2022 Vol. 4, No. 28
Microscopy is the gold standard for parasitological confirmation, but the accuracy of microscopic diagnosis is influenced by the skill of the technicians. An alternative is the immunologic-based malaria rapid diagnostic tests (mRDTs).
Our study evaluated standard microscopy in health system (SMHS) and mRDTs for focused screening and treatment of malaria (FSAT) in Southern Tanzania. We showed that mRDTs were more sensitive than local SMHS for diagnosing malaria infection.
Malaria rapid diagnostic tests can be useful as an alternative to SMHS for FSAT in the local context of Tanzania.
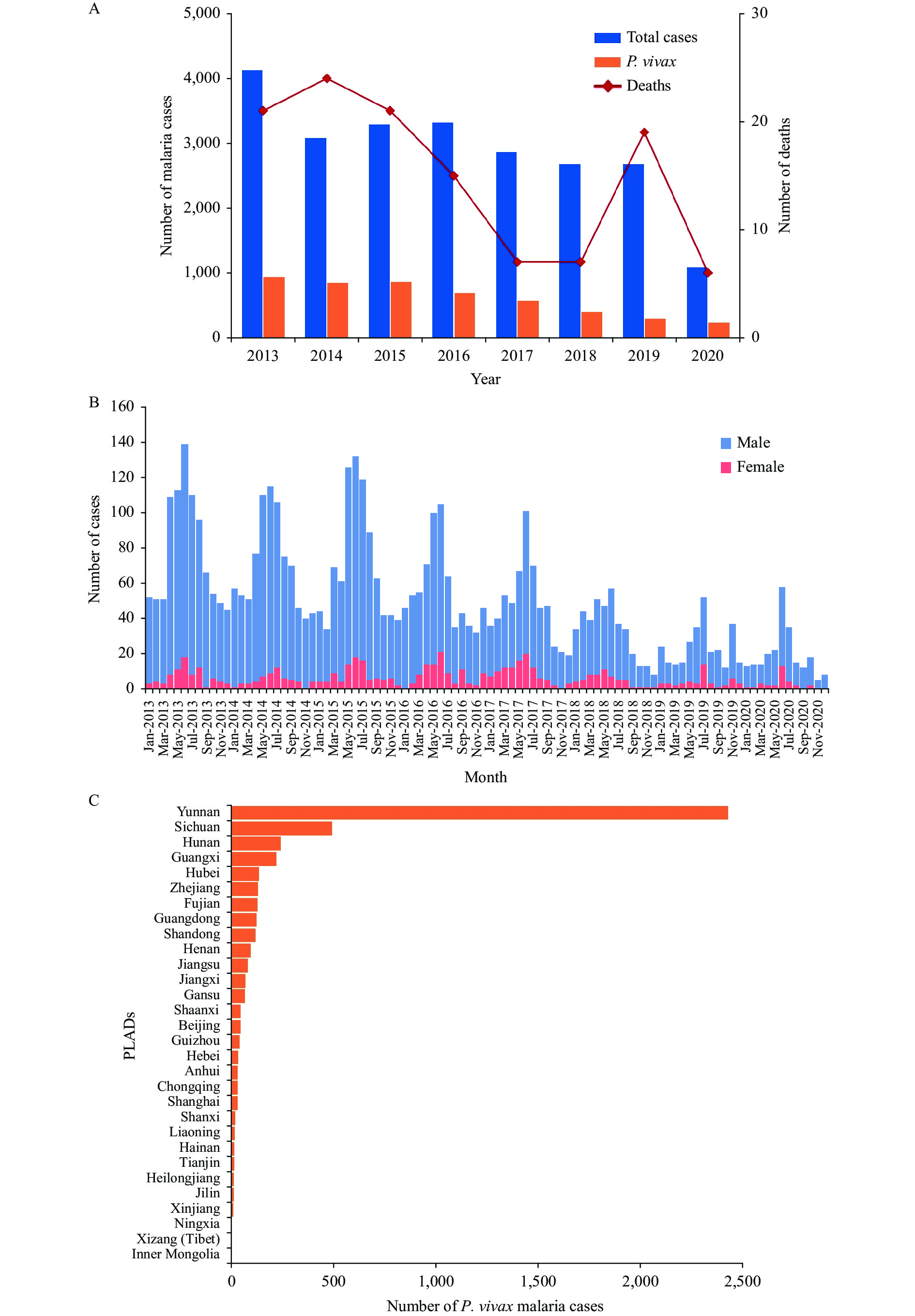
Plasmodium vivax (P. vivax) was the most widely distributed and major human malaria parasite in China, considered the last parasite to be eliminated.
The last domestic P. vivax case was reported in 2016, while hundreds of imported cases were reported annually from 2013–2020, predominantly from Southeast Asia.
In the post-elimination phase, adaptive and practical strategies focusing on imported P. vivax cases should be updated and adopted to prevent malaria resurgence.
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) is the most serious form of leishmaniasis. In recent years, reported cases of VL have been gradually increasing in Shanxi Province, China.
The report describes the epidemiology of VL from 1950 to 2019 in Shanxi Province and the recent trend of VL reemergence.
Measures to prevent and control VL, such as health education, improving clinical diagnostics, strengthening epidemiological investigation capacity for VL cases, monitoring surveillance, and use of other evidence-based preventive measures, should be undertaken in Shanxi Province.
Neurocysticercosis is the most severe form of infection caused by ingesting cysticerci, the larval cysts of the pork tapeworm, Taenia solium. Approximately 50 million people worldwide have neurocysticercosis, which is the leading cause of acquired epilepsy in many endemic countries.
The health of neurocysticercosis patients can be seriously impaired, including through loss of mobility, inability to do self-care, impairment of usual activities, pain/discomfort, anxiety/depression, and impaired cognition. Cognitive impairment is the major consequence of neurocysticercosis and significant contributor to decreased health-related quality of life. Our study made the first estimate of disability weight from neurocysticercosis as a key parameter for disease burden assessment in China.
To prevent severe health outcomes from neurocysticercosis in China, it is necessary to improve public awareness of neurocysticercosis and relevant health behaviors.
China was certified malaria-free on June 30, 2021. However, imported malaria continuously threatens the effort to prevent re-establishment of malaria in China.
Measures such as international travel restrictions, entry quarantine, and screening in fever clinics during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) period were associated with a significant decrease of imported malaria cases in Anhui Province, a higher proportion of non-Plasmodium falciparum (non-P. falciparum) malaria reported infections, and a higher proportion of cases requiring medical attention at their initial visit.
It is necessary to be vigilant about imported malaria during the COVID-19 epidemic, especially for non-P. falciparum infections which are more difficult to detect, and to promote research, development, and introduction of more sensitive and specific point-of-care detection methods for non-P. falciparum species.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed