2020 Vol. 2, No. 34
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a global pandemic, while the profile of antibody response against the COVID-19 virus has not been well clarified.
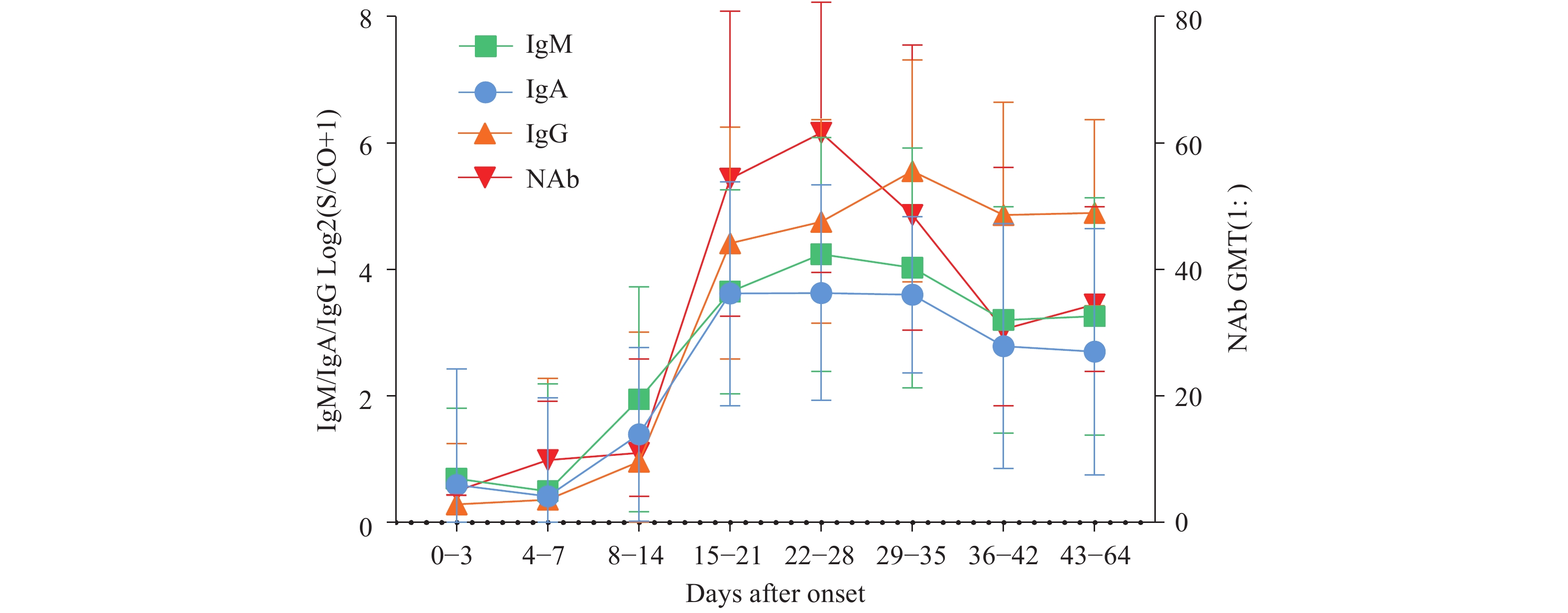
In this study, 210 serum samples from 160 confirmed COVID-19 cases with different disease severities were recruited. The IgM, IgA, IgG, and neutralizing antibodies (NAb) against COVID-19 virus were determined. Our findings indicated that four antibodies could be detectable at low levels within 2 weeks of disease onset, then rapidly increasing and peaking from the 3rd to 5th Weeks. NAb decreased between 5th and 9th Weeks, and a higher IgM/IgA level was observed in the groups with mild/moderate severity within 2 weeks (p<0.05), while all 4 types of antibodies were higher in the group with severe/critical severity after 4 weeks (p<0.05).
Our study on the dynamics of serological antibody responses against COVID-19 virus among COVID-19 patients complements the recognition regarding the humoral immune response to COVID-19 virus infection. The findings will help in the interpretation of antibody detection results for COVID-19 patients and be beneficial for the evaluation of vaccination effects.
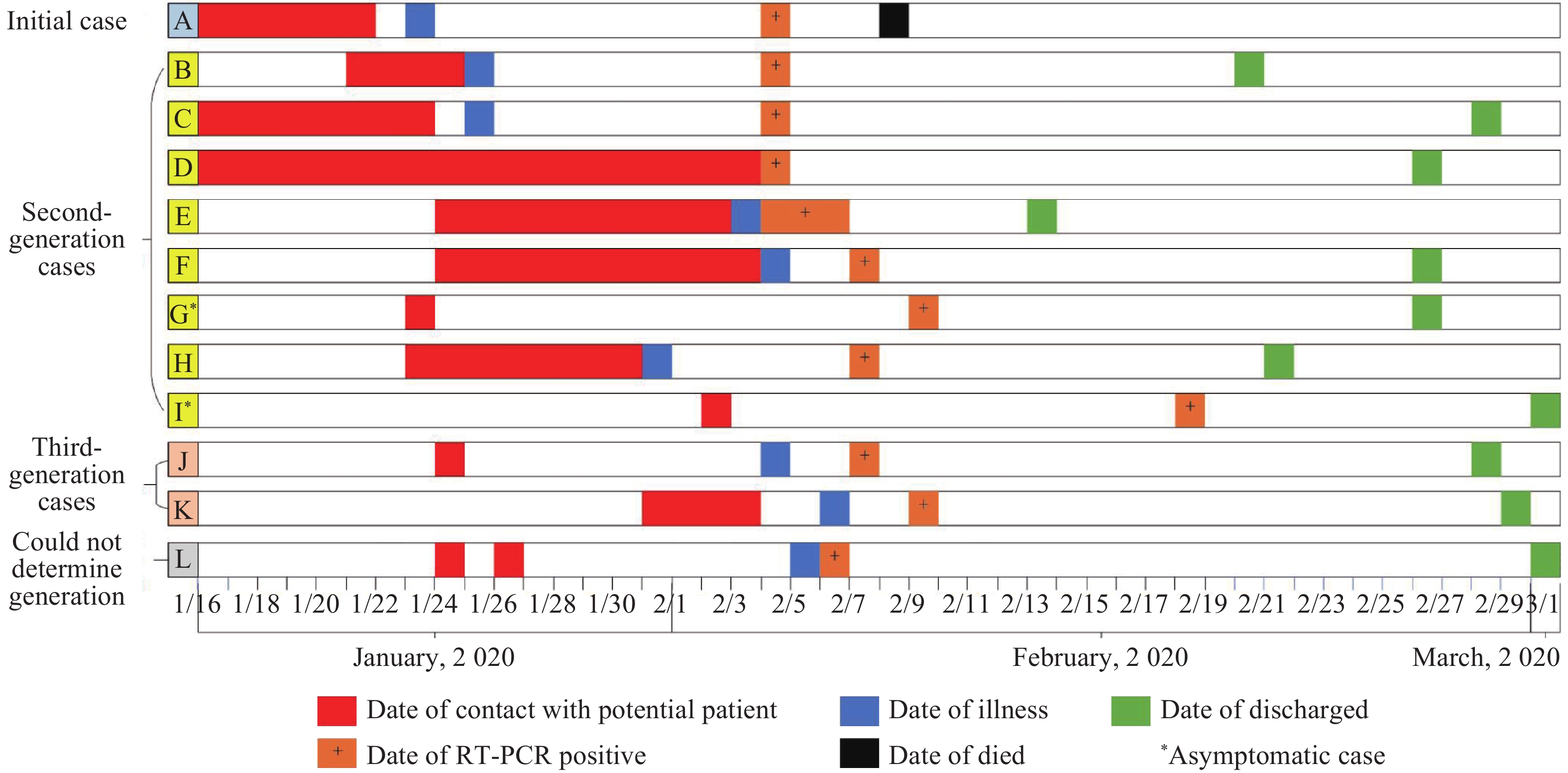
COVID-19 has a high transmissibility calculated by mathematical model. The dynamics of the disease and the effectiveness of intervention to control the transmission remain unclear in Jilin Province, China.
This is the first study to report the dynamic characteristics and to quantify the effectiveness of interventions implemented in the second outbreak of COVID-19 in Jilin Province, China. The effective reproduction number of the disease before and after May 10 was 4.00 and p<0.01, respectively. The combined interventions reduced the transmissibility of COVID-19 by 99% and the number of cases by 98.36%.
The findings of this study would add data on the transmission of COVID-19 and provide evidence to prepare the second outbreak transmission of the disease in other areas of China even in many other countries.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed