2024 Vol. 6, No. 33
Highly fluoroquinolone-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky (S. Kentucky) of sequence type (ST) 198 has emerged as a global multidrug-resistant (MDR) clone, posing a threat to public health.
Whole genome sequencing and antibiotic susceptibility testing was used to characterize the population structure and evolutionary history of 54 S. Kentucky isolates recovered from food and human clinical cases in Beijing from 2016 to 2023.
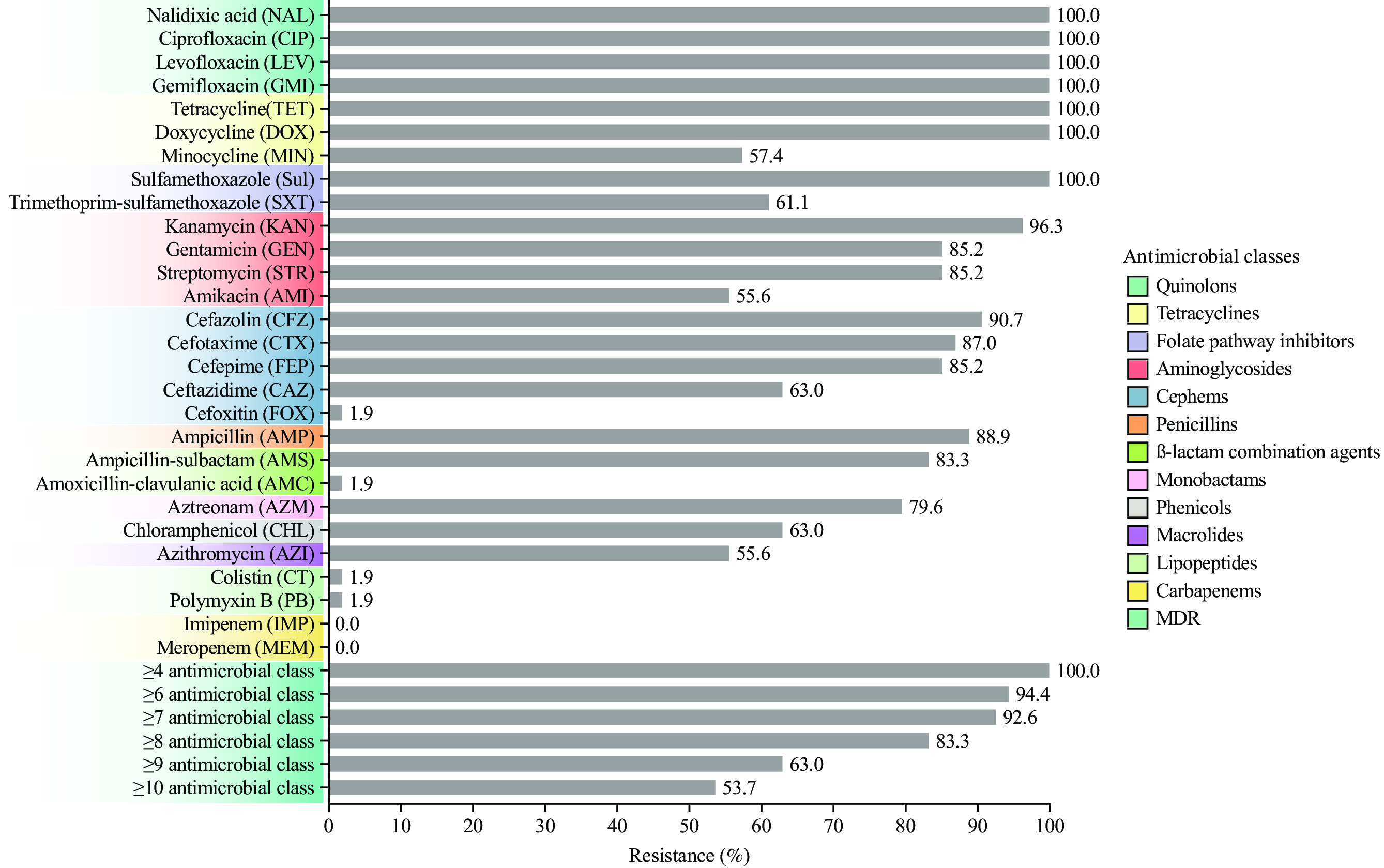
All 54 S. Kentucky ST198 isolates exhibited resistance to quinolones, carrying point mutations in the quinolone resistance-determining regions (gyrA_S83F and parC_S80I). Resistance to other antibiotics (folate pathway inhibitors, cephems, aminoglycosides, phenicols, rifamycin, fosfomycin, macrolides, and tetracyclines), mediated by the sul1, sul2, dfrA14, blaCTX-M, blaTEM-1B, aac(3)-Id, aadA2, aadA7, aph(3')-I, aph(3'')-Ib, rmtB, floR, arr-2, fosA, mph(A), and tet(A) genes, was also observed in different combinations. The Beijing S. Kentucky ST198 evolutionary tree was divided into clades 198.2-1 and 198.2-2, which were further differentiated into three subclades: 198.2-2A, 198.2-2B, and 198.2-2C. Compared with the extended-spectrum β-lactamase-encoding gene blaCTX-M-14b in 198.2-1, the co-existence of blaCTX-M-55 and blaTEM-1B, as well as chromosomally located qnrS1, was detected in most 198.2-2 isolates, which showed more complex MDR phenotypes. S. Kentucky ST198 outbreak isolates derived from two predominant clonal sources: 198.2-1 with cgST236434 and 198.2-2A with cgST296405.
The S. Kentucky population in Beijing is genetically diverse, consisting of multiple co-circulating lineages that have persisted since 2016. Strengthening surveillance of food and humans will aid in implementing measures to prevent and control the spread of AMR.
The Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine is widely administered in China.
We extracted data on Hib vaccine doses administered and adverse events following immunization (AEFI) reported between 2010 and 2021 from the Chinese National Immunization Information System (CNIIS). A descriptive analysis was conducted to examine the characteristics and incidence rates of AEFI with the Hib vaccine.
In China, between 2010 and 2021, a total of 52,910 AEFIs with the Hib vaccine were reported, resulting in an overall AEFI reporting rate of 38.10 per 100,000 doses. Common (typically minor) and rare (potentially serious) vaccine reactions occurred at rates of 34.71 and 2.78 per 100,000 doses, respectively. Among the common vaccine reactions, the incidences of fever (axillary temperature ≥38.6 ℃), injection site redness and swelling (>2.5 cm in diameter), and injection site induration (>2.5 cm in diameter) were 11.93, 9.69, and 3.38 per 100,000 doses, respectively. Rare vaccine reactions included anaphylactic rash, angioedema, and febrile convulsion with reported incidences of 2.42, 0.10, and 0.05 per 100,000 doses, respectively. The incidence of serious rare vaccine reactions was 0.16 per 100,000 doses.
The reported incidence of AEFI with the Hib vaccine was low, with the occurrence of serious rare adverse reactions also being markedly low throughout the period 2010–2021 in China.
Norovirus is the leading cause of global acute gastroenteritis outbreaks. Norovirus outbreaks mainly occur in schools and kindergartens in China, always causing public health issues.
Conditional logistic regression method was used to analyze the risk factors for norovirus outbreaks in schools and kindergartens, and found that students vomiting at school or kindergarten, case activity in public areas, and the first case’s classroom less than 5 meters from toilets were risk factors.
Effective measures to address these factors can help reduce the risk of norovirus outbreaks in schools and kindergartens.
A 20-month-old boy was admitted to the hospital with a maximum temperature of 40 °C and a single convulsion. Unexpectedly, blood culture detected Francisella tularensis (F. tularensis) using the VITEK 2 Compact System.
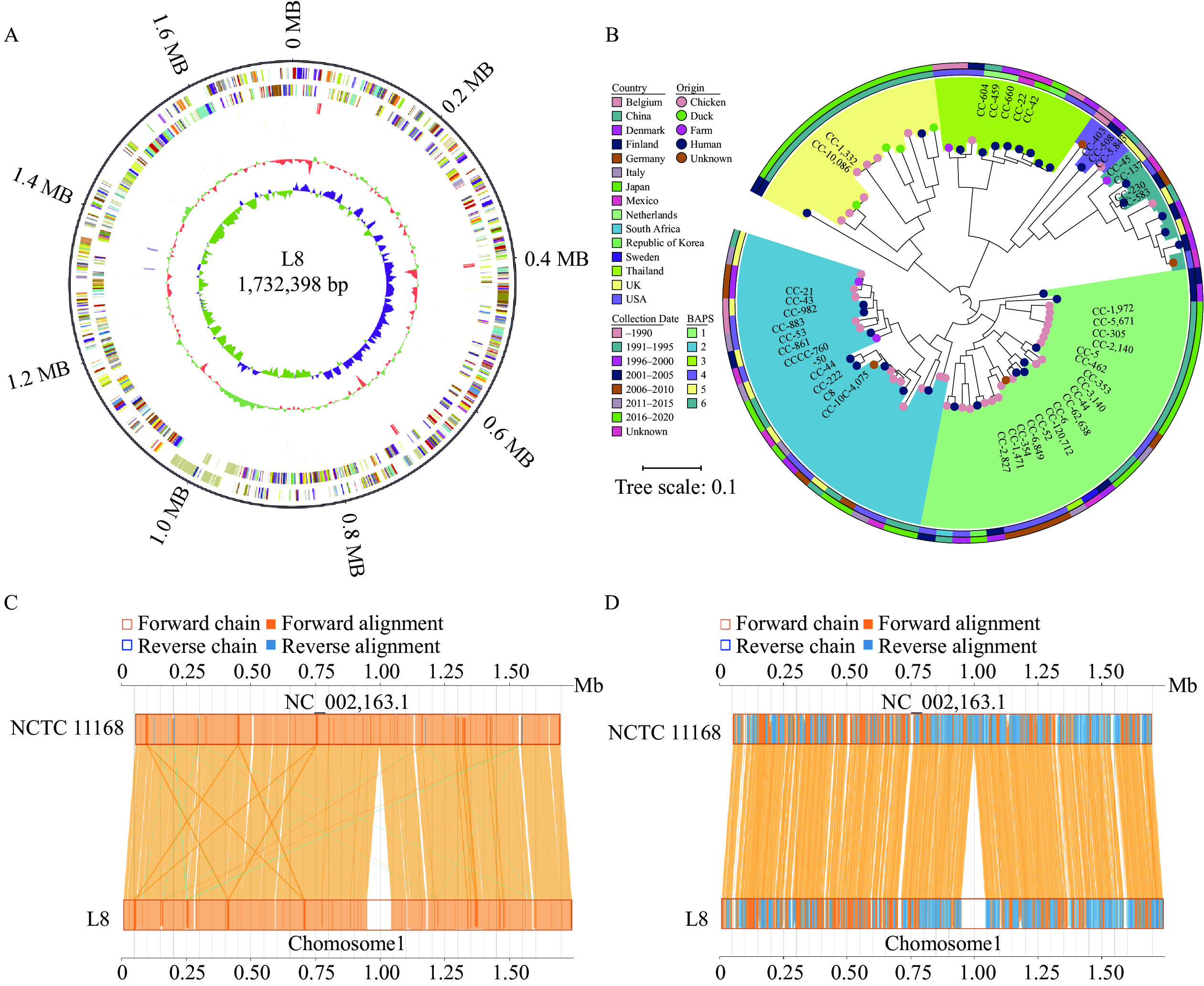
After incubation of the patient’s blood for 48 hours, the cultured strain was identified as Campylobacter jejuni, named L8, excluding F. tularensis. In the genome sequence of L8, we found a novel Type VI Secretion System (T6SS), of which the conserved C-terminal VgrG domain from positions 561 to 884 showed significant changes.
It should be underscored that relying solely on automatic bacterial identification instruments for accurate strain identification is unreliable. Moreover, our study suggests that the potential effect of T6SS should be considered when studying the genetic features of a patient’s clinical phenotypes.
Mosquito-borne diseases are persistent and potentially severe posing a threat to global pandemic preparedness. The risk of mosquito-borne virus transmission is rapidly increasing due to the unprecedented spread of viruses such as dengue and chikungunya, the disruption of global mosquito-borne disease control efforts following the emergence of coronavirus diseases 2019 (COVID-19) in 2019, global warming, and human activities. To address this global challenge, various innovative mosquito control technologies are being developed worldwide. This paper summarizes the latest advances in mosquito vector control, focusing on China’s latest mosquito control strategies, to provide insights into implementing novel mosquito-borne disease control measures.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed