2023 Vol. 5, No. 14
The effective implementation of cervical cancer examination programs requires improved cervical cancer screening coverage and quality.
The detection rate of ≥high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) in 6 hospitals was 19.6%. Not having undergone screening in the last 5 years and abnormal screening results had a negative association with detection of ≥HSIL, and abnormal screening results would increase the risk of detection by 75% compared with normal screening results. Additionally, low-grade, high-grade, and cancer of colposcopic impression were associated with a higher risk for detecting ≥HSIL.
It is essential to disseminate health knowledge about cervical cancer control to women in order to increase their awareness and screening rates. Additionally, it is necessary to further strengthen the training of professional staff to improve the quality of cervical cancer prevention, including screening, colposcopic examination, and follow-up for target female populations.
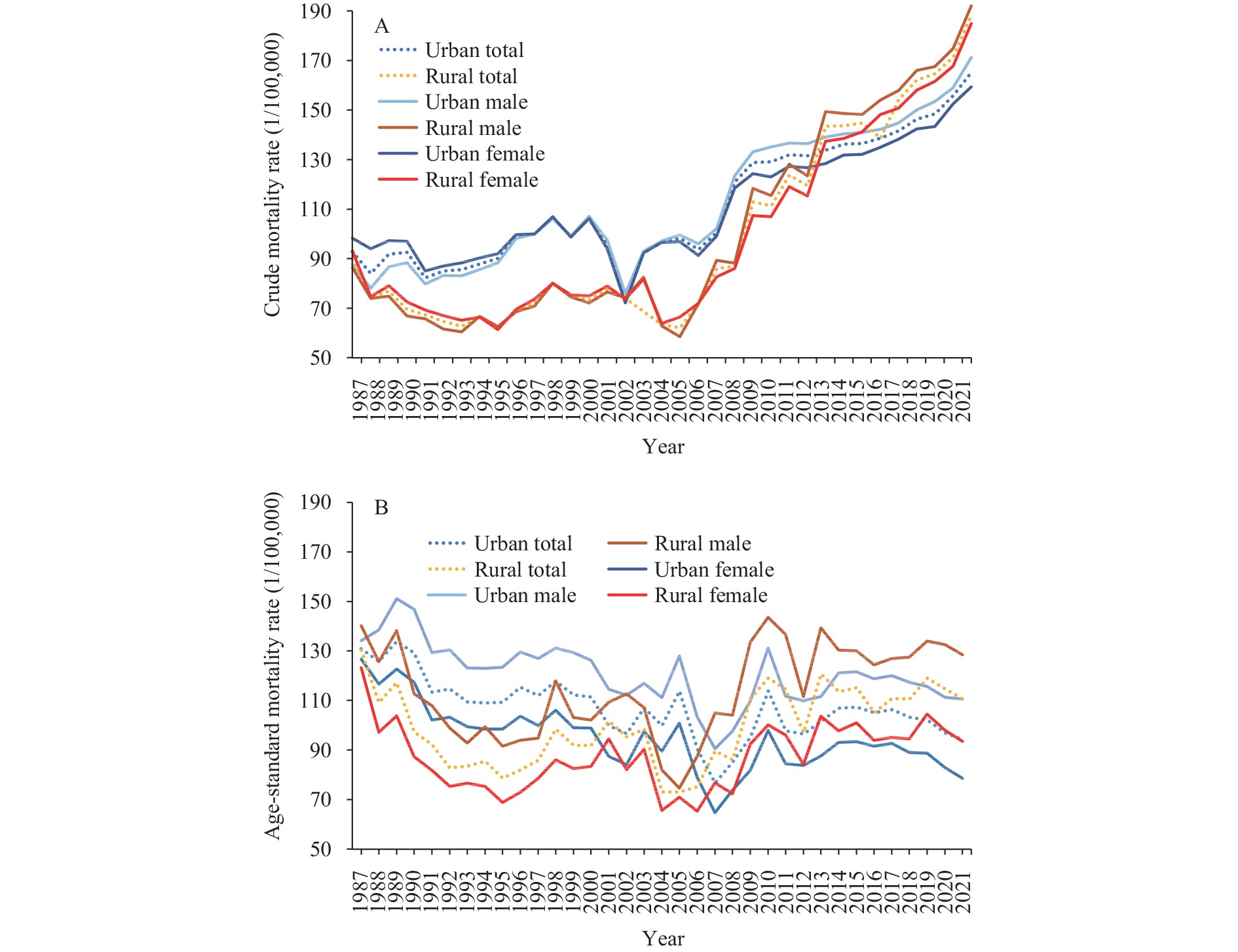
The burden of heart disease is increasing rapidly due to the aging population and changing lifestyles in China.
This study investigated the evolution of mortality rates due to heart disease in urban and rural areas of China over the past 35 years, and identified the age-period-cohort effects on mortality changes.
Healthcare providers should prioritize attention to heart disease among older males living in rural areas.
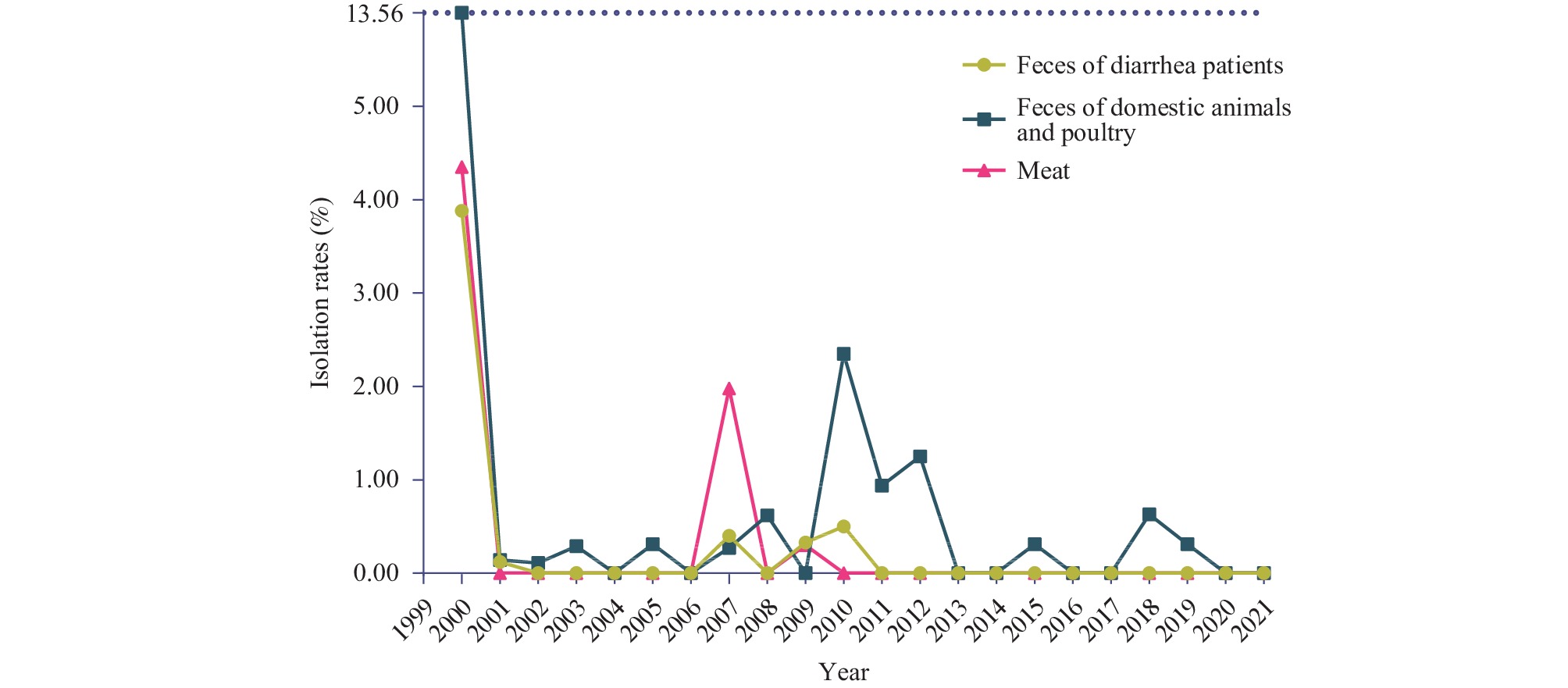
The largest and longest outbreak of diarrhea, which was complicated with hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) caused by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7, occurred in Xuzhou City and its adjacent areas from 1999 to 2000 in China.
According to surveillance results from 2001 to 2021, there was a significant decrease in the isolation rate of O157:H7, and cattle and sheep remained the primary hosts. However, non-Shiga toxin-producing O157:H7 emerged as the dominant strain, with stx2+stx1- strains following closely behind.
National surveillance of O157:H7 effectively serves as an early warning system and guidance for assessing the intensity and trend of disease epidemics. It is crucial to raise awareness of the public health risks associated with Shiga toxin-producing E. coli.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed