2021 Vol. 3, No. 15
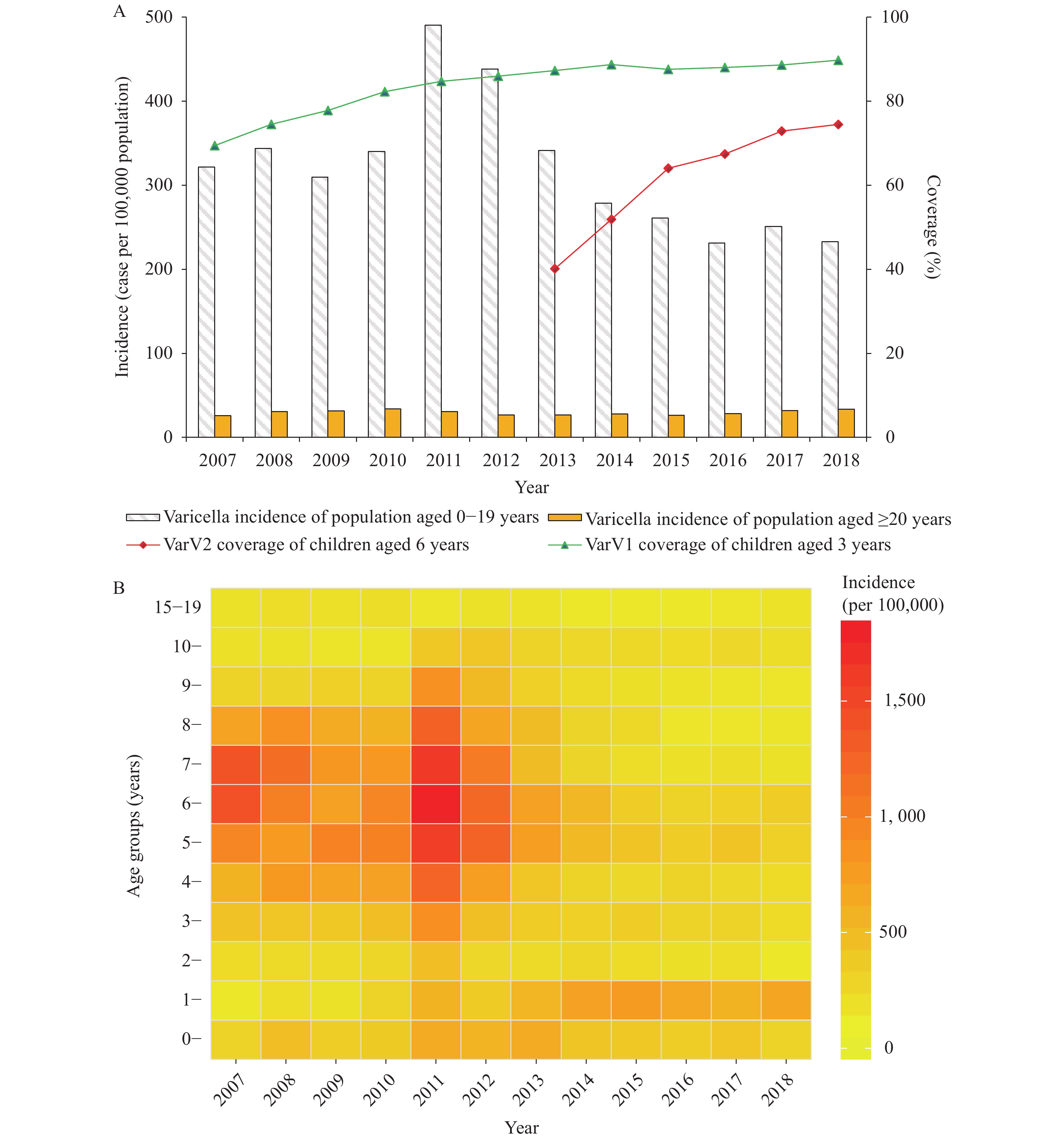
The World Health Organization (WHO) varicella vaccines position paper states that countries where varicella is an important public health burden could consider introducing varicella vaccine (VarV) in the routine childhood immunization program (1). VarV has been available for many years in China but is not included in most routine immunization programs in China. As a result, substantial heterogeneity in vaccination coverage exists across regions.
In Beijing, adding a second dose of VarV for children and increasing coverage reduced the incidence of varicella. Lowering the age of the first dose of VarV to 12 months could further reduce varicella, especially among toddlers.
Governments should use economic analysis to consider inclusion of VarV into the routine children immunization program as a free vaccine and adopting a 2-dose schedule that starts at 12 months of age.
Significant changes in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) transmission modes have occurred in China, and the proportion of heterosexual transmission increased in recent years.
The proportions of diverse transmission routes and subgroups of heterosexual transmission were analyzed by provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs), and nationwide spatial clustering of HIV transmission through commercial heterosexual contact (CHC) and non-marital non-commercial heterosexual contact (NMNCHC) was explored.
This report provides evidence for geographic clustering of HIV transmission through CHC and NMNCHC in China and identifies priority regions where specified research and targeted HIV prevention and control strategies should be implemented.
What is already known on this topic?
The increase of heart rate will increase blood pressure, and the cardiovascular risk will increase when heart rate >80 beats/min (bpm) in patients with hypertension.
What is added by this report?
Compared with patients who were female, <65 years old, and with hypertension, patients who were male, ≥65 years old, and with hypertension had the lowest risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) at baseline heart rate (HR) of 70–74 bpm.
What are the implications for public health practice?
Patients with hypertension should control their blood pressure well, and the HR of male and elderly patients should be managed well at the same time.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed