2022 Vol. 4, No. 29
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a major public health problem in China. In 2016, the World Health Organization (WHO) proposed a goal to eliminate viral hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030, and in 2018, the National Health Commission of China launched Hepatitis C Elimination Action by 2030. Hepatitis C control and prevention has made significant progress in China in recent years. To implement the “Healthy China 2030” plan and the Healthy China Initiative (2019–2030), and to contribute to the global target of eliminating viral hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030, the National Health Commission of China and eight other government departments jointly issued the National Action Plan for Eliminating Hepatitis C as a Public Health Threat (2021–2030) (hereinafter referred to as the “National Plan”) in 2021. The National Plan has an overarching goal and 15 specific targets that cover health education, comprehensive prevention interventions, testing and treatment, and capacity building. The National Plan introduces key tasks and strategies of “five strengthenings, one expanding, and one implementation,” i.e., strengthening health education, comprehensive prevention, referral and treatment, drug supply, and information management; expanding testing; and implementing relevant medical insurance policies. The National Plan also proposes key guaranteeing measures of “four intensifications and one mobilization,” i.e., intensification of organizational leadership, capacity building, scientific research and international cooperation, and supervision and fulfillment; mobilization of social participation. The National Plan is an important component of the Healthy China initiative, adhering to the integration of treatment and prevention and deepening the “integration of medical treatment, medical insurance, and medicine supplies.” In this review, we describe the National Plan and discuss its challenges and prospects.
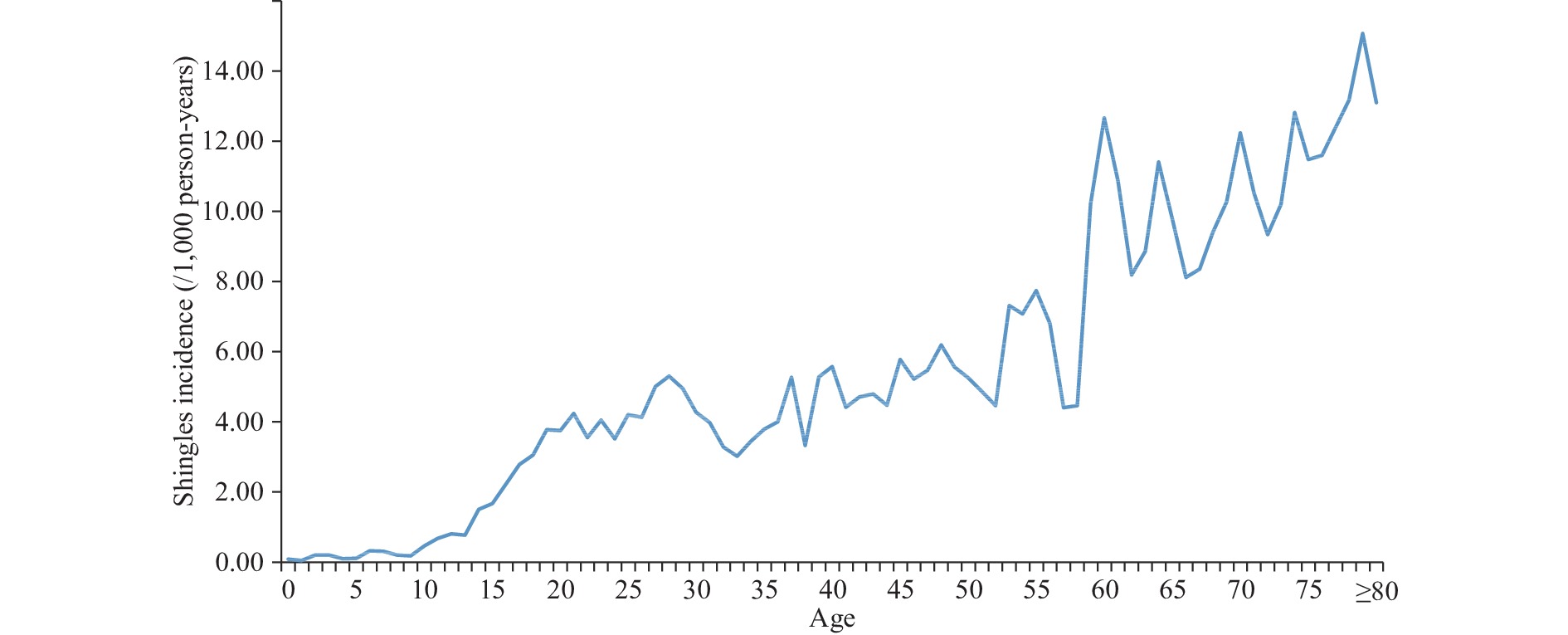
Herpes zoster (shingles) is a common skin condition in older adults, which usually presents as a painful rash with blisters. Vaccination is the most effective method to prevent shingles. However, there is not sufficient population-based epidemiological data in China to optimize the timing of zoster vaccination.
Clustering analyses of population-wide epidemiological data from the Healthcare Big Data Platform in Yichang, China showed that the average annual zoster incidence is the highest among people 55 years or older, at 10 cases per thousand persons per year, making this age group the optimal target population for vaccination. Incidence was lower but increased with age among younger adults, 28–54 years old.
With limited vaccination resources, zoster vaccinations should be targeted at adults 55 years or older who are at the greatest risk for shingles. Research should be conducted to understand the risk of shingles among young and middle-aged adults and identify triggers of shingles: potentially leading to preventive measures.
Previous studies on electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) use in China among secondary school students have provided information on the awareness and usage of e-cigarettes.
This study not only described e-cigarette usage rates, but also explored the characteristics of e-cigarette users’ behavior and factors associated with the current use of e-cigarettes among secondary school students.
E-cigarette use among secondary school students, especially among vocational senior high school students, requires more attention. Although some policies have been developed to protect youths from the harmful effects of e-cigarettes, enforcement of these policies needs to be strengthened.
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is one of the most easily available health indicative markers for cardiovascular diseases, and it has become a major public health problem worldwide due to increasing urbanization and aging populations. The prevalence of MetS increased dramatically in China, however, there are no records of MetS defined by the 2017 Chinese Diabetes Society for Beijing by far.
In this study, the data of 24,412 participants aged 18–74 years from a large population-based study in Beijing was collected. The overall prevalence of MetS among Beijing residents was 24.5%. The prevalence was 35.2% in males and 15.4% in females.
Effective public health strategies should target males, people with older age, lower education, higher body mass index, smokers, those who drink alcohol, those who are unemployed or retired, and those who live in rural areas on MetS prevention and control.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed