2023 Vol. 5, No. 18
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) reinfection by variants is being reported commonly and has caused waves of epidemic in many countries. Because of dynamic zero policy, the SARS-CoV-2 reinfection was less reported in China.
SARS-CoV-2 reinfections were observed in Guangdong Province between December 2022 and January 2023. This study estimated that the reinfection incidence was 50.0% for the original strain primary infections, 35.2% for the Alpha or Delta variants, and 18.4% for the Omicron variant; The reinfection incidence within 3-6 months after primary infection by Omicron variant was 4.0%. Besides, 96.2% reinfection cases were symptomatic while only 7.7% sought medical attention.
These findings suggest a reduced likelihood of an Omicron-driven epidemic resurgence in the short term but emphasize the importance of maintaining vigilant surveillance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and conducting population-based antibody level surveys to inform response preparedness.
The first nationwide wave of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), driven by the Omicron variant, has largely subsided. However, subsequent epidemic waves are inevitable due to waning immunity and the ongoing evolution of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Insights gleaned from other nations offer guidance regarding the timing and scale of potential subsequent waves of COVID-19 in China.
Understanding the timing and magnitude of subsequent waves of COVID-19 in China is crucial for forecasting and mitigating the spread of the infection.
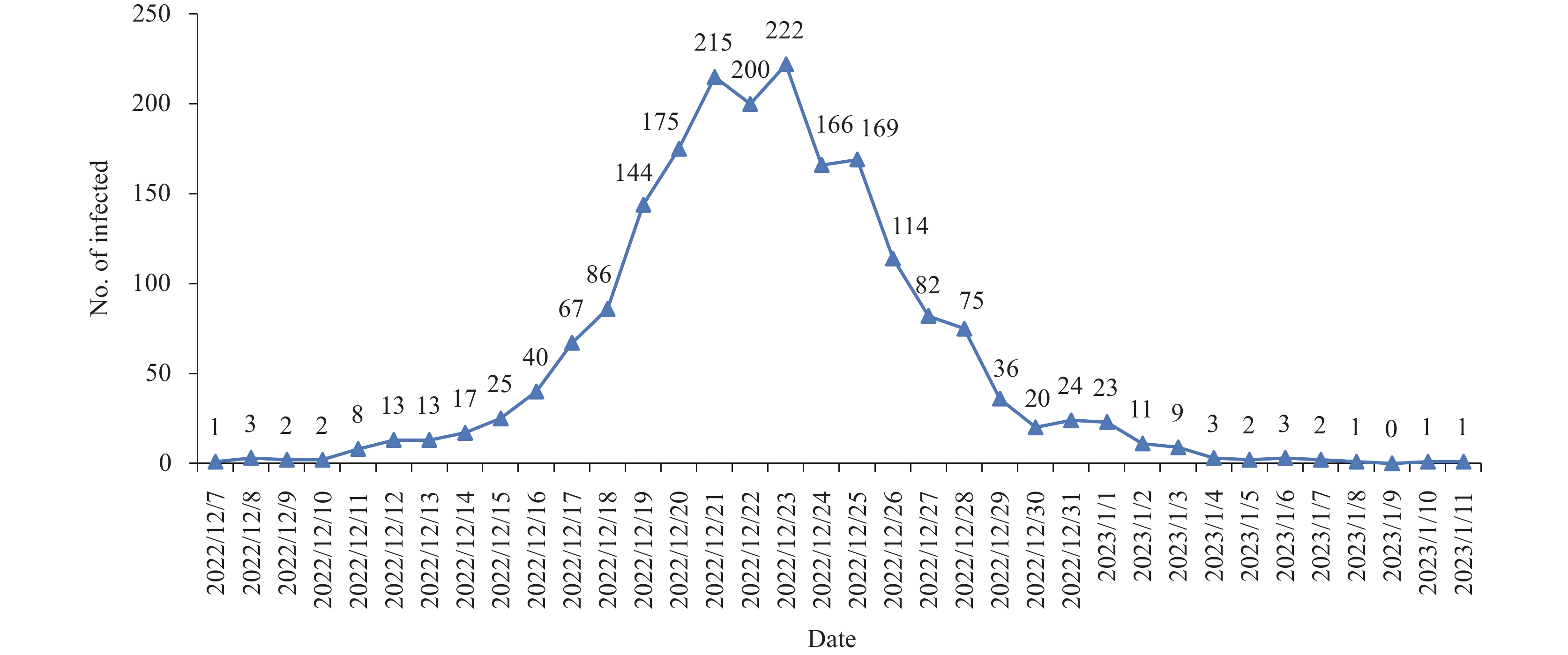
Healthcare workers (HCWs) and previously infected patients (PIPs) may experience a wave of epidemic following the modification of the country’s coronavirus disease (COVID)-zero policy in China.
As of early January 2023, the initial wave of the COVID-19 pandemic among HCWs had effectively subsided, with no statistically significant differences observed in infection rates compared to those of their co-occupants. The proportion of reinfections among PIPs was relatively low, particularly in those with recent infections.
Medical and health services have resumed normal operations. For patients who have recently experienced severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections, appropriate relaxation of policies may be considered.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has had profound disruptions worldwide. For a population or individual, it is critical to assess the risk of death for making preventative decisions.
In this study, clinical data from approximately 100 million cases were statistically analyzed. A software and an online assessment tool were developed in Python to evaluate the risk of mortality.
Our analysis revealed that 76.51% of COVID-19-related fatalities occurred among individuals aged over 65 years, with frailty-associated deaths accounting for more than 80% of these cases. Furthermore, over 80% of the reported deaths involved unvaccinated individuals. A notable overlap was observed between aging and frailty-associated deaths, both of which were connected to underlying health conditions. For those with at least two comorbidities, the proportion of frailty and the proportion of COVID-19-related death were both close to 75 percent. Subsequently, we established a formula to calculate the number of deaths, which was validated using data from twenty countries and regions. Using this formula, we developed and verified an intelligent software designed to predict the death risk for a given population. To facilitate rapid risk screening on an individual level, we also introduced a six-question online assessment tool.
This study examined the impact of underlying diseases, frailty, age, and vaccination history on COVID-19-related mortality, resulting in a sophisticated software and a user-friendly online scale to assess mortality risk. These tools offer valuable assistance in informed decision-making.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed