2022 Vol. 4, No. 27
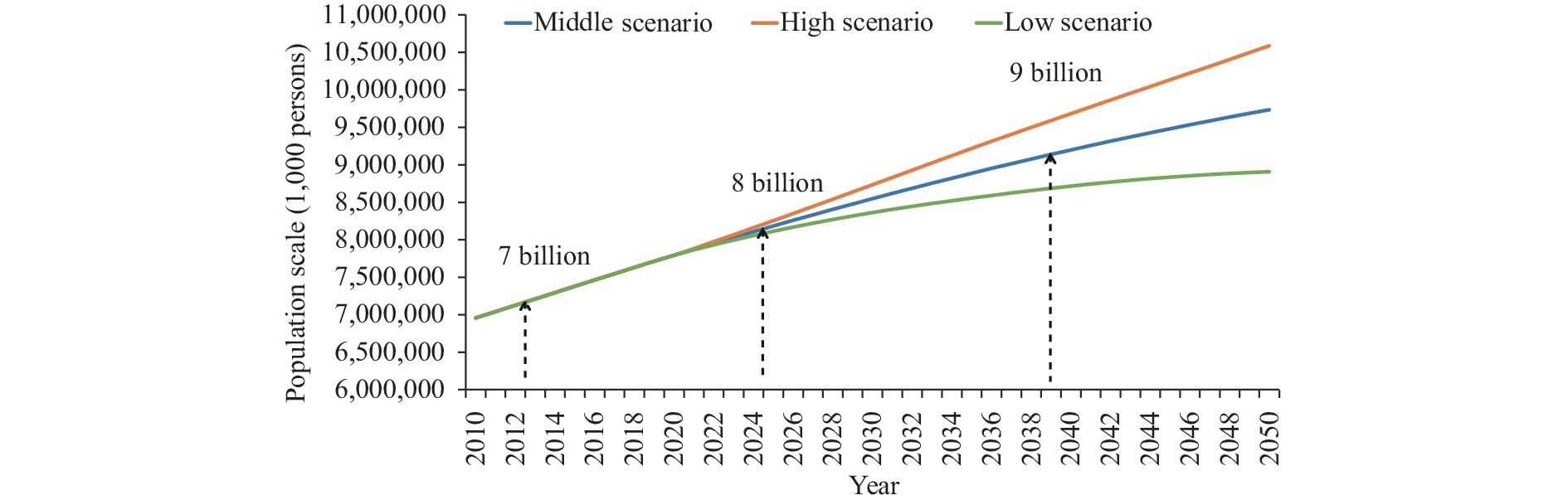
The global population is predicted to reach 8 billion by the end of 2022, which can delay the progress and exacerbate the challenges of achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially the goal of “Zero Hunger.”
During the next 15 years, it is predicted that the world’s population will increase from 8 billion to 9 billion people. Although food insecurity is anticipated to decrease over the next three decades for most of the world, food insecurity is anticipated to increase in Africa. Accelerating population growth is projected to lead to larger percentages of infants with low birth weight and of children under 5 years old with stunted growth.
Rapid population growth will make it more difficult to achieve the SDGs for ending hunger and ensuring good health and well-being. It is important to develop foresight and adopt proactive planning that is guided by careful demographic analysis.
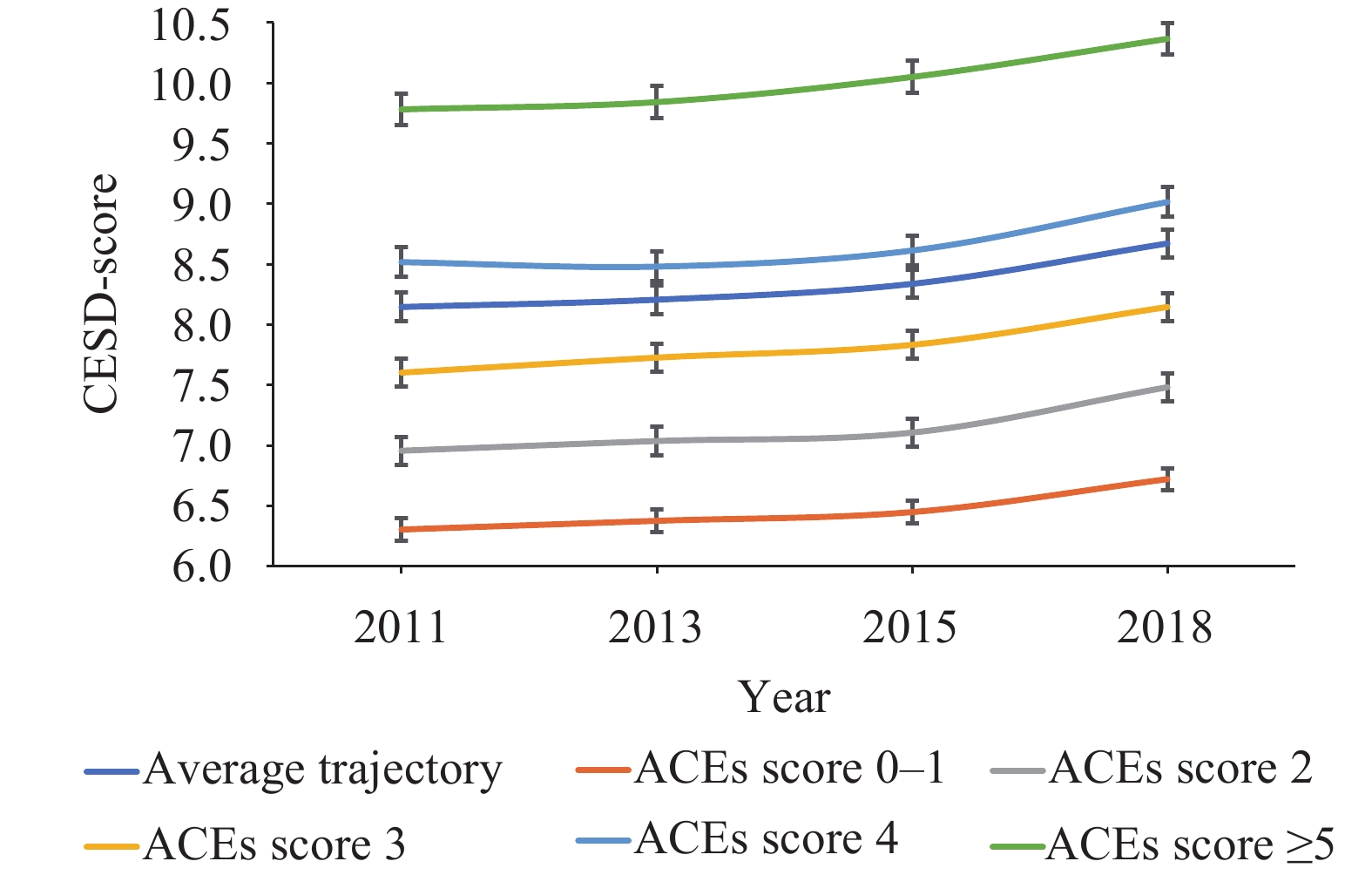
Previous studies in western populations have found consistent relationships between adverse childhood experiences and the development of mood and anxiety disorders, especially depressive symptoms in adolescence and adulthood.
This study used a longitudinal design and analytic method to model depressive symptom trajectories from 2011 to 2018 among the middle-aged and elderly in China. This study also investigated the association between adverse childhood experiences and adulthood depressive symptoms in the Chinese population.
Future public policy could consider early prevention and intervention on adverse childhood experiences to prevent adult depressive symptoms. Besides, it is essential to create safe, stable, and nurturing environments for children’s development.
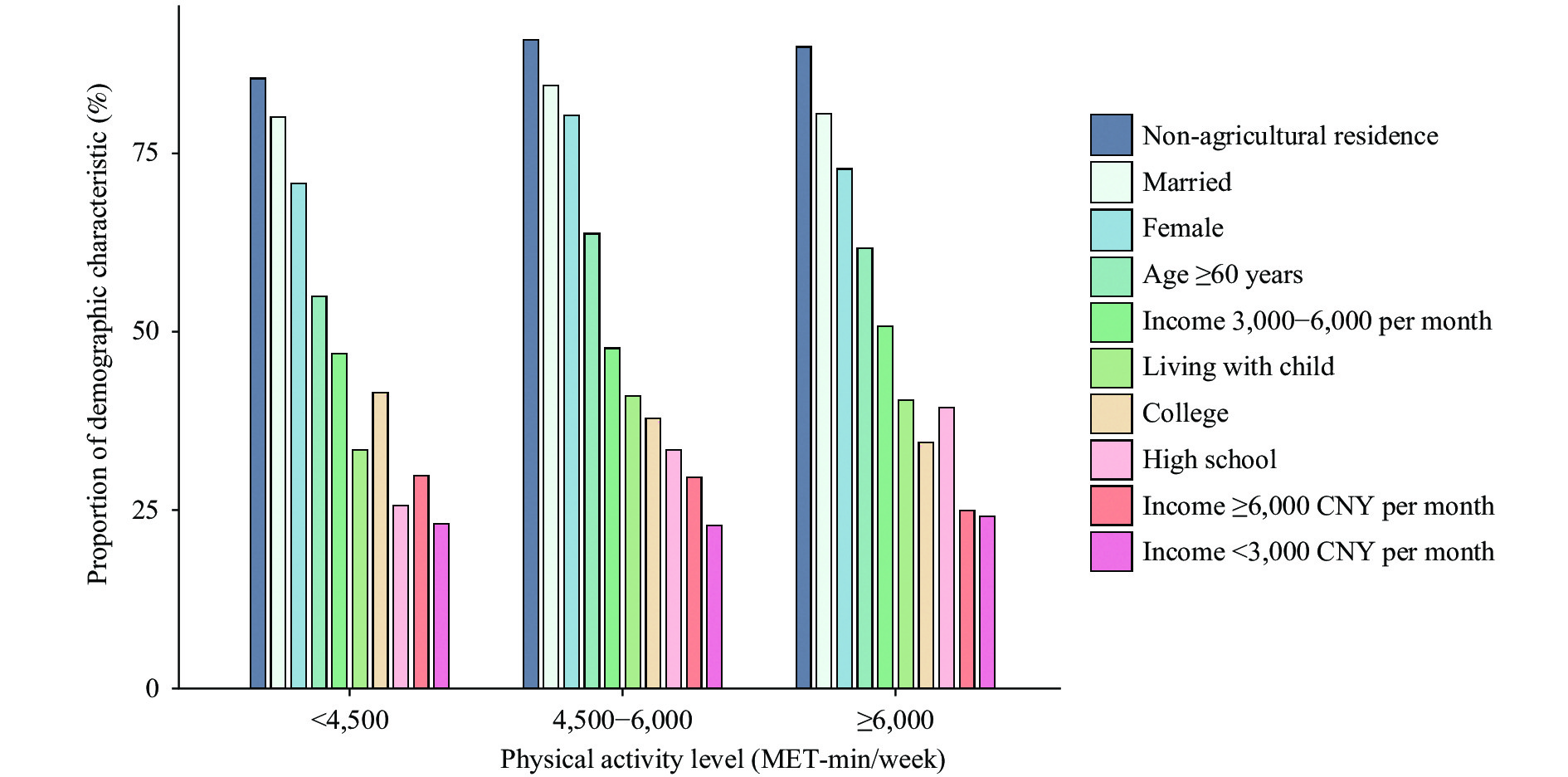
Available evidence suggested that 31% of the world’s population do not meet the minimum recommendations for physical activity.
The latest findings showed that physical activity level (PAL), metabolic equivalents (MET) in min/week with <4,500 (low), 4,500–6,000 (moderate) and ≥6,000 (high) accounted for 45.72%, 25.62%, and 28.66% of middle-aged and elderly population in Changchunyuan Community, Weixiuyuan Community, Zhongguanyuan Community, Yanbeiyuan Community, Kangzeyuan Community, and Xima Community, respectively. The moderate and high PAL was associated with a decreased risk of hypertension, cardiovascular disease, dyslipidemia, and poor sleep.
More attention should be given to the middle-aged population who may be at high risk of insufficient physical activity in urban environments as it is of public health significance for improving the community population health.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed