2023 Vol. 5, No. 8
Children in kindergartens and primary schools are the high-incidence groups of norovirus acute gastroenteritis. However, asymptomatic norovirus infection among them is seldom reported.
The norovirus positive rate was 3.48% among asymptomatic children in kindergartens and primary schools in Beijing Municipality in June 2021, the most common genotype was GII.4 Sydney, and no acute gastroenteritis outbreak was reported over the study period.
The asymptomatic norovirus infection was relatively low among kindergarten children and primary school students in summer. Norovirus genotypes in asymptomatic children were similar to those circulating in the symptomatic cases. Asymptomatic norovirus infection may play a limited role in causing acute gastroenteritis outbreaks.
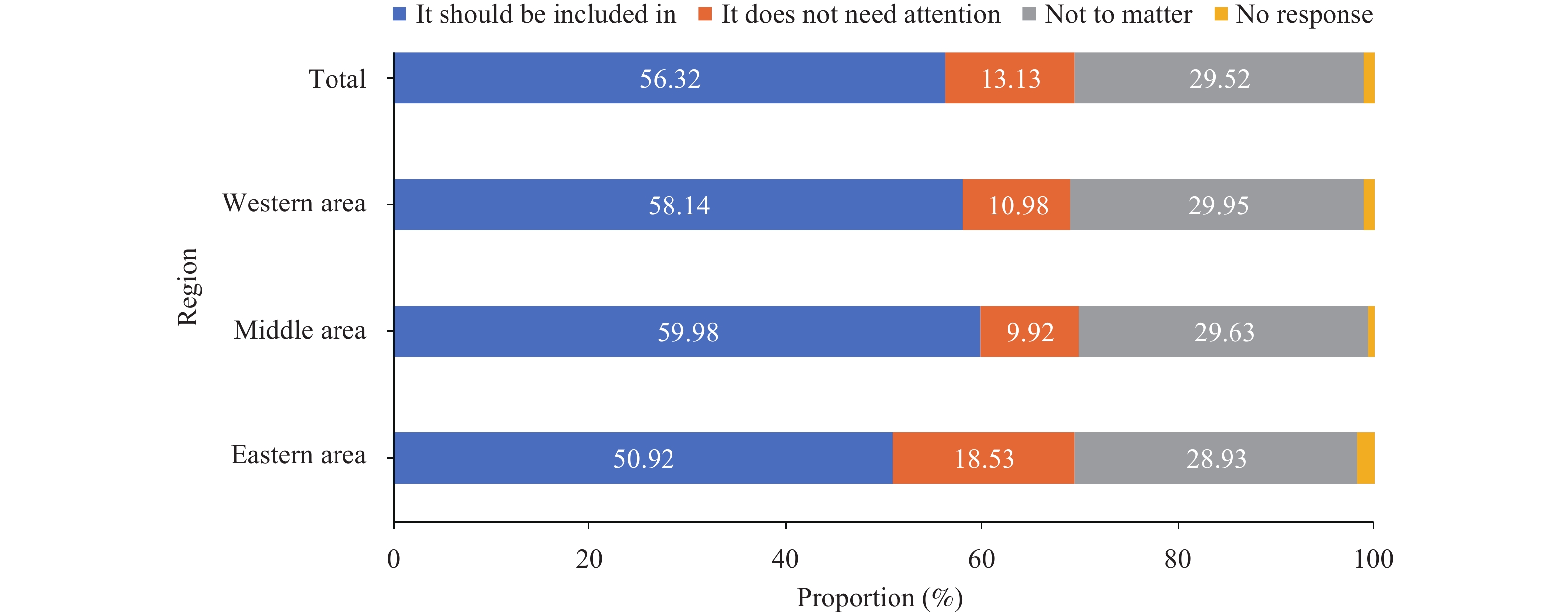
Tuberculosis (TB) is a multisystem disease that might affect any organ. Currently, the National TB Program (NTP) issued by the State Council of China, only covers pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB), and the status of extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) remains unclear nationwide.
The survey conducted by China CDC reported that there were no specific health facilities responsible for diagnosis, treatment and management of EPTB in China, while more than half of counties thought it should be included into NTP.
China should include EPTB into NTP to achieve the target of End-TB strategy, a world free of TB. Zero deaths, disease and suffering due to TB.
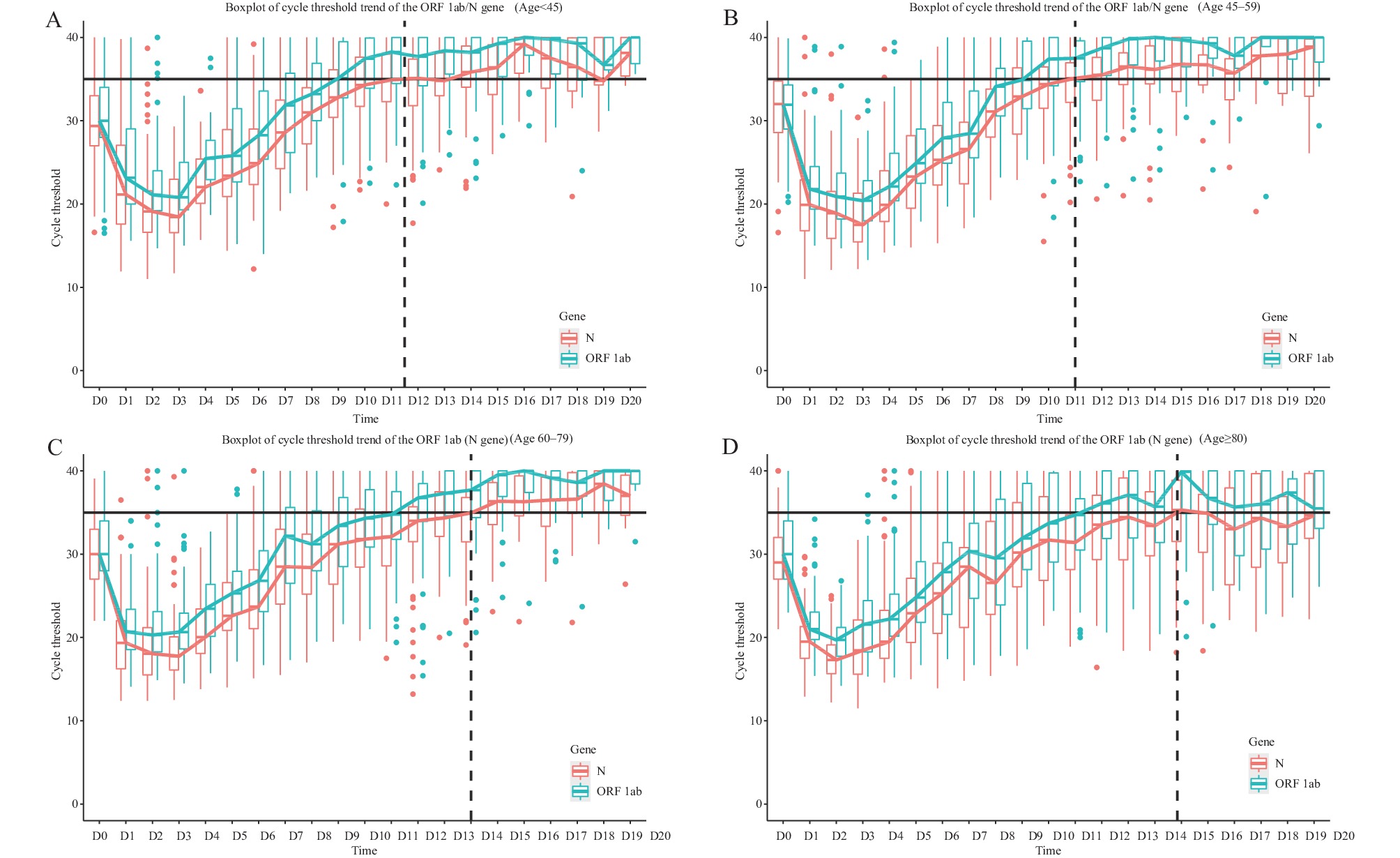
In November 2021, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant was identified as the variant of concern and has since spread globally, replacing other cocirculating variants. To better understand the dynamic changes in viral load over time and the natural history of the virus infection, we analyzed the expression of the open reading frames 1ab (ORF1ab) and nucleocapsid (N) genes in patients infected with Omicron.
We included patients initially admitted to the hospital for SARS-CoV-2 infection between November 5 and December 25, 2022. We collected daily oropharyngeal swabs for quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction tests using commercial kits. We depicted the cycle threshold (Ct) values for amplification of ORF1ab and N genes from individual patients in age-specific groups in a time series.
A total of 480 inpatients were included in the study, with a median age of 59 years (interquartile range, 42 to 78; range, 16 to 106). In the <45-year-old age group, the Ct values for ORF1ab and N gene amplification remained below 35 for 9.0 and 11.5 days, respectively. In the ≥80-year-old age group, the Ct values for ORF1ab and N genes stayed below 35 for 11.5 and 15.0 days, respectively, which was the longest among all age groups. The Ct values for N gene amplification took longer to rise above 35 than those for ORF1ab gene amplification.
The time to test negative varied among different age groups, with viral nucleic acid shedding taking longer in older age groups compared to younger age groups. As a result, the time to resolution of Omicron infection increased with increasing age.
Population aging is an irreversible process in the development of modern society, which brings challenges to comprehensive modernized social governance. Population aging is a “dualistic” development issue that not only leads to aging of the labor force structure but also creates new demographic dividends. This study describes the core thoughts of developmental gerontology (DG), which provides new insight into the relationship between active aging and comprehensive governance for modernized society. The development of DG will provide a feasible and sustainable path to integrate and coordinate the relationship between population aging, society, and economy.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed