2024 Vol. 6, No. 20
Pertussis has reemerged as a significant public health threat, primarily due to variations in Bordetella pertussis strains, antimicrobial resistance, and vaccine evasion.
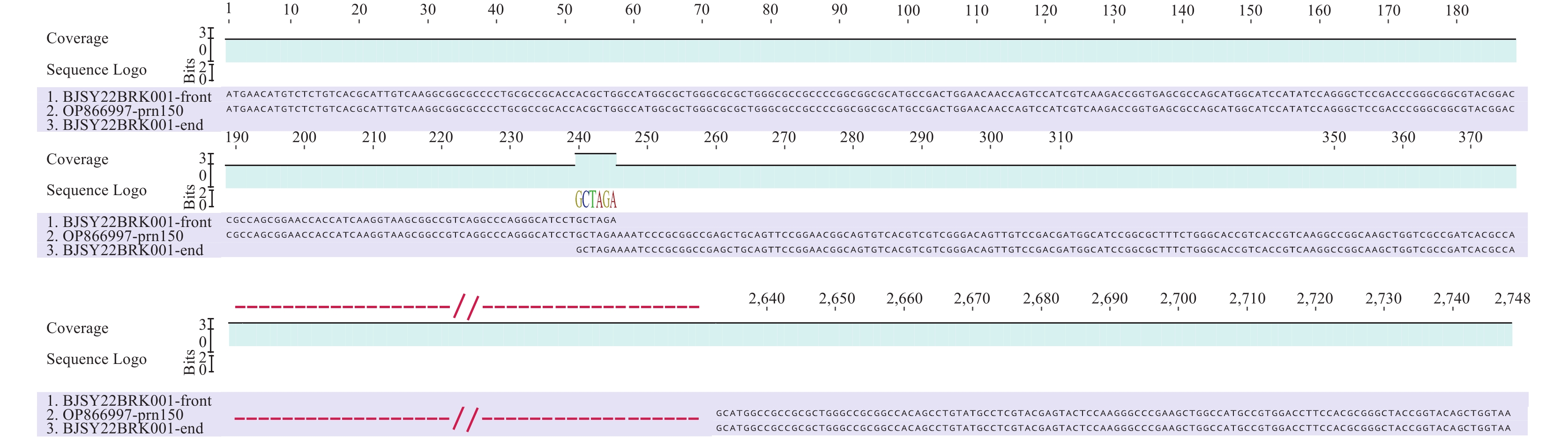
All isolated strains were identified as ptxA1/ptxC2/ptxP3/prn150/fim2-1/fim3-1/fhaB1/tcfA2 type and exhibited resistance to erythromycin. Two strains showed a deficiency in Fha, thirty in Prn, and one strain exhibited multiple immunogen deficiencies.
The emergence and spread of immunogen-deficient strains likely result from prolonged vaccine selection pressure, posing challenges to the efficacy of pertussis vaccines. Additionally, the ongoing dissemination of ptxP3 strains with high-level macrolide resistance presents a significant obstacle to clinical treatment strategies.
Coxsackievirus A6 (CVA6) has emerged as a significant pathogen responsible for severe cases of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). This study aims to delineate the demographic characteristics and analyze the viral evolution of severe HFMD associated with CVA6, thereby assisting in its surveillance and management.
In this investigation, 74 strains of CVA6 were isolated from samples collected from severe HFMD cases between 2012 and 2023. The VP1 gene sequences of CVA6 were amplified and analyzed to assess population historical dynamics and evolutionary characteristics using BEAST, DnaSP6, and PopART.
A significant portion (94.4%) of severe CVA6-associated HFMD cases (51 out of 54, with 20 lacking age information) were children under 5 years old. Among the 74 CVA6 strains analyzed, 72 belonged to the D3a sub-genotype, while only two strains were D2 sub-genotype. The average genetic distance between VP1 sequences prior to 2015 was 0.027, which increased to 0.051 when compared to sequences post-2015. Historical population dynamics analysis indicated three significant population expansions of severe CVA6-associated HFMD during 2012–2013, 2013–2014, and 2019–2020, resulting in the formation of 65 distinct haplotypes. Consistent with the MCC tree findings, transitioning between regional haplotypes required multiple base substitutions, showcasing an increase in population diversity during the evolutionary process (from 14 haplotypes in 2013 to 55 haplotypes over the subsequent decade).
CVA6, associated with severe HFMD, is evolving and presents a risk of outbreak occurrence. Thus, enhanced surveillance of severe HFMD is imperative.
This study examines the seasonal and genetic characteristics of human metapneumovirus (HMPV) in Henan from 2017 to 2023.
Samples from patients with acute respiratory infection (ARI) testing positive for HMPV were subjected to real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction The G gene was amplified and sequenced from these samples for epidemiological and phylogenetic analysis.
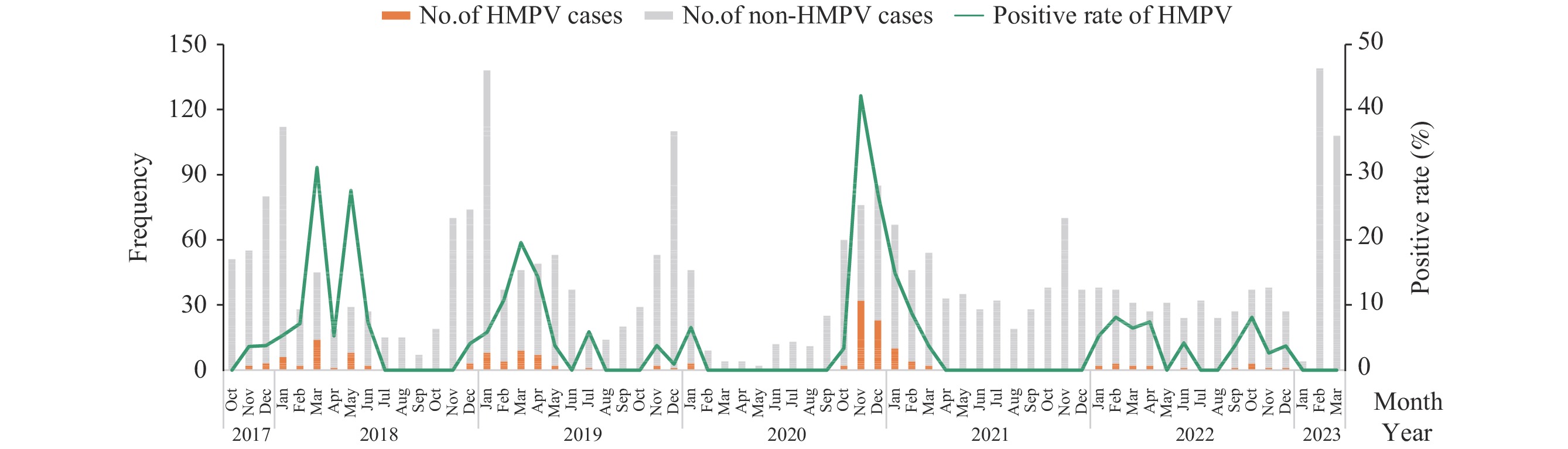
We enrolled 2,707 ARI patients from October 2017 to March 2023, finding an HMPV positivity rate of 6.17% (167/2,707). Children under five exhibited the highest infection rate at 7.78% (138/1,774). The 2018 and 2019 HMPV outbreaks predominantly occurred in spring (March to May), with peak positivity rates of 31.11% in May 2018 and 19.57% in May 2019. A notable increase occurred in November 2020, when positivity reached a historic high of 42.11%, continuing until January 2021. From February 2021 through March 2023, no significant seasonal peaks were observed, with rates ranging from 0% to 8.70%. Out of 81 G gene sequences analyzed, 46.91% (38/81) were identified as subtype A (A2c: 45.67%, 37/81; A2b: 1.23%, 1/81) and 53.09% (43/81) as subtype B (B1: 9.88%, 8/81; B2: 43.21%, 35/81). Notably, an AAABBA switch pattern was observed in HMPV subtypes. The dominant strains were A2c111nt-dup in subtype A and B2 in subtype B.
Six years of surveillance in Henan Province has detailed the seasonal and genetic dynamics of HMPV, contributing valuable insights for the control and prevention of HMPV infections in China. These findings support the development of targeted HMPV vaccines and immunization strategies.
The goal of this study is to analyze the epidemiological patterns of dengue fever across different districts and counties in Yunnan Province from 2010 to 2021.
In this study, we employed joinpoint regression analysis, spatial autocorrelation analysis, and space-time scan analysis to illustrate the spatio-temporal propagation and demographic influence of dengue fever, using both graphical and tabular presentations to clearly demonstrate the findings.
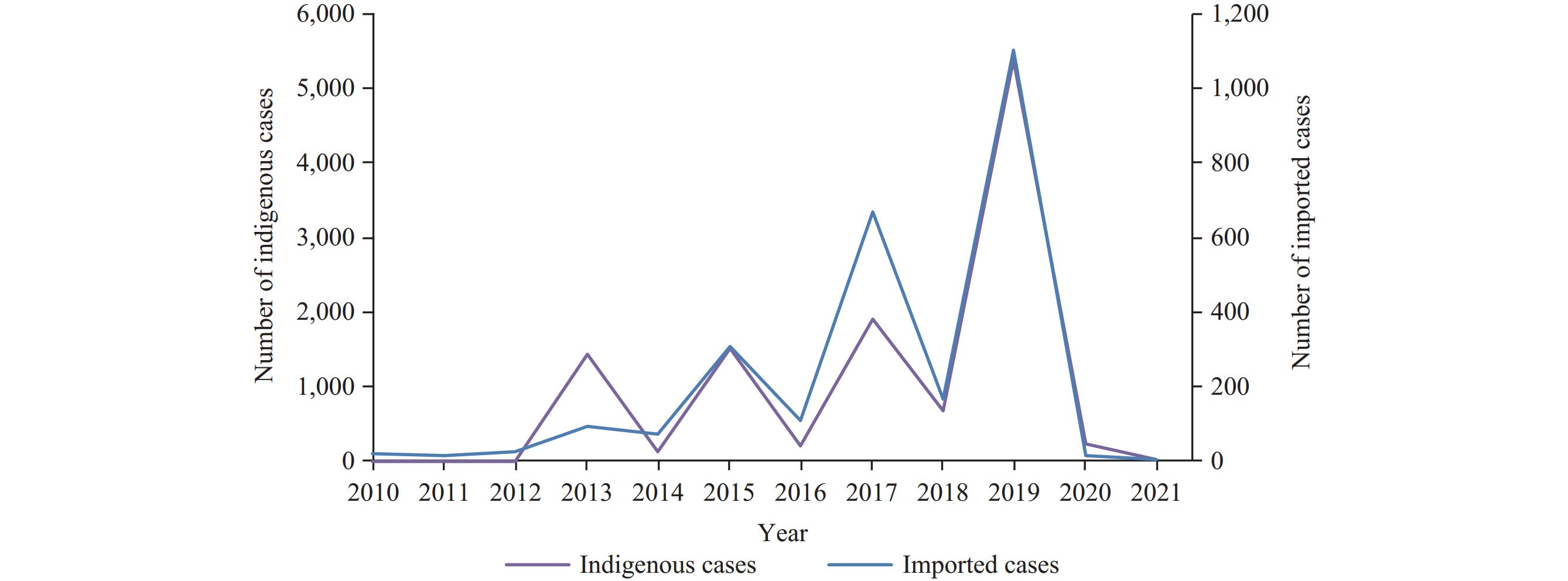
Yunnan Province reported 14,098 cases of dengue fever during the period from 2010 to 2021. Of these, 11,513 cases were caused by local transmission, 2,566 were imported internationally, and 19 were inter-provincial imports. Seasonal trends emerged, revealing a surge in incidences during the summer and autumn months. The sex ratio of male to female cases was 1:0.88, with a significant majority of 82.00% of cases involving individuals belonging to the age group of 15–60. Commercial service workers constituted the most impacted occupational group, forming 20.96% of total cases. A spatio-temporal scan identified significant clustering of dengue fever cases across space and time, with the most pronounced cluster observed in southern Yunnan, primarily between 2015 and 2019.
Dengue fever in Yunnan Province manifests as biennial outbreaks, underscoring the necessity for increased surveillance, particularly in counties bordering other regions.
In order to enhance the effectiveness of resource allocation, regions must tailor their responses to their specific epidemiological and economic situations.
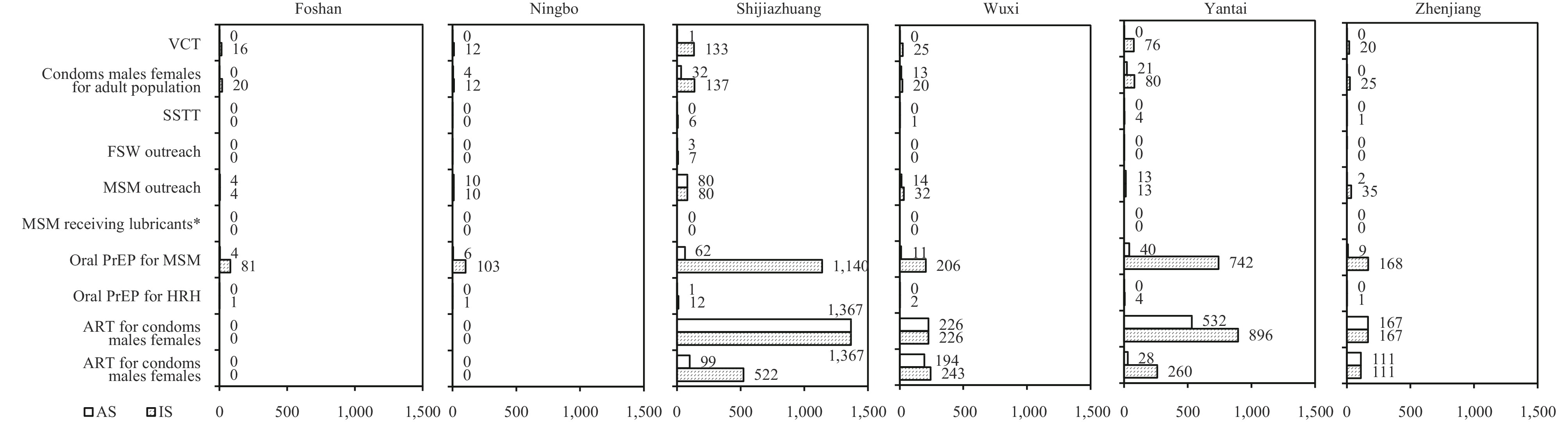
Utilizing Spectrum software, we projected the cost-effectiveness of 10 chosen HIV interventions in six cities in eastern China from 2019 to 2028. We assessed three scenarios — Base, Achievable, and Idealized — for each city. The analysis included the projected number of HIV infections and deaths averted, as well as the incremental cost-effectiveness ratios for each intervention in the six cities.
In Shijiazhuang, Wuxi, Yantai, and Zhenjiang, cities with initially low antiretroviral therapy (ART) coverage, ART showed significant effectiveness, especially for males. Conversely, in Foshan and Ningbo, where ART coverage was notably high, oral pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for men who have sex with men (MSM) proved effective in the Idealized scenario. MSM outreach, ART for males, and ART for females demonstrated cost-effectiveness across all six cities in both Achievable and Idealized scenarios at the predefined thresholds for each city.
Maintaining an appropriate coverage rate for outreach to MSM can lead to cost-effectiveness. In cities with low ART coverage, scaling up ART remains a crucial intervention. In regions with high ART coverage, consideration may be given to the utilization of oral PrEP for MSM individuals, requiring budget allocation.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed