2022 Vol. 4, No. 16
The task force has comprehensively reviewed efforts for air pollution prevention and control, the acute health effects of fine particles (PM2.5), and the health benefits of air pollution prevention and control in China. It has been found that the overall prevention and control of ambient PM2.5 pollution in China has made remarkable progress in recent years. However, it still remains at a relatively high level. Short-term exposure to ambient PM2.5 significantly increases the mortality and morbidity risk of Chinese residents, resulting in changes to levels of relevant biological markers. Prolonged PM2.5 heavily polluted weather greatly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality. Among chemical composition of PM2.5, carbon-containing components, some inorganic salts, and heavy metals are linked with the health impacts. The health risks of PM2.5 pollution are higher for children, the elderly, and patients with cardiovascular or respiratory diseases than for the general population because the former groups are vulnerable subpopulations. The implementation of air pollution prevention and control policies has significantly improved human health. The implementation of personal protective equipment can significantly reduce the health damage caused by short-term exposure to ambient PM2.5 pollution. Based on scientific evidence of PM2.5 pollution and acute health risks in China, the following three recommendations are proposed. 1) The policy recommendations for the prevention and control of ambient PM2.5 pollution include the following: to continuously strengthen the widespread use and efficient development of clean energy; to further promote industrial upgrading; to focus on the control of transportation pollution; to keep improving the modernization system of air pollution control; to formulate and refine relevant standards for air quality gradually; and to estimate the effects and health benefits after the implementation of clean air actions, and relevant policies. 2) Prevention of ambient PM2.5 pollution and protection of public health recommendations include the following: to strengthen the release of air pollution monitoring and relevant information; to strengthen awareness of air pollution hazards; to clarify the guidance and recommendations for protecting population health from air pollution; and to strengthen the health protection of population vulnerable to ambient air pollution. 3) Recommendations for research on health risks of air pollution include the following: to strengthen research on air pollutant monitoring technology and monitoring system based on the promotion of accurate exposure assessment; to systematically carry out full-spectrum identification and correlation studies of air pollutants and health effects; to conduct studies on key toxic components and early biomarker inventory of air pollution health effects; to discover the toxicity mechanisms of the key toxic components of air pollutants; to carry out research on population health risk assessment and early warning of combined exposure to air pollutants; and to execute comprehensive studies on the health and economic benefits of pollution and carbon reduction under the national strategies of carbon neutrality and beautiful China.
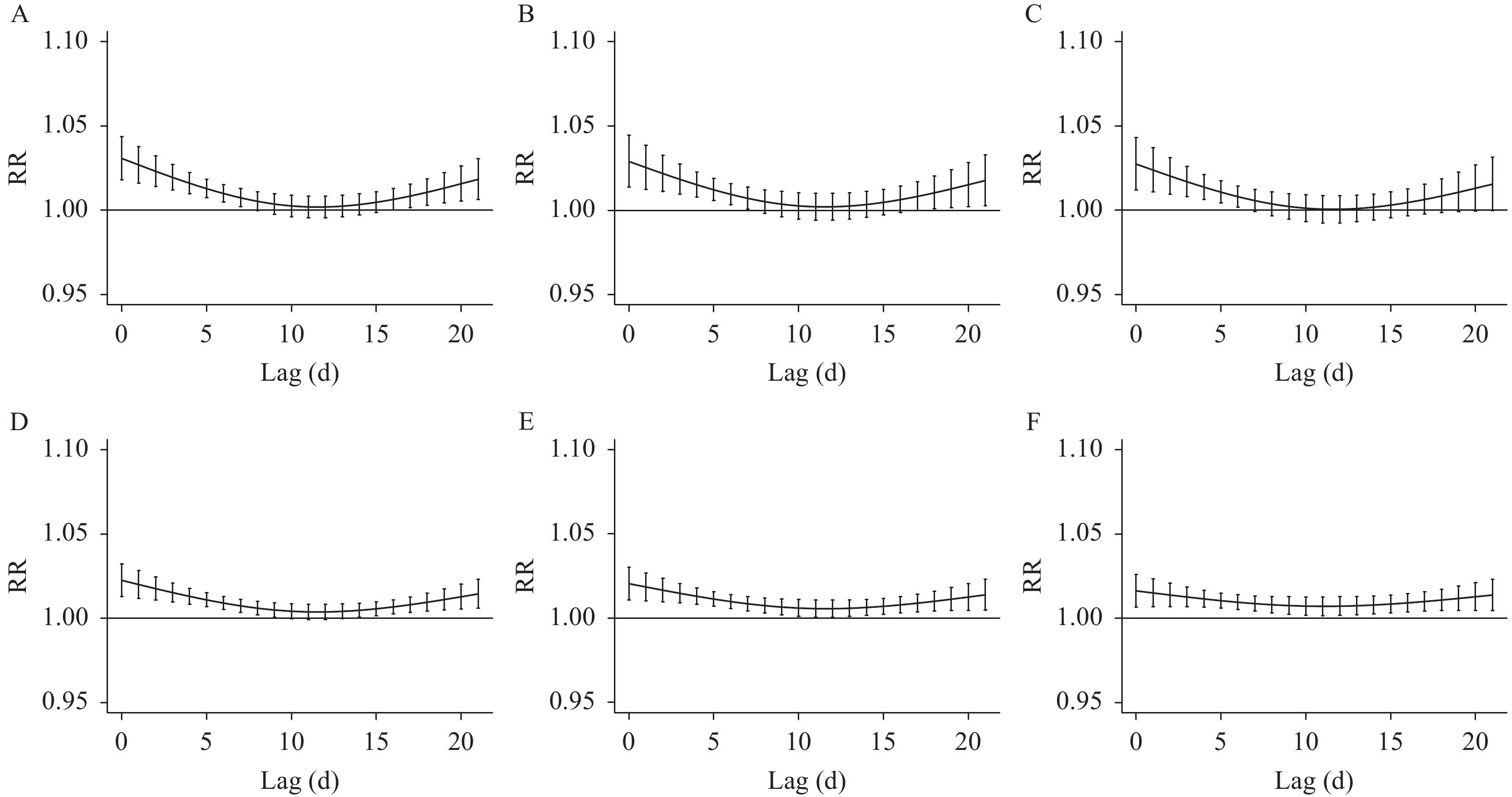
In recent years, climate change may lead to an increase in cold spells in the middle latitudes, and there is a positive correlation between cold spells and population mortality.
The acute response period and the vulnerable population were identified under the optimal definition of cold spells, and the mortality burden caused by cold spells were estimated.
This research would provide evidence on the acute mortality effects of cold spells in southern China. Therefore, vulnerable populations, especially the elderly, should take timely measures to reduce the health damage caused by cold spells, especially in the first week after cold waves.
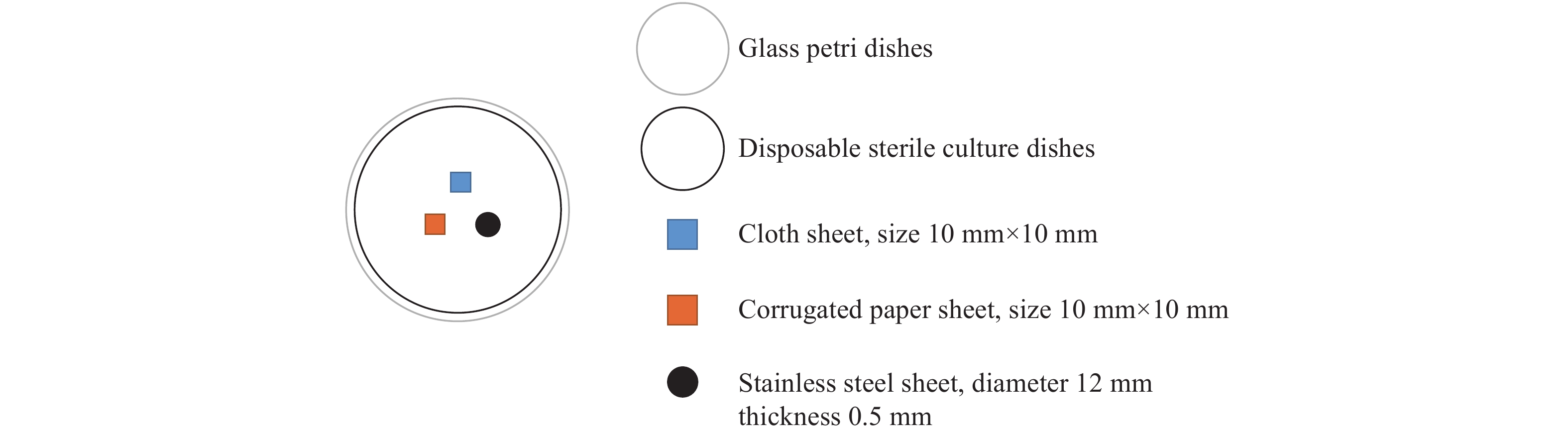
To explore the feasibility of pulsed ultraviolet (UV) light technology for low-temperature disinfection, a series of experiments were conducted.
Pulsed UV technology’s effectiveness in disinfecting Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus and Gram-negative Escherichia coli on different carriers were studied under varying temperatures.
Under different temperatures and constant radiation illumination (i.e., distance), the disinfection effect was correlated with irradiation time; among the three carriers, the disinfection effect of cloth sheets was the best, followed by stainless steel sheets, and corrugated paper sheet. The disinfection effect on Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli was better than that on Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus overall.
Temperature has a limited effect on pulsed UV disinfection. Irradiation times and carrier types are influencing factors.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed