2024 Vol. 6, No. 44
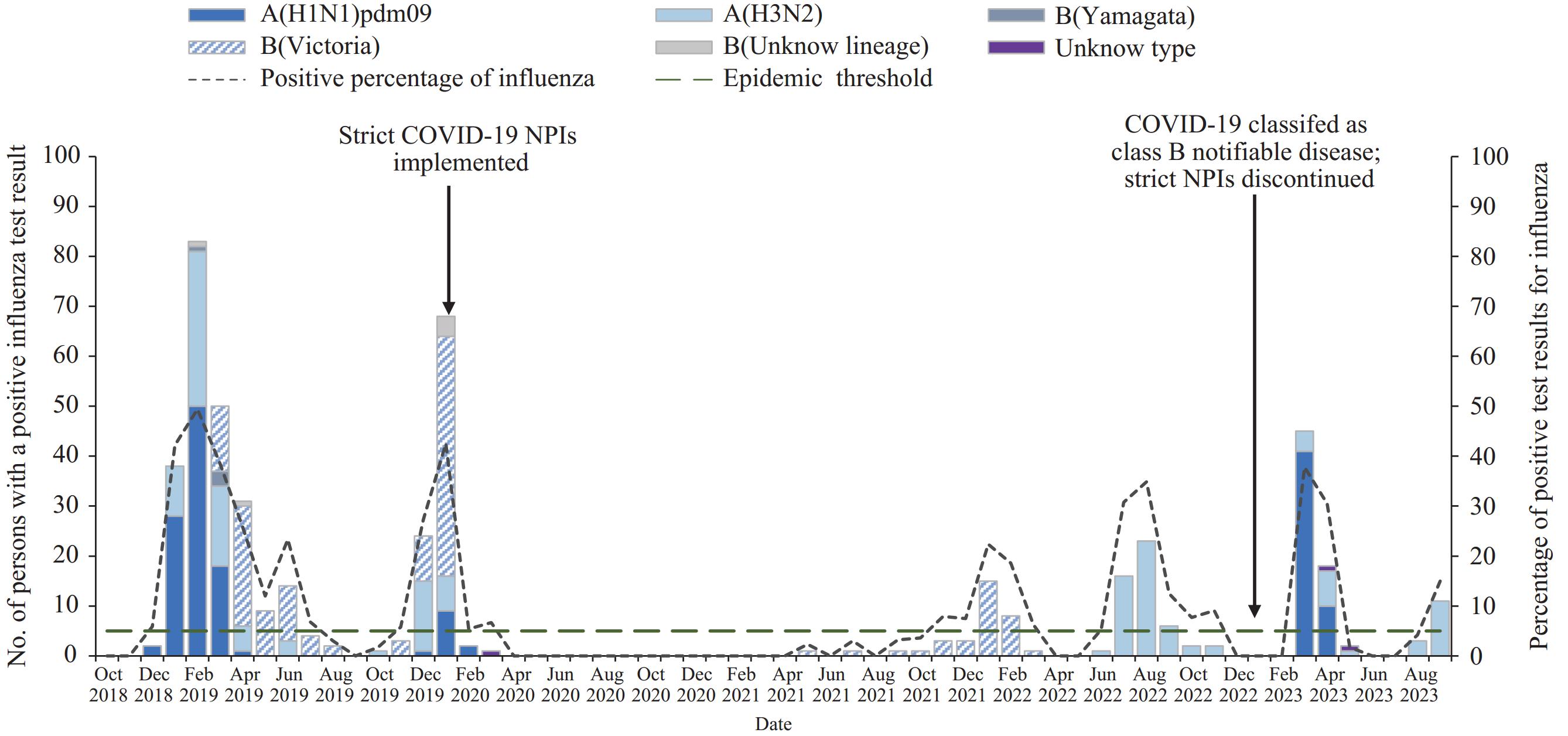
Pregnancy is associated with increased risk for severe illness and complications attributable to influenza infection. Information about the incidence of influenza hospitalization among pregnant and early postpartum women in China is limited.
Population-based data from a large city in southern China estimated the annual influenza hospitalization rate to be 2.1 per 1,000 live births. Among hospitalized pregnant and postpartum women with influenza, 86% were admitted to obstetrics rather than respiratory medicine wards; fewer than one third received antiviral treatment. Influenza vaccination coverage among hospitalized pregnant and postpartum women with influenza was <0.1%.
Increasing vaccination coverage among pregnant women can reduce influenza-associated morbidity. Raising awareness about early detection, treatment, and infection control of influenza in obstetrics wards is needed to reduce the adverse impact of influenza on pregnant women.
The investigations and analyses limited to epidemiological characteristics are insufficient to analyze the spread patterns of norovirus outbreaks in schools.
Norovirus outbreaks in primary schools are a dynamic process that spreads through social networks. The use of a social network analysis method to measure and identify key nodes for simulating control evolution was proven effective.
Infected students exhibit priority connection characteristics at different developmental stages in the network topology. Identifying and deliberately targeting key nodes could destroy network connectivity and help reduce the spread of the outbreak.
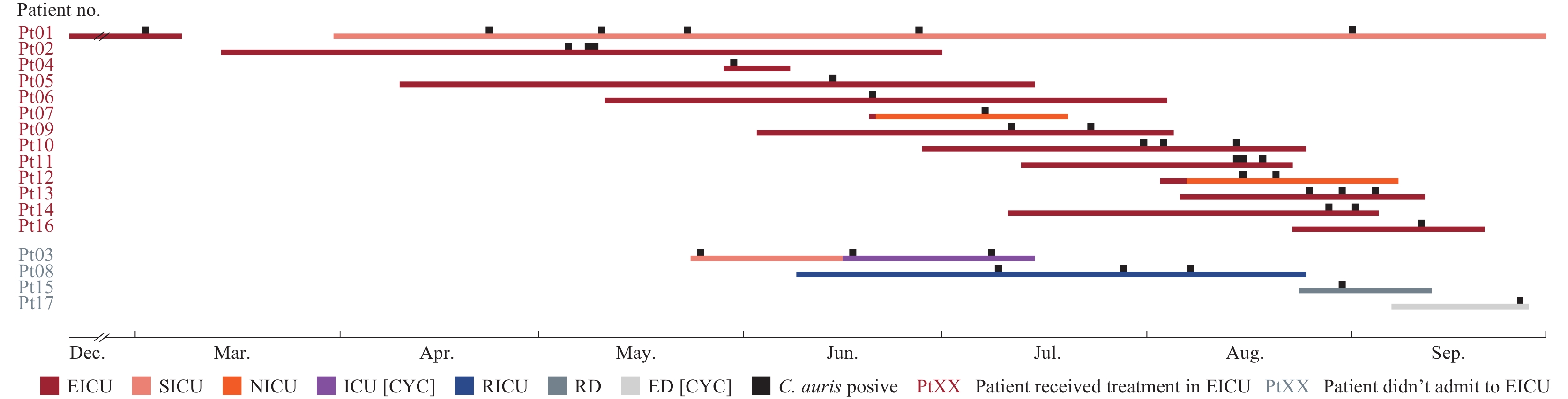
Candida auris (C. auris) is an emerging multidrug-resistant fungal pathogen classified as a global public health threat with notable mortality and nosocomial transmission capacity. In China, the first C. auris case was reported from Beijing in 2018. However, large cases of nosocomial transmission have rarely been identified in this municipality.
During March–September 2023, C. auris was isolated from 17 patients admitted to CY Hospital in Beijing. All strains were resistant to fluconazole and amphotericin B. In addition, three isolates were resistant to echinocandins. Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) analysis revealed that all strains found in this hospital belonged to C. auris Clade I. These strains were genetically closely related to the C. auris strains reported in two other hospitals in Beijing since 2021, forming a new sublineage different from the Clade I strains causing previous outbreaks in the Eastern Provincial-level administrative divisions and Hong Kong Special Administrative Region.
The dissemination of C. auris has become an increasing threat to healthcare facilities in China. The WGS analysis indicates the spread of a unique sublineage of C. auris Clade I isolates in Beijing. Further, enhanced surveillance and hospital infection control of C. auris are warranted to resolve the public health challenge.
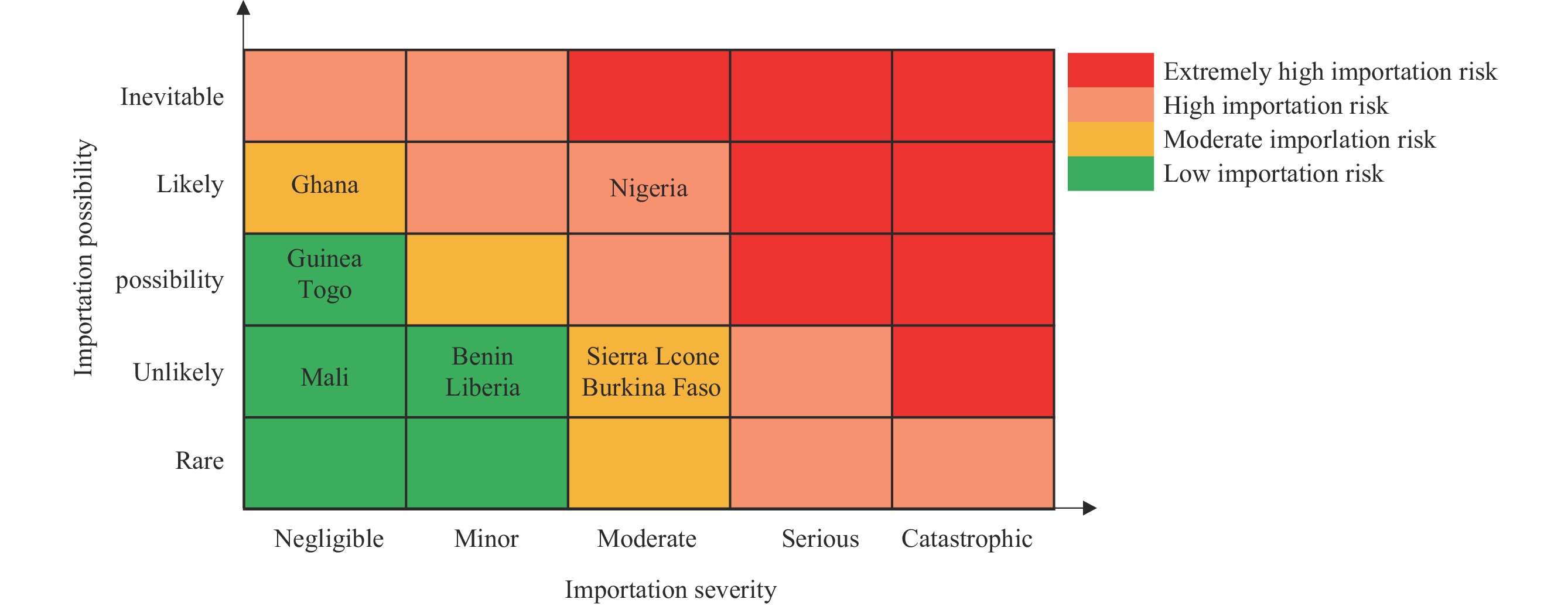
Common methods for assessing and responding to outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) are usually applied in isolation and have limitations. This study aimed to integrate the risk matrix and Borda count methods to assess the importation risk of EIDs to China, using Lassa fever (LF) as an example.
This study used a mixed-methods approach combining multi-source data with an integrated risk matrix and Borda count method. Data were obtained from the World Health Organization, the Concise Statistics of International Students dataset, the United Nations World Tourism Organization, and the Statistical Yearbook. Importation risk was assessed across two dimensions: possibility and severity. Total importation risk was then categorized into 4 levels (low, moderate, high, and extremely high), corresponding to green, yellow, orange, and red zones, respectively, in the risk matrix assessment index. The Borda count method was used to rank the risks.
The importation risk for 9 countries that experienced LF outbreaks from 1996 to 2023 was scored and ranked by importation possibility and severity to derive overall importation risks. This study determined that Nigeria posed the highest LF importation risk to China, ranking first among West African countries with the highest Borda points. Countries with moderate importation risk included Sierra Leone, Burkina Faso, and Ghana.
An integrated risk matrix and Borda count method presented in this study may serve as a significant supplement to other risk assessment methods and enrich the current toolbox of public health countermeasures and inform future risk management of the importation of EIDs.
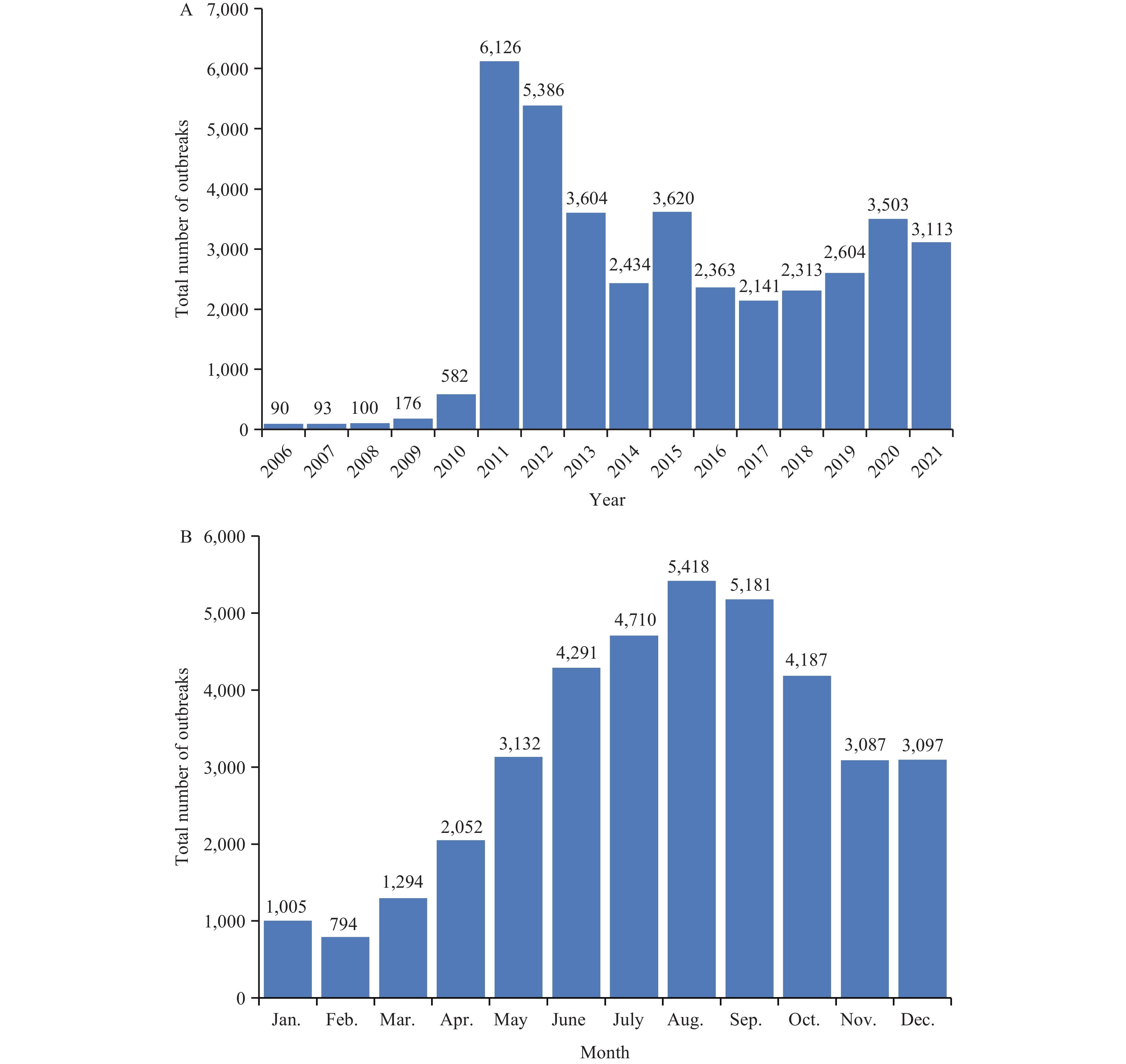
Brucellosis poses a significant threat to public health in China. This study utilized a range of epidemiological indices, including seroprevalence and the number of reported cases, to illustrate the epidemic profile of the disease. Although the seroprevalence of brucellosis in animals (including sheep, goats, cattle, and swine) steadily decreased from a severe epidemic level in the 1950s to a low endemic level by 1989, the disease reemerged in 2000. Subsequently, there has been a persistent increase in the frequency of outbreaks and the number of reported cases from 2006 to 2021, with over 98% of reported cases occurring in sheep and cattle. During this period, the culling rate declined, while infection rates increased, nearly reversing their respective trajectories. The decrease in the culling rate of positive animals coincided with an increase in infection rates, indicating that infection among these animals was persistent and circulating. In the southern regions of China, 6.34% (34,070 of 537,797) of cases were reported between 2006 and 2021, whereas in the northern regions, 93.67% (503,727 of 537,797) of cases occurred during the same timeframe. Each time cases increased in the south, they lagged 2 to 5 years behind those in the north, suggesting that stringent control measures for sheep and cattle in the north should be prioritized. These findings provide critical insights into developing control strategies to mitigate the spread of the disease.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed