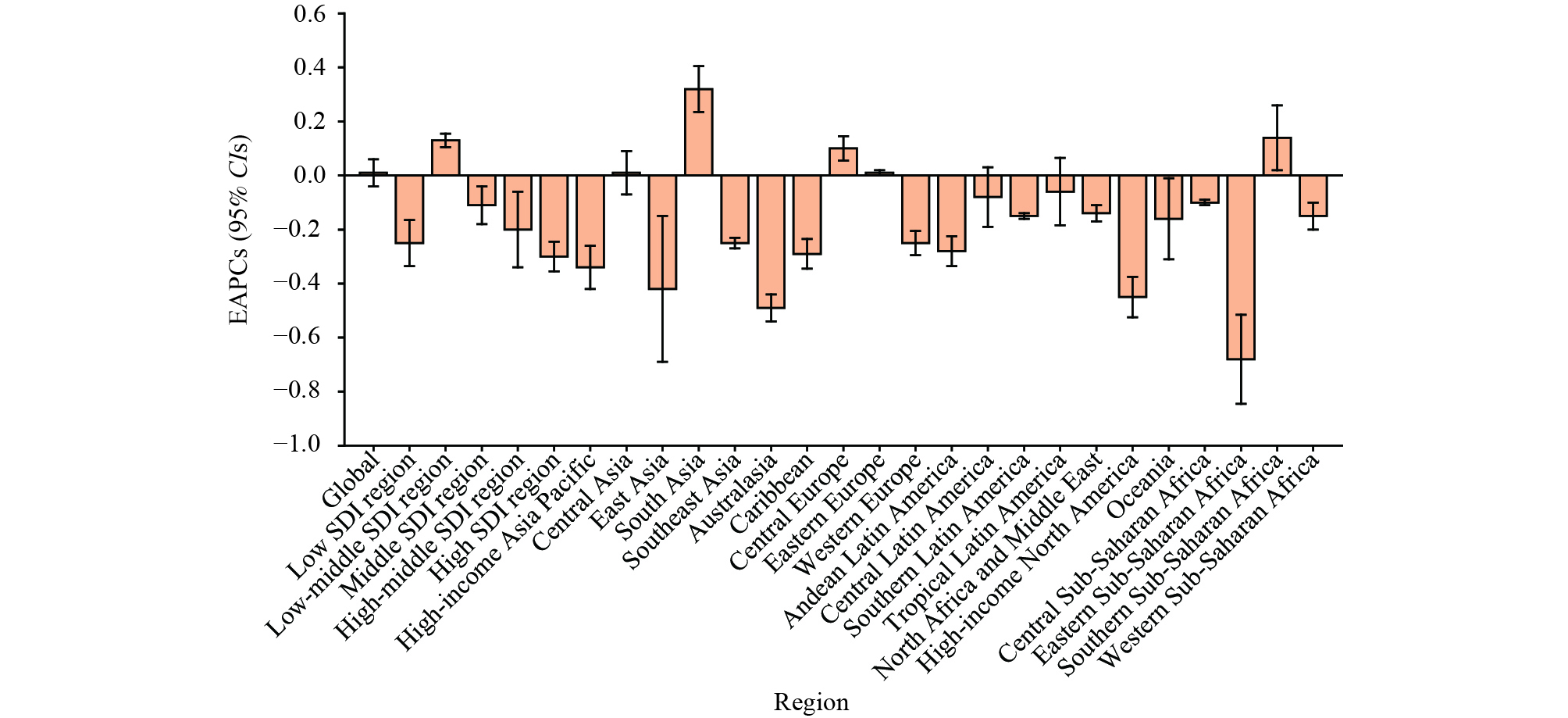 Figure 1.
Figure 1.EAPCs in incidence rates of genital herpes among the population aged 15–49 years between 1990 and 2021 at the regional level.
Abbreviation: CI=confidence interval; EAPCs=estimated annual percentage changes; SDI=socio-demographic index.The incident cases of genital herpes among the population aged 15–49 years increased in low, low-middle, middle, and high-middle socio-demographic index (SDI) regions from 1990 to 2021. Specifically, the incidence rates increased in low-middle SDI region (EAPC=0.13; 95% CI: 0.07, 0.20) during this period (Table 1 and Figure 1). Among the 21 GBD regions, approximately half of the global incident cases of genital herpes in 2021 were concentrated in South Asia (5.44 million), East Asia (4.78 million), Eastern Sub-Saharan Africa (3.99 million), and Southeast Asia (3.58 million). The incidence rates of genital herpes in 2021 varied across regions, ranging from 0.43% in Central Europe to 2.20% in Central Sub-Saharan Africa. From 1990 to 2021, there was a significant increasing trend in the incidence rates of genital herpes in South Asia (EAPC=0.32; 95% CI: 0.24, 0.41), Southern Sub-Saharan Africa (EAPC=0.14; 95% CI: 0.02, 0.26), and Central Europe (EAPC=0.10; 95% CI: 0.05, 0.14). In contrast, the incidence rates remained stable in Eastern Europe, Tropical Latin America, Central Asia, and Central Latin America. The remaining 14 GBD regions experienced a significant decreasing trend between 1990 and 2021 (Table 1 and Figure 1).
Across 204 countries and territories, the absolute number of incident cases of genital herpes among the population aged 15–49 years in China (4.65 million), India (4.41 million) and Brazil (2.03 million) accounted for approximately one-third of the global incident cases (35.81 million) in 2021. Over the three decades from 1990 to 2021, there was an upward trend in cases across 150 countries and territories, with Qatar experiencing the highest surge at a 631.76% increase, followed by the United Arab Emirates at 412.35%. The incidence rates of genital herpes within the same age demographic also exhibited substantial global variation, with Malawi (2.35%), Lesotho (2.32%), and Uganda (2.31%) having the highest incidence rates in 2021. A closer examination of the trends over the 30-year period reveals a decrease in the incidence rates in 134 countries or territories, with Uganda demonstrating the most substantial decline (EAPC= −1.59; 95% CI: −1.82, −1.36). On the other hand, 28 countries or territories, including Hungary (EAPC=0.81; 95% CI: 0.50, 1.12) and Canada (EAPC=0.66; 95% CI: 0.36, 0.95) with the greatest rise, exhibited an increase in incidence rates. The rates remained stable in 42 additional countries or territories, such as Spain, Oman, and Yemen, during the same timeframe.
-
Genital herpes infections are characterized by lifelong viral reactivation and shedding from mucosal surfaces, causing significant health consequences for individuals, particularly those of reproductive age (1). Immunocompetent people with genital herpes may experience recurrent painful genital lesions, leading to considerable psychosocial distress (1). Our study utilized data from the GBD 2021 and revealed a 51.97% increase in incident cases of genital herpes among individuals aged 15–49 years between 1990 and 2021. While the global incidence rates of genital herpes remained stable during this period, variations were observed between regions and countries. Specifically, the incidence rates increased in low-middle SDI region, South Asia, Southern Sub-Saharan Africa, and Central Europe. At the national level, a significant upward trend in incidence rates was observed in 28 countries and territories.
In this study, we observed a 51.97% increase in global incident cases of genital herpes among individuals aged 15–49 years from 1990 to 2021. However, the global incidence rate remained stable during this period, which may be attributed to population growth. According to the World Population Prospects 2022, the population of individuals aged 15–49 years worldwide rose from 2.69 billion in 1990 to 3.96 billion in 2021 (6). Our findings indicate that in 2021, the global incidence rate of genital herpes among females aged 15–49 years was 1.13%, nearly twice the rate among males in the same age group (0.69%). A previous study also reported a higher incidence rate of HSV-2 infection among females (0.8%) compared to males (0.5%) in 2016 (4). This discrepancy can be attributed to the greater biological susceptibility of women to HSV-2 infection, the primary cause of genital herpes (7). Additionally, variations in sexual behavior patterns between genders might expose women to a higher risk of infection. It is crucial to provide counseling to women, particularly those who are seronegative and have an infected partner, regarding the use of condoms and the avoidance of oral-genital sex.
This study examines the disparities in genital herpes incidence among individuals aged 15–49 years across different regions and countries worldwide. The findings indicate a significant upward trend in the incidence rates of genital herpes among the same population in low-middle SDI region, South Asia, Southern Sub-Saharan Africa, and Central Europe from 1990 to 2021. Particularly, almost all countries in Sub-Saharan Africa experienced the highest incidence rate of genital herpes among individuals aged 15–49 years in 2021. These estimates provide updated information on the distribution and trends of genital herpes incidence across regions and countries worldwide. Given the chronic and lifelong nature of HSV infections, there is a pressing need to develop effective prevention strategies, including the creation of new vaccines for HSV-2. While candidate vaccines for HSV have been tested in humans, there are currently no approved vaccines for either HSV-1 or HSV-2 (8). Therefore, the development of vaccines against HSV is a crucial objective for global health. Existing prevention methods, such as condom usage or antiviral medications, are insufficient in preventing HSV infection (9). It is vital to raise awareness about HSV infection and its symptoms, promote the acceptance of condom use, and improve access to antiviral medications, particularly in countries with high rates of genital herpes infection.
There are several limitations that should be noted in this study. First, the estimates provided in the study only pertain to the incidence of genital herpes caused by HSV-2, and do not include HSV-1 or oral herpes caused by HSV-2 as part of the GBD 2021 (10). This may result in an underestimation of the incidence of genital herpes among individuals aged 15–49 years in our study population. Second, the accuracy and reliability of our incidence estimates for genital herpes were limited by the availability and quality of the data used in the modeling process. This could introduce bias, particularly when national surveillance systems and population-based studies were lacking or insufficient. Lastly, in assessing the long-term trends from 1990 to 2021, we utilized the EAPCs in incidence rates and relative changes in the numbers of incident cases. However, this approach may mask recent short-term trends that have occurred in more recent years.
In summary, the global incident cases of genital herpes among the population aged 15–49 years increased by 51.97% from 1990 to 2021. Low-middle SDI region, South Asia, Southern Sub-Saharan Africa, and Central Europe experienced a significant increase in incidence rates of genital herpes among individuals aged 15–49 years between 1990 and 2021. Among these regions, countries in Sub-Saharan Africa faced the most severe threat, with the highest incidence rate in 2021. Therefore, there is an urgent need to promote preventive strategies and measures for genital herpes infection, particularly the development of vaccines.
HTML
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:






