2023 Vol. 5, No. 9
Joint effects of gestational weight gain (GWG) and hyperglycemia on adverse pregnancy outcomes suggest that lower optimal GWG is optimal for women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). However, there is still a lack of guidelines.
Optimal weekly GWG range after diagnosis of GDM for underweight, normal-weight, overweight, and obese women was 0.37–0.56 kg/week, 0.26–0.48 kg/week, 0.19–0.32 kg/week, and 0.12–0.23 kg/week, respectively.
The findings may be used to inform prenatal counseling regarding optimal gestational weight gain for women with gestational diabetes mellitus, and suggest the need for weight gain management.
Hematological parameters may indicate the presence of chronic low-grade inflammation and increasing viscosity, which are involved in the pathological processes of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). However, the association between several hematological parameters in early pregnancy and GDM has yet to be elucidated.
Hematological parameters in the first trimester, particularly red blood cell (RBC) count and systematic immune index, have a significant impact on GDM incidence. The neutrophils (NEU) count in the first trimester was particularly pronounced for GDM. The upward trend of RBC, white blood cell (WBC), and NEU counts was consistent across all GDM subtypes.
Early pregnancy hematological parameters are associated with the risk of GDM.
Cervical cancer is a significant public health problem with approximately 570,000 cases and 311,000 deaths occurring in 2018 globally. It is imperative to raise awareness of cervical cancer and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Compared to previous studies, this is one of the largest cross-sectional studies of cervical cancer and HPV in Chinese adult females in recent years. We found that knowledge level of cervical cancer and HPV vaccine was still inadequate among women aged 20–45 years old, and the willingness to receive HPV vaccination was highly associated with knowledge level.
Intervention programs should aim to improve awareness and knowledge about cervical cancer and HPV vaccines, primarily focusing on women of lower socio-economic status.
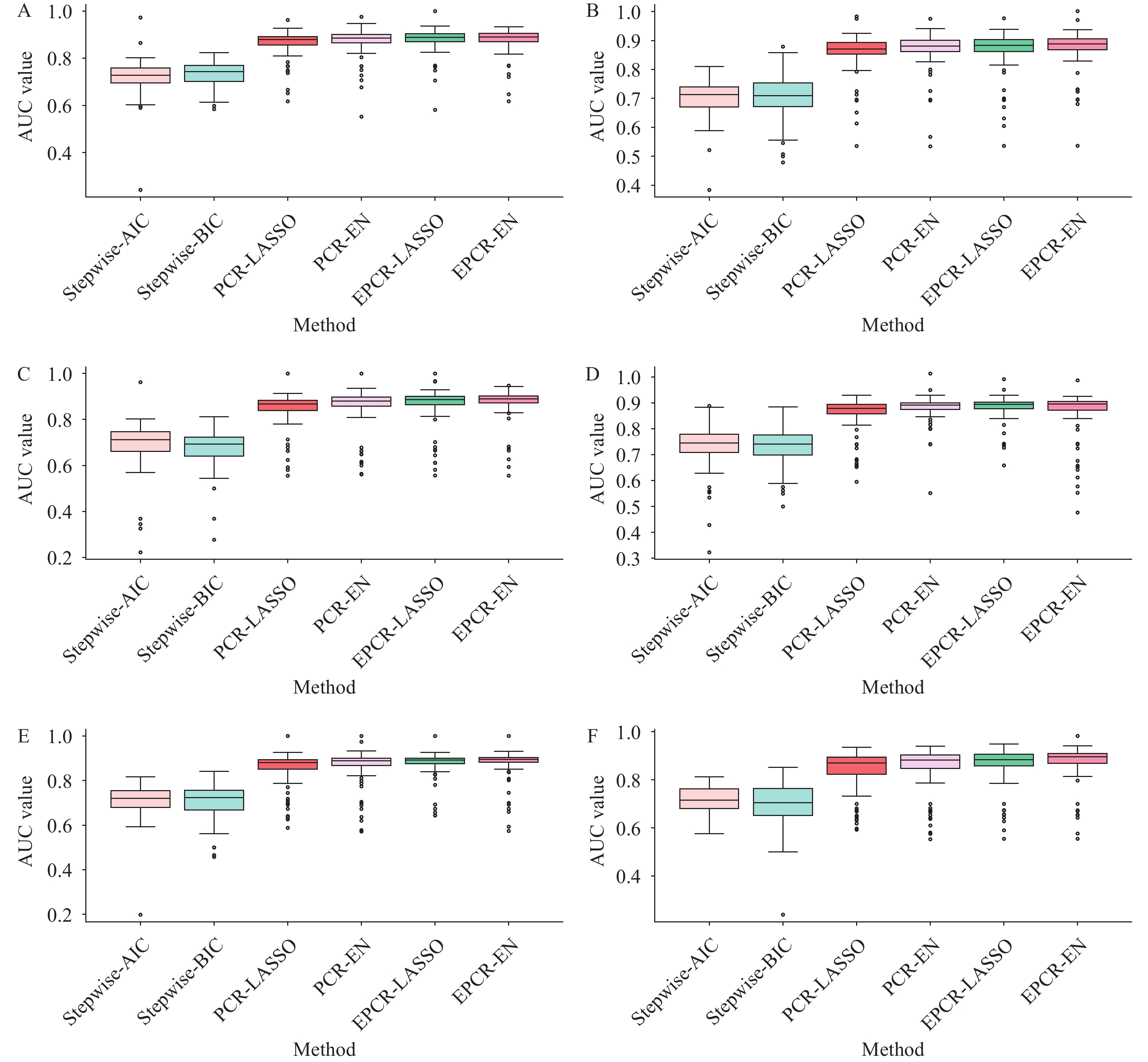
Biases in cancer incidence characteristics have led to significant imbalances in databases constructed by prospective cohort studies. Since they use imbalanced databases, many traditional algorithms for training cancer risk prediction models perform poorly.
To improve prediction performance, we introduced a Bagging ensemble framework to an absolute risk model based on ensemble penalized Cox regression (EPCR). We then tested whether the EPCR model outperformed other traditional regression models by varying the censoring rate of the simulated data.
Six different simulation studies were performed with 100 replicates. To assess model performance, we calculated mean false discovery rate, false omission rate, true positive rate, true negative rate, and the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) values. We found that the EPCR procedure could reduce the false discovery rate (FDR) for important variables at the same true positive rate (TPR), thereby achieving more accurate variable screening. In addition, we used the EPCR procedure to build a breast cancer risk prediction model based on the Breast Cancer Cohort Study in Chinese Women database. AUCs for 3- and 5-year predictions were 0.691 and 0.642, representing improvements of 0.189 and 0.117 over the classical Gail model, respectively.
We conclude that the EPCR procedure can overcome challenges posed by imbalanced data and improve the performance of cancer risk assessment tools.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed