-
China CDC Weekly was established in November 2019. It is a weekly periodical focusing on all fields and topics related to public and global health and is managed by the National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, prepared by China CDC, and published by the editorial department of China CDC Weekly that was established in and by China CDC. China CDC Weekly serves as a channel for China CDC to disseminate timely, reliable, authoritative, accurate, objective, and useful public health information, as well as recommendations for health professionals and the public. China CDC Weekly is the Voice of China CDC.
Since the journal was established, China CDC Weekly implemented firm guidelines and policies, with objectives that reflecting the aspirations of the editors, authors, and readers; it has played a vital role in communication, facilitation, and guidance of public health. By adhering to proper orientation and management and paying attention to a combination of theory and practice, China CDC Weekly is becoming increasingly influential and is making significant contributions to international research and cooperation in disease prevention and control. We conducted a systematic, quantitative analysis of articles published in China CDC Weekly from 2019 to 2020 to explore development of the journal and understand its academic contribution in the field of preventive medicine, as well as to look forward toward future developmental goals.
-
The research obtained articles published on the official China CDC Weekly website between November 29, 2019, and December 25, 2020. The analytic domains were the following: 1) funding sources in five categories including national, provincial, municipal, institution/organization, and non-governmental; 2) study types (1): observational study and experimental study, including descriptive research, analytical research, experimental research, theoretical and methodological research, and also public health monitoring, et al; 3) according to the branch of preventive medicine in the National Natural Science Foundation (2), type of subject in eight categories includes infectious disease epidemiology, non-infectious disease epidemiology, maternal and child health, environmental health, occupational health, health toxicology, human nutrition (including food hygiene), and other subjects; 4) first authors’ institutions; and 5) number of views and downloads through February 9, 2021.
-
The study analyzed downloads and views using standard bibliometric methods with SPSS software (version 22.0, IBM, NYC, USA). Because downloads and views were not normally distributed, we represented central tendencies with medians and quartiles (P25, P75). We used VOSviewer 1.6.15 (Leiden university, Leiden, Netherlands)to illustrate author collaboration networks with network visualization maps composed of nodes and links based on the ris file type (file type (3-4). In the network visualization, authors were represented by a label and a circle. The sizes of the label and the circle were proportional to the number of author publications in China CDC Weekly. Clusters were grouped by label and circle color. The strength of links was in direct proportion to the degree of connection between authors. A key parameter of VOSviewer was the minimum number of documents by the author; we considered three articles as the minimum.
-
China CDC Weekly published 283 articles in 2019 and 2020, representing 1,100 pages at 3.89 pages per article. This corpus of articles had 2,404,882 views and 58,760 downloads. The median (P25, P75) number of views and downloads for each article was 2,575 [interquartilerange (IQR): 1,566, 3,770] and 23 (IQR: 11, 45). Overall, 96 articles (33.9%) were from funded projects.
Highly Viewed and Downloaded Articles
The article with the most views and downloads had 1,244,826 views and 38,978 downloads. A total of 13 articles were browsed online more than 7,000 times; 11 of these articles were related to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); and 3 were viewed more than 50,000 times. There were 4 articles that had been downloaded more than 2,000 times; all were related to COVID-19.
Views and Downloads by Paper Type
This research analyzed 18 types of articles: Announcements, Commentaries, Forewords, Health China, Insights, Key Statistics, Methods and Applications, Notes from the Fields, Notifiable Infectious Disease Reports, Outbreak Reports, Perspective, Policy Notes, Preplanned Studies, Profiles, Recollection, Recommendations, Reviews, and Vital Surveillance. The most common article type was Preplanned Studies (83 articles, 29.33%), followed by Perspectives and Notes from the Field. Article types with more than 4,500 views were those in Vital Surveillance, Notes from the Field, and Preplanned Studies (Table 1).
Type Number of articles Number of pages Pages per article Downloads Downloads per article Views Views per article Announcement 22 28 1.27 293 13.32 53,603 2,436.50 Commentary 18 48 2.67 832 46.22 58,017 3,223.17 Foreword 10 16 1.60 265 26.50 19,395 1,939.50 Healthy China 7 28 4.00 250 35.71 16,792 2,398.86 Insights 1 3 3.00 17 17.00 2,453 24,53.00 Key Statistics 3 5 1.67 55 18.33 7,788 2,596.00 Methods and Applications 2 10 5.00 41 20.50 2,106 1,053.00 Notes from the Field 27 90 3.33 10,214 378.30 317,578 11,762.15 Notifiable Infectious Diseases Reports 12 20 1.67 295 24.58 30,443 2,536.92 Outbreak Reports 16 64 4.00 672 42.00 45,590 2,849.38 Perspectives 28 94 3.36 1,309 46.75 80,546 2,876.64 Policy Notes 4 15 3.75 152 38.00 8,254 2,063.50 Preplanned Studies 83 450 5.42 3,826 46.10 390,015 4,698.98 Profiles 14 28 2.00 145 10.36 20,335 1,452.50 Recollection 13 63 4.85 376 28.92 37,025 2,848.08 Recommendations 1 2 2.00 200 200.00 10,926 10,926.00 Review 1 4 4.00 104 104.00 3,974 3,974.00 Vital Surveillance 21 132 6.29 39,714 1,891.14 1,300,042 61,906.76 Total 283 1,100 3.89 58,760 207.63 2,404,882 8,497.82 Table 1. Comparison of views and downloads by article type in China CDC Weekly from 2019 to 2020.
Views and Downloads by Subject
Most articles (55.5%, 157 articles) were on infectious disease epidemiology; the next most common subject was “other” (21.9%, 62 articles). Epidemiology of infectious diseases, epidemiology of non-infectious diseases, and maternal and child health had over 3,500 additional page views more than the overall average number per article (Table 2).
Subjects Number of articles Number of pages Pages per article Downloads Downloads per article Views Views per article Epidemiology of infectious diseases 157 621 3.96 55,138 351.20 2,001,997 12,751.57 Epidemiology of non-communicable diseases 19 90 4.74 575 30.26 67,233 3,538.58 Maternal and child health 15 83 5.53 423 28.20 79,483 5,298.87 Environmental health 9 46 5.11 250 27.78 21,354 2,372.67 Other subjects 62 162 2.61 1,734 27.97 168,371 2,715.66 Human nutrition (including food hygiene) 7 30 4.29 189 27.00 19,262 2,751.71 Health toxicology 3 16 5.33 168 56.00 10,226 34,08.67 Occupational health 11 52 4.73 283 25.73 36,956 3,359.64 Total 283 1,100 3.89 58,760 207.63 2,404,882 8,497.82 Table 2. Comparison of views and downloads by subject in China CDC Weekly from 2019 to 2020.
Views and Downloads by Study Type
More than half the articles were descriptive research (55.1%, 156 articles). The study types of descriptive research and public health monitoring each had more than 3,000 page views per article (Table 3).
Study Type Number of articles Number of pages Pages per article Downloads Downloads per article Views Views per article Analytical research 4 24 6.00 149 37.25 9,411 2,352.75 Public health monitoring 14 73 5.21 908 64.86 50,742 3,624.43 Research on theory and methodology 6 22 3.67 103 17.17 7,295 1,215.83 Descriptive research 156 731 4.69 54,500 349.36 2,076,637 13,311.78 Others (including no research methods) 102 245 2.40 3,087 30.26 258,849 2,537.74 Experimental research 1 5 5.00 13 13.00 1,948 1,948.00 Total 283 1,100 3.89 58,760 207.63 2,404,882 8,497.82 Table 3. Comparison of views and downloads by study type in China CDC Weekly from 2019 to 2020.
Institutional Source of Articles
The 284 published articles came from 101 institutions, 22 (21.8%) of which were overseas institutions. The top five institutions were China CDC, the National Center for Chronic and Non-Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, the National Institute of Environmental Health, and the National Institute of Occupational Health and Poison Control. Together, these 5 institutions produced 95 articles (33.5% of all articles).
Authors
China CDC Weekly has attracted many authors who were experts and scholars of public health. There were 220 first authors, with 1.29 articles per first author; 20 (9.09%) authors published more than two papers.
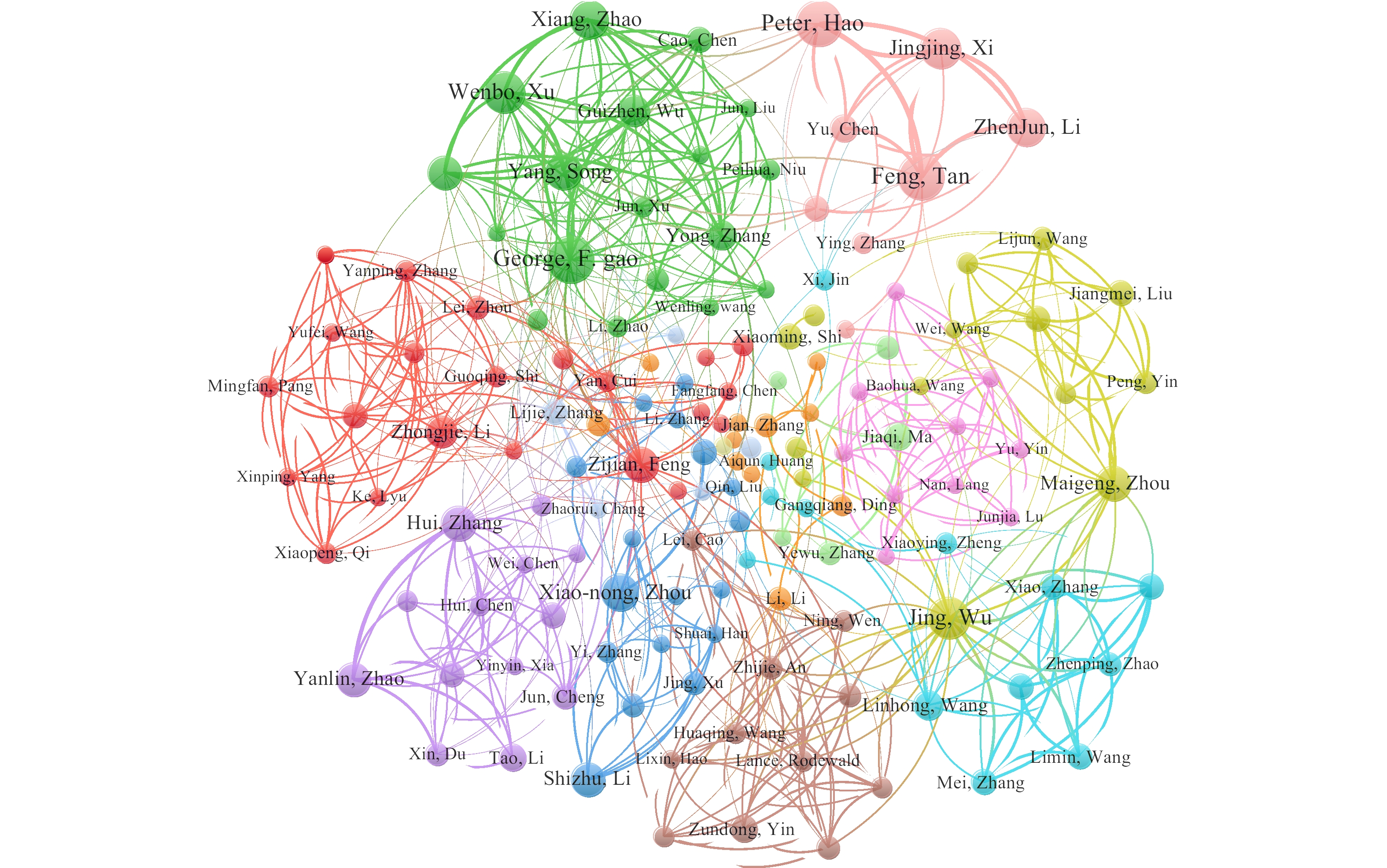
The author collaboration network showed which teams had the most influence (Figure 1). The most influential authors and teams included the following: George F. Gao, Feng Tan, Zijian Feng, Xiaonong Zhou, and Peter Hao; a team from the Institute for Viral Disease Prevention and Control of Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention with Wenbo Xu and Guizhen Wu at its center; a team from the National Center for Chronic and Non-Communicable Disease Control and Prevention with Jing Wu and Maigeng Zhou at its center; and a team from National Center for Tuberculosis Control and Prevention with Hui Zhang and Yanlin Zhao at its center.
-
Citation frequency is an important indicator of the quality and influence of academic journals (5-6). However, long publication cycles may make it difficult for articles to be cited in a timely manner, which lags behind the possibilities brought forth by our current digital environment (7). Given the widespread use of electronic resources and literature databases, the views or downloads per article reflects the usefulness of the article, and to some extent has become a common index for evaluating the communication power and influence of articles (8). Therefore, we used downloads and views to evaluate the influence of China CDC Weekly.
According to our download and view analyses, Vital Surveillance, Notes from the Field, and Preplanned Studies have the highest viewing frequency, while Profiles and Methods and Applications have comparatively low viewing frequency — a finding that differs from a previous study (9). Vital Surveillance articles are based on monitoring data from the national-level CDC, so that a standard of data quality is ensured. We suggest that manuscripts should be optimally organized to improve the influence of the journal. “Methods and Applications” is an article type that was established after the others had been established; perhaps leading to its lower viewing frequency. Further analysis is warranted.
The influence of articles from different disciplines and research types varied greatly. Epidemiology of infectious and non-infectious diseases, which are the main components of traditional public health disciplines, had a higher average viewing frequency, consistent with a previous study (9). Among research types, descriptive research and public health monitoring had relatively higher levels of downloads and views, while theoretical and methodological research received less attention. A large proportion of articles related to COVID-19 were viewed more than 7,000 times, indicating that China CDC Weekly has played an important role in the academic exchange concerning COVID-19 and has provided strong scientific and technological support for epidemic prevention and control.
In conclusion, since its inception, China CDC Weekly has played a clear role in the field of public health in China. China CDC Weekly came into existence before COVID-19, and therefore has been able to play a highly active role in the global fight against the pandemic. Based on our analyses, we have some recommendations to improve the journal’s quality and communication ability. First, according to view and download analyses, adjusting article types at the right time is essential. For instance, the number of times Vital Surveillance and Preplanned Studies articles were viewed was highest, so soliciting these articles should be prioritized. Second, special issues should be organized to publish collections of timely articles on specific and important topics. Third, as China CDC Weekly enters the Web of Science database, the editorial department can use citation frequency, page views, and downloads to analyze the influence of the journal and help solicit the highest-quality manuscripts for publication. Fourth, the journal should continue to adhere to international norms and standards of publication and further increase the proportion of internationally-sourced articles, currently 21.8% of articles. The number of international editorial board members and international peer reviewers should be increased to improve the international influence of the journal (10). Finally, mature digital publishing technologies should be applied to provide high-quality services for authors and readers from multiple perspectives and levels to open a rapid publication channel for excellent papers as is being done with pre-prints (11).
HTML
Data Acquisition
Analytical Strategies
| Citation: |



 Download:
Download:




